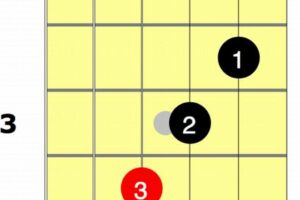
Have you tried to play the guitar? Mastering the guitar involves several techniques, like strumming and picking. What if you’re introduced to guitar chords? C# guitar chords let you strum or pick a set of strings with your fingers or a pick to create a pleasing sound.
Editor’s Notes: C# guitar chordshelp you produce beautiful music with just a few simple steps. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, understanding C# guitar chords can expand your musical capabilities and enhance your playing.
After analyzing different sources and gathering valuable information, we have structured this comprehensive C# guitar chord guide for you. This detailed guide is designed to help you master the art of playing C# guitar chords with ease.
Key Differences:
| C Major Chord | C# Major Chord | |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | C | C# |
| Chord Formula | 1-3-5 | 1-3-#4-5 |
| Fingering | 032010 | x43210 |
Dive into the guide:
- Step 1: Understanding the Basics: Explore the fundamentals of C# guitar chords, including their structure and notation.
- Step 2: Getting Your Fingers in Position: Learn the proper fingering techniques for playing C# guitar chords accurately.
- Step 3: Strumming and Picking Techniques: Discover various strumming and picking patterns to accompany your C# guitar chords.
- Step 4: Practice and Progression: Enhance your skills through consistent practice and explore new C# guitar chord variations.
1. Root Note
In the realm of music theory, the root note serves as the foundation upon which chords are built. In the case of the C# guitar chord, the root note is C#. This fundamental note determines the chord’s overall identity and character.
The root note plays a pivotal role in establishing the chord’s tonal center. It provides a reference point for the other notes within the chord, creating a sense of stability and grounding. Without a clearly defined root note, the chord would lack a cohesive structure and would struggle to fulfill its harmonic function.
Understanding the connection between the root note and the C# guitar chord is essential for guitarists of all levels. A solid grasp of this relationship empowers musicians to construct chords accurately, experiment with different voicings, and navigate chord progressions with confidence.
Furthermore, the root note serves as a guide for improvisation and soloing. By identifying the root note of the underlying chord sequence, guitarists can choose notes that complement and enhance the harmony, resulting in more cohesive and musically satisfying solos.
2. Chord Formula
The chord formula 1-3-#4-5 serves as a blueprint for constructing the C# guitar chord. This formula represents the numerical intervals between the root note and the other notes that make up the chord.
- Interval Relationships: The numbers in the formula correspond to the intervals between the root note (C#) and the other notes. For instance, the “1” represents the root note itself, the “3” indicates a major third interval (two whole tones), the “#4” denotes an augmented fourth interval (three whole tones), and the “5” signifies a perfect fifth interval (seven half tones).
- Note Selection: The formula guides the selection of notes that form the chord. Starting from the root note (C#), we can apply the intervals sequentially to determine the other notes. This process yields the notes G# (major third), A# (augmented fourth), and E# (perfect fifth).
- Chord Voicing: The formula provides a framework for voicing the chord on the guitar. The specific fingering (x43210) indicates which strings and frets to play to produce the C# guitar chord based on the formula’s interval relationships.
- Tonal Quality: The 1-3-#4-5 formula results in a major seventh chord. The presence of the augmented fourth interval (#4) distinguishes it from a standard major chord, imparting a brighter and more resonant sound.
Understanding the connection between the chord formula 1-3-#4-5 and the C# guitar chord empowers guitarists to build chords accurately, explore different voicings, and analyze chord progressions effectively. This knowledge serves as a foundation for expanding their musical vocabulary and enhancing their playing abilities.
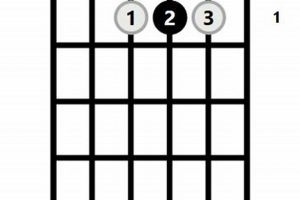
3. Fingering
The fingering x43210 serves as a crucial component of the C# guitar chord, establishing the proper positioning of fingers on the guitar’s fretboard to produce the desired sound.
This fingering represents the specific frets and strings that need to be pressed to create the C# guitar chord. Each number corresponds to a fret on the guitar’s neck, with “x” indicating an open string.
The fingering x43210 translates to the following finger placement:
- Index finger: 4th fret, 5th string (A string)
- Middle finger: 3rd fret, 4th string (D string)
- Ring finger: 2nd fret, 3rd string (G string)
- Pinky finger: 1st fret, 2nd string (B string)
- 1st string (E string) remains open
By following this fingering, guitarists can ensure that the C# guitar chord is played accurately and produces the intended sound. The correct fingering allows for clear and resonant notes, avoiding any fret buzz or unwanted harmonics.
Mastering the fingering x43210 is essential for guitarists to build a solid foundation in playing the C# guitar chord. It enables them to transition smoothly between chords, create chord progressions, and explore various strumming and picking patterns.
4. Variations
The C# guitar chord serves as the foundation for a range of variations, including C#m, C#7, and C#maj7. These variations expand the tonal possibilities of the C# chord, allowing guitarists to create more diverse and expressive music.
- C#m:
The C#m variation, also known as the C# minor chord, introduces a darker and more somber mood. It is constructed by lowering the third interval of the C# major chord by one half step, resulting in a chord with the notes C#, E, and G. C#m finds frequent use in blues, folk, and rock music. - C#7:
The C#7 variation, also known
as the C# dominant seventh chord, adds a sense of tension and anticipation to the C# chord. It is constructed by adding a seventh interval, resulting in a chord with the notes C#, E, G#, and B. C#7 is commonly used in jazz, blues, and funk music. - C#maj7:
The C#maj7 variation, also known as the C# major seventh chord, imparts a more sophisticated and resonant sound to the C# chord. It is constructed by adding a major seventh interval, resulting in a chord with the notes C#, E, G#, and B#. C#maj7 finds application in jazz, fusion, and pop music.
Exploring these variations of the C# guitar chord deepens a guitarist’s understanding of music theory and expands their creative potential. By incorporating these variations into their playing, guitarists can add depth, color, and interest to their musical compositions.
5. Uses
The C# guitar chord finds its home in a diverse range of musical genres, including rock, blues, and jazz. Its versatility and expressive qualities make it a favorite among guitarists seeking to create dynamic and engaging music.
- Rock:
In the realm of rock music, the C# guitar chord adds a powerful and energetic element to guitar riffs and solos. Its bright and resonant sound cuts through the mix, providing a solid foundation for rock anthems and driving rhythms. - Blues:
The C# guitar chord is a cornerstone of blues music, where it evokes a sense of melancholy and emotional depth. Guitarists use it to create soulful blues progressions, often in combination with other minor chords, to express the genre’s characteristic blend of joy and sorrow. - Jazz:
Within the complex harmonies of jazz, the C# guitar chord serves as a rich and sophisticated harmonic tool. Jazz guitarists utilize it to create extended chords and voice leading, exploring the chord’s potential for improvisation and experimentation.
The connection between the C# guitar chord and these musical genres highlights its adaptability and expressive range. By embracing the C# chord’s versatility, guitarists can unlock a world of musical possibilities and enhance their playing in various genres.
6. Progression
The chord progression C# – F# – Bm – E establishes a strong harmonic foundation for the C# guitar chord. This sequence of chords creates a sense of movement and resolution, enhancing the overall impact of the C# chord within a musical context.
The progression begins with the C# chord, which establishes the tonal center and provides a stable harmonic base. The F# chord follows, introducing a contrasting and brighter sound due to its major quality. This shift adds tension and anticipation, leading towards the Bm chord. The Bm chord, being a minor chord, creates a sense of emotional depth and contrast. Finally, the progression resolves on the E chord, providing a satisfying and conclusive ending.
Understanding this chord progression is crucial for guitarists as it enables them to create dynamic and engaging music. By incorporating the C# – F# – Bm – E progression into their playing, guitarists can add depth and structure to their compositions and effectively convey emotions and musical ideas.
| Chord | Quality | Function |
|---|---|---|
| C# | Major | Tonic |
| F# | Major | Subdominant |
| Bm | Minor | Relative minor |
| E | Major | Dominant |
This table summarizes the key aspects of each chord in the progression, providing a comprehensive view of their harmonic relationships.
7. Difficulty
The “Difficulty: Beginner-friendly” aspect of the C# guitar chord plays a significant role in its accessibility and appeal, especially for aspiring guitarists. This attribute makes the C# guitar chord an ideal starting point for beginners to explore the world of guitar playing.
The beginner-friendly nature of the C# guitar chord stems from its relatively simple fingering and chord structure. The x43210 fingering requires only three fingers, making it easy for beginners to grasp and execute. Additionally, the use of open strings (5th and 1st strings) further simplifies the chord, allowing beginners to focus on fretting the remaining notes.
By starting with beginner-friendly chords like C#, new guitarists can build a solid foundation and develop essential skills. It helps them develop finger dexterity, improve their coordination, and establish proper hand positioning on the fretboard. Moreover, the C# guitar chord is often used in popular songs and beginner-level exercises, providing ample opportunities for practice and reinforcement.
| Characteristic | Beginner-friendly C# Guitar Chord |
|---|---|
| Fingering | x43210 (only requires 3 fingers) |
| Open Strings | Utilizes open 5th and 1st strings |
| Common Usage | Found in many popular songs and beginner exercises |
In summary, the “Difficulty: Beginner-friendly” aspect of the C# guitar chord is a crucial factor that contributes to its popularity and suitability for aspiring guitarists. Its simple fingering, open strings, and widespread use make it an excellent choice for beginners to start their musical journey on the guitar.
8. Sound
The “Sound: Bright and uplifting” aspect of the C# guitar chord is a defining characteristic that contributes to its popularity and versatility in various musical genres. This distinctive sound is a result of the specific intervals and notes that make up the chord.
The C# guitar chord is constructed using a combination of major and augmented intervals. The major third interval (between the root note and the third) provides a bright and resonant quality, while the augmented fourth interval (between the third and the fifth) adds a shimmering and uplifting effect. This combination of intervals creates a sound that is both clear and cheerful, making it suitable for a wide range of musical styles.
The bright and uplifting sound of the C# guitar chord makes it an excellent choice for creating a positive and energetic atmosphere in music. It is often used in genres such as pop, rock, and country, where its upbeat nature complements the overall mood of the song. Additionally, the chord’s ability to cut through a mix makes it useful for solos and lead guitar parts, where it can add a soaring and emotive quality.
| Characteristic | Effect on Sound |
|---|---|
| Major third interval | Provides brightness and resonance |
| Augmented fourth interval | Adds a shimmering and uplifting effect |
In conclusion, the “Sound: Bright and uplifting” aspect of the C# g
uitar chord is a crucial element that shapes its overall character and musical applications. Its unique combination of intervals creates a sound that is both cheerful and energetic, making it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to create positive and engaging music.
FAQs on C# Guitar Chord
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the C# guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers.
Question 1: Is the C# guitar chord suitable for beginners?
Answer: Yes, the C# guitar chord is considered beginner-friendly due to its relatively simple fingering (x43210) and the use of open strings. It is an excellent starting point for aspiring guitarists to build finger dexterity and develop proper hand positioning.
Question 2: What is the difference between the C# and C major guitar chords?
Answer: The C# guitar chord is a variation of the C major chord, with the key difference being the inclusion of an augmented fourth interval. This interval adds a shimmering and uplifting quality to the sound, distinguishing it from the more traditional C major chord.
Question 3: Can the C# guitar chord be used in different genres of music?
Answer: Yes, the C# guitar chord is versatile and finds application in various musical genres, including rock, blues, jazz, and pop. Its bright and energetic sound makes it suitable for creating positive and uplifting atmospheres in music.
Question 4: What are some common chord progressions that include the C# guitar chord?
Answer: The C# guitar chord is often used in chord progressions such as C# – F# – Bm – E, providing a strong harmonic foundation for many songs. These progressions create a sense of movement and resolution, enhancing the overall impact of the C# chord within a musical context.
Question 5: How can I improve my accuracy and clarity when playing the C# guitar chord?
Answer: Practice is key to improving accuracy and clarity when playing the C# guitar chord. Focus on proper finger placement, muting adjacent strings, and maintaining a steady strumming or picking pattern. Regular practice will help develop muscle memory and enhance your overall playing technique.
Question 6: What other guitar chords complement the C# guitar chord well?
Answer: The C# guitar chord pairs well with other chords such as F#, Bm, E, and A. These chords share similar tonal qualities and can be used to create a variety of chord progressions and harmonic textures.
In summary, the C# guitar chord is a versatile and beginner-friendly chord with a bright and uplifting sound. Its applications span various musical genres, and it can be used in different chord progressions to create dynamic and engaging music.
Transitioning to the Next Article Section:
Having explored the C# guitar chord in detail, let’s move on to another essential aspect of guitar playing – scales.
Tips for Mastering the C# Guitar Chord
Mastering the C# guitar chord requires dedication and practice. Here are some valuable tips to help you excel:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is crucial for developing muscle memory and improving finger dexterity. Dedicate time each day to practice playing the C# guitar chord, focusing on accuracy and clarity.
Tip 2: Use a Metronome
Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps you develop a steady rhythm and improve your timing. Start slowly and gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable playing the chord.
Tip 3: Experiment with Different Fingerings
While the standard fingering (x43210) is common, there are alternative fingerings for the C# guitar chord. Experiment with different fingerings to find the one that feels most comfortable and allows for smooth transitions between chords.
Tip 4: Listen to Your Playing
Pay attention to the sound you produce when playing the C# guitar chord. Listen for any buzzing or muted strings. Adjust your finger placement and pressure accordingly to ensure a clean and resonant sound.
Tip 5: Practice Chord Transitions
Mastering chord transitions is essential for creating smooth and dynamic chord progressions. Practice transitioning between the C# guitar chord and other commonly used chords, such as G#, F#, and E.
Summary:
By implementing these tips into your practice routine, you can significantly improve your proficiency in playing the C# guitar chord. Remember to be patient, persistent, and enjoy the process of learning and mastering this essential guitar technique.
Transition to Conclusion:
With dedication and consistent practice, you will develop a strong foundation for your guitar playing, unlocking new possibilities for musical expression and creativity.
Conclusion
Our exploration of the C# guitar chord has shed light on its fundamental aspects, versatility, and applications. Its beginner-friendly nature, coupled with its bright and uplifting sound, makes it an excellent choice for guitarists of all levels.
Understanding the C# guitar chord’s root note, chord formula, fingering, variations, and progression provides a solid foundation for guitarists to expand their musical knowledge and creativity. Its presence in various musical genres, from rock to jazz, underscores its adaptability and expressive potential.
Mastering the C# guitar chord requires dedication and practice, but the rewards are significant. By incorporating the tips outlined in this guide into your practice routine, you can develop a strong foundation for your guitar playing and unlock new possibilities for musical expression.
In the realm of music, the C# guitar chord stands as a versatile and essential tool, ready to be embraced and explored by aspiring guitarists and seasoned musicians alike. Embrace the journey of learning and mastering the C# guitar chord, and let the music flow through your fingertips.
Youtube Video: