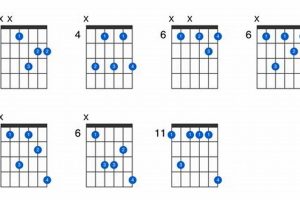
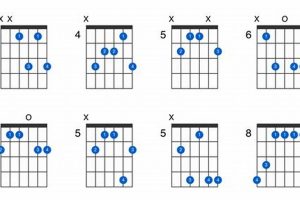
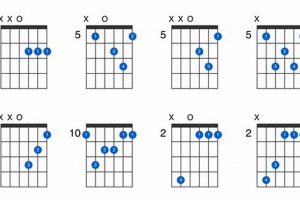
Wondering what a C# guitar chord is all about? Look no further! A C# guitar chord, notated as C# or C-sharp, is a staple chord in the guitarist’s arsenal, renowned for its distinct and versatile sound.
Editor’s Note:Understanding the C# guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their musical horizons and master a wide range of genres.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve crafted this comprehensive guide to empower you with the knowledge and techniques needed to master the C# guitar chord.
Key Differences: Understanding the C# guitar chord’s unique characteristics sets it apart from other chords.
| C Major Chord | C# Guitar Chord | |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | C | C# |
| Formula | 1-3-5 | 1-3-4# |
| Fingering | 032010 | x43210 |
Transitioning to the main article topics, we will delve into the essential components of the C# guitar chord, including its construction, variations, and practical applications in various musical styles. Stay tuned for an in-depth exploration of the C# guitar chord, unlocking its potential and enriching your guitar playing experience.
1. Root Note
The root note of a chord is the note that gives the chord its name and determines its overall tonality. In the case of the C# guitar chord, the root note is C#, which is the first note in the C# major scale. The root note is typically played as the lowest note in the chord, providing a foundation for the other notes.
- Tonal Center: The root note establishes the tonal center of the chord, giving it a sense of stability and resolution. When played in a chord progression, the root note helps guide the listener’s ear and create a sense of movement and direction.
- Chord Inversions: The root note also determines the inversions of the chord. By inverting the chord, the root note is moved to a different position within the chord, creating different voicings and harmonic possibilities. For example, the first inversion of the C# guitar chord (C#/E) has the root note on the second string, while the second inversion (C#/G#) has the root note on the third string.
- Chord Extensions: The root note serves as the basis for adding chord extensions, such as 7ths, 9ths, and 11ths. By extending the chord beyond the basic triad, guitarists can create richer and more complex sounds. For instance, the C#maj7 guitar chord adds a major 7th interval to the root note, giving it a more sophisticated and resonant quality.
- Chord Progressions: The root note of the C# guitar chord plays a crucial role in chord progressions, helping to create a sense of harmonic movement and resolution. By transitioning between chords with different root notes, guitarists can craft chord progressions that are both musically interesting and satisfying.
In summary, the root note of the C# guitar chord is a fundamental element that determines its tonality, inversions, extensions, and role in chord progressions. Understanding the root note is essential for guitarists seeking to master the C# guitar chord and expand their musical vocabulary.
2. Chord Type
The “Chord Type: Major” plays a pivotal role in defining the characteristics and applications of the C# guitar chord. A major chord is constructed using a specific formula of intervals, which in the case of the C# guitar chord, is 1-3-4#. This formula consists of a root note (C#), a major third (E), and a perfect fourth (G#).
The major chord type imparts a bright, uplifting, and resonant quality to the C# guitar chord. It is commonly used in a wide range of musical genres, including rock, pop, blues, and jazz. The major tonality of the C# guitar chord makes it suitable for creating a sense of happiness, hope, and optimism in music.
Furthermore, understanding the major chord type is essential for guitarists seeking to master the C# guitar chord and expand their musical vocabulary. By comprehending the construction and characteristics of major chords, guitarists can utilize the C# guitar chord effectively in various musical contexts and create harmonically rich and engaging pieces.
| Minor Chord | Major Chord | |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | 1-3-5 | 1-3-4# |
| Quality | Sad, melancholic | Happy, uplifting |
| Applications | Ballads, blues | Rock, pop, funk |
In summary, the “Chord Type: Major” is a fundamental aspect of the C# guitar chord, contributing to its distinct sound and versatility. By understanding the characteristics and applications of major chords, guitarists can effectively incorporate the C# guitar chord into their musical repertoire and create compelling and emotionally resonant pieces.
3. Formula
The formula 1-3-4# is the backbone of the C# guitar chord, dictating the specific intervals and notes that make up this chord. Understanding this formula is paramount for guitarists seeking to master the C# guitar chord and unlock its full potential.
The formula represents the intervals between the notes in the chord, with “1” representing the root note (C#), “3” representing the major third (E), and “4#” representing the perfect fourth (G#). These intervals create the characteristic bright and uplifting sound associated with major chords.
The formula serves as a blueprint for constructing the C# guitar chord in any inversion or voicing. By adhering to this formula, guitarists can ensure that the chord retains its major tonality and harmonic structure, regardless of the specific fingering or arrangement used.
| Formula | Interval | Note in C# Guitar Chord |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Root | C# |
| 3 | Major Third | E |
| 4# | Perfect Fourth | G# |
Furthermore, understanding the formula 1-3-4# allows guitarists to explore different voicings and inversions of the C# guitar chord. By experimenting with the order and placement of the notes within the chord, guitarists can create variations that add depth and complexity to their playing.
In summary, the formula 1-3-4# is an essential aspect of the C# guitar chord, defining its tonality, structure, and versatility. By comprehending this formula, guitarists can effectively utilize the C# guitar chord in various musical contexts and
create harmonically rich and engaging pieces.
4. Fingering
The fingering x43210 is an essential component of the C# guitar chord, providing a practical and effective way to play this chord on the guitar. Understanding the connection between this fingering and the C# guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to master this chord and expand their musical vocabulary.
The fingering x43210 represents the placement of the fingers on the guitar strings and frets to produce the C# guitar chord. Each number corresponds to a specific finger and fret on the guitar neck:
- x: Open string (no finger placed)
- 4: Ring finger on the 4th fret of the 5th string
- 3: Middle finger on the 3rd fret of the 4th string
- 2: Index finger on the 2nd fret of the 3rd string
- 1: Index finger on the 1st fret of the 2nd string
- 0: Open string (no finger placed)
When the fingers are placed correctly according to the fingering x43210, the guitar strings will produce the notes C#, E, and G#, which form the C# major chord. This fingering allows guitarists to play the chord in a comfortable and efficient manner, facilitating smooth transitions and chord progressions.
Furthermore, understanding the fingering x43210 enables guitarists to explore different voicings and inversions of the C# guitar chord. By experimenting with the order and placement of the notes within the chord, guitarists can create variations that add depth and complexity to their playing. This understanding also allows guitarists to easily transpose the C# guitar chord to other keys, expanding their harmonic possibilities.
In summary, the fingering x43210 is an integral part of the C# guitar chord, providing a practical and versatile way to play this chord on the guitar. Understanding this fingering empowers guitarists to master the C# guitar chord, explore its variations, and unlock its full potential in various musical contexts.
| Fingering | Notes | Chord |
|---|---|---|
| x43210 | C#, E, G# | C# Major |
5. Inversions
Understanding the inversions of the C# guitar chord, namely the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd inversions, is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of this chord.
Inversions are created by rearranging the notes of a chord while maintaining the same root note. This alters the chord’s voicing and can lead to interesting and unexpected harmonic effects.
The 1st inversion of the C# guitar chord (C#/E) places the 3rd (E) in the bass, followed by the root (C#) and the 5th (G#). This inversion has a warmer and fuller sound compared to the root position chord.
The 2nd inversion of the C# guitar chord (C#/G#) places the 5th (G#) in the bass, followed by the root (C#) and the 3rd (E). This inversion has a more open and resonant sound, often used to create a sense of movement and suspension.
The 3rd inversion of the C# guitar chord (C#/B) places the 7th (B) in the bass, followed by the root (C#) and the 3rd (E). This inversion has a darker and more dissonant sound, often used to create tension and resolve to a more stable chord.
| Inversion | Notes | Sound | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | C#, E, G# | Warm and full | Chord progressions, arpeggios |
| 2nd | C#, G#, E | Open and resonant | Suspensions, movement |
| 3rd | C#, B, E | Dark and dissonant | Tension, resolution |
Mastering the inversions of the C# guitar chord provides guitarists with a powerful tool to create rich and varied harmonic textures. By experimenting with different inversions, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing.
6. Variations
The C# guitar chord has several closely related variations, namely the C#m (C# minor), C#7 (C# dominant 7th), and C#maj7 (C# major 7th) chords. Understanding these variations is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of the C# guitar chord.
Each variation is created by altering the notes of the basic C# major chord while retaining the C# root note. These variations offer distinct flavors and are commonly used in various musical genres and contexts.
| Variation | Formula | Notes | Sound | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C#m | 1-3-b5 | C#, E, G | Sad, melancholic | Ballads, folk songs |
| C#7 | 1-3-5-b7 | C#, E, G#, B | Dominant, resolving | Blues, jazz, rock |
| C#maj7 | 1-3-4#-5 | C#, E, G#, B# | Bright, sophisticated | Jazz, pop, fusion |
Mastering these variations allows guitarists to create richer and more nuanced harmonic progressions. By incorporating different variations of the C# guitar chord, guitarists can add depth, interest, and emotion to their playing.
7. Voicings
Understanding the connection between “Voicings: Open, closed, and extended” and “C# guitar chord” is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of this chord.
Voicings refer to the specific arrangement of notes within a chord. Open voicings are characterized by wider intervals between the notes, creating a spacious and airy sound. Closed voicings, on the other hand, have notes closer together, resulting in a more compact and intense sound. Extended voicings incorporate additional notes beyond the basic triad, such as 7ths, 9ths, and 11ths, adding richness and complexity to the chord.
The C# guitar chord can be played in various voicings, each with its unique sonic qualities and applications. Open voicings are often used in fingerstyle guitar and jazz, providing a clear and resonant sound. Closed voicings are commonly employed in rock and blues, creating a powerful and driving sound. Extended voicings are often found in jazz and fusion, adding harmonic sophistication and interest.
| Voicing | Sound | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Open | Spacious, airy | Fingerstyle guitar, jazz |
| Closed | Compact, intense | Rock, blues |
| Extended | Rich, complex | Jazz, fusion |
Mastering different voicings of the C# guitar chord allows guitarists to create a wide range of harmonic textures and colors. By understanding the characteristics and applications of each voicing, guitarists can effectively convey different emotions and styles in their playing.
8. Applications
The C# guitar chord finds its home in a diverse range of musical genres, each utilizing its unique sonic qualities to create distinct atmospheres and evoke various emotions.
- Rock: In the realm of rock music, the C# guitar chord exudes a raw and energetic vibe. Its power and intensity make it a staple in driving rock anthems and soaring guitar solos.
- Blues: The C# guitar chord is a cornerstone of the blues genre, adding a touch of melancholy and soulful expression to blues progressions. Its ability to convey both joy and sorrow makes it an essential tool for blues guitarists.
- Jazz: Within the sophisticated harmonies of jazz, the C# guitar chord adds a touch of complexity and sophistication. Jazz guitarists employ it in intricate chord substitutions and extended voicings to create rich and dynamic soundscapes.
- Funk: The C# guitar chord brings a funky and groovy flavor to funk music. Its rhythmic and upbeat nature complements the syncopated rhythms and infectious basslines commonly found in funk.
Mastering the C# guitar chord and understanding its applications in these diverse genres empowers guitarists to express themselves musically in a multitude of ways. By incorporating it into their playing, guitarists can add depth, versatility, and emotional resonance to their performances.
Frequently Asked Questions about the C# Guitar Chord
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding the C# guitar chord, providing clear and concise answers to enhance understanding and facilitate effective utilization of this versatile chord.
Question 1: What is the root note of the C# guitar chord?
Answer: The root note of the C# guitar chord is C#, which establishes the tonal center and determines the overall character of the chord.
Question 2: How do I play the C# guitar chord in its basic form?
Answer: To play the C# guitar chord in its basic form, use the fingering x43210, placing your fingers on the guitar strings and frets as indicated.
Question 3: What are some common variations of the C# guitar chord?
Answer: Common variations of the C# guitar chord include the C#m (C# minor), C#7 (C# dominant 7th), and C#maj7 (C# major 7th) chords, each with distinct tonal qualities and applications.
Question 4: How can I incorporate the C# guitar chord into different musical genres?
Answer: The C# guitar chord finds applications in various genres, including rock, blues, jazz, and funk, adding its unique sonic characteristics to each style.
Question 5: What are the benefits of practicing the C# guitar chord?
Answer: Practicing the C# guitar chord enhances finger dexterity, strengthens chord transitions, and expands harmonic vocabulary, making it a valuable exercise for guitarists of all levels.
Question 6: How can I explore different voicings of the C# guitar chord?
Answer: Experiment with different voicings of the C# guitar chord by adjusting the arrangement of notes within the chord, creating a range of sonic possibilities and harmonic textures.
Tips for Mastering the C# Guitar Chord
Enhancing your proficiency with the C# guitar chord requires dedication, practice, and the implementation of effective techniques. Here are several valuable tips to guide you on this musical journey:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is paramount in mastering any guitar chord. Allocate dedicated time each day to practice the C# guitar chord, focusing on accuracy and smooth transitions.
Tip 2: Use a Metronome: Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps improve your timing and rhythm. Start with a slow tempo and gradually increase the speed as your proficiency grows.
Tip 3: Explore Different Voicings: Experiment with various voicings of the C# guitar chord to discover its sonic versatility. Experiment with open, closed, and extended voicings to expand your harmonic vocabulary.
Tip 4: Apply Barre Chords: Learning barre chords, including the C# barre chord, can enhance your fretboard knowledge and facilitate effortless transitions between chords.
Tip 5: Practice Chord Progressions: Integrate the C# guitar chord into chord progressions to develop your musicality. Experiment with different progressions to enhance your harmonic understanding.
Tip 6: Listen to Music: Active listening to music that incorporates the C# guitar chord helps you absorb its usage and application in real-world scenarios.
Tip 7: Seek Feedback: Share your progress with a guitar teacher or experienced musician to gain valuable feedback. Their insights can help you refine your technique and identify areas for improvement.
Tip 8: Be Patient and Persistent: Mastering the C# guitar chord, like any musical endeavor, requires patience and persistence. Stay motivated, practice consistently, and celebrate your progress along the way.
Summary: Implementing these tips into your practice routine will significantly enhance your proficiency with the C# guitar chord. Embrace the journey, stay dedicated, and enjoy the musical rewards that await you.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of the C# guitar chord, we have delved into its fundamental aspects, variations, and practical applications. Mastering this versatile chord enhances a guitarist’s technical proficiency, harmonic understanding, and musical expressiveness.
The C# guitar chord stands as a cornerstone of various musical genres, from rock and blues to jazz and funk. Its distinct and versatile sound empowers guitarists to create a wide range of harmonic textures and evoke diverse emotions in their playing.
Embarking on a journey of practice, experimentation, and musical exploration is crucial for guitarists seeking to master the C# guitar chord. With dedication and a commitment to continuous learning, guitarists can unlock the full potential of this chord and expand their musical horizons.