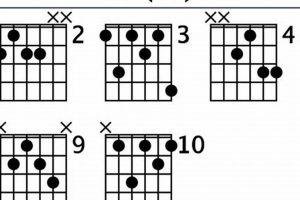
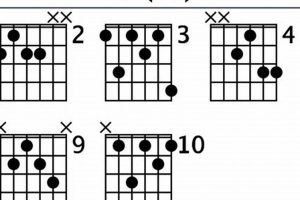
Learning to play the guitar can be a rewarding experience, but it can also be challenging. One of the most important things to learn is how to play different chords. A guitar chord c# minor is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of songs and genres.
Editor’s Note:Understanding the guitar chord c# minor is essential for guitarists of all levels, as it is a fundamental chord used in countless songs.
This guide will provide you with everything you need to know about the guitar chord c# minor, including how to play it, where to use it, and some tips for mastering it.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways:
| C#m Chord | |
|---|---|
| Root Note: | C# |
| Chord Type: | Minor |
| Voicings: | Multiple |
| Difficulty: | Beginner-friendly |
Main Article Topics:
- How to Play the C#m Chord
- Where to Use the C#m Chord
- Tips for Mastering the C#m Chord
1. Root Note
In the context of the C#m guitar chord, the root note, C#, plays a crucial role in defining its harmonic structure and tonal characteristics. The root note serves as the foundation upon which the chord is built, determining its fundamental pitch and overall sound.
The C#m chord comprises three distinct notes: C#, E, and G#. C#, being the root note, establishes the chord’s identity and provides a sense of stability and resolution. The other notes, E and G#, harmonize with the root, contributing to the chord’s overall tonality and emotional impact.
Understanding the relationship between the root note and the guitar chord is essential for guitarists seeking to master chord construction, improvisation, and music theory. By grasping the role of the root note, guitarists can effectively navigate chord progressions, create harmonic movement, and develop a deeper comprehension of music composition.
In practical terms, identifying the root note allows guitarists to:
- Easily transpose chords to different keys
- Construct and harmonize melodies
- Analyze and understand chord progressions
- Improvise and create original music
Furthermore, the root note serves as a reference point for understanding chord inversions. Inversions occur when the root note is not played in the lowest position, resulting in variations of the chord’s voicing. By understanding the root note, guitarists can quickly identify and utilize inversions to add harmonic interest and melodic variety to their playing.
Overall, the connection between the root note, C#, and the guitar chord C#m is fundamental to comprehending chord structure, tonality, and music theory. This understanding empowers guitarists to navigate the fretboard with confidence, enhance their musical expression, and delve deeper into the art of guitar playing.
2. Chord Type
The term “Chord Type: Minor” in relation to the “guitar chord C#m” holds significant importance in understanding its harmonic function and emotional impact. Minor chords, characterized by their distinct sound and expressive qualities, play a vital role in shaping the overall mood and atmosphere of music.
- Tonal Quality: Minor chords evoke a sense of sadness, melancholy, or introspection. The C#m guitar chord, with its combination of C#, E, and G#, embodies this tonal quality, often employed in genres like blues, folk, and emotive rock music.
- Interval Structure: Minor chords are constructed using a specific interval pattern of root, minor third, and perfect fifth. In the case of C#m, the interval between C# (root) and E (minor third) creates the characteristic minor sound.
- Harmonic Function: Minor chords often serve as a contrasting element to major chords within a chord progression. The C#m guitar chord can create a sense of tension or resolution when used in conjunction with major chords, adding depth and emotional weight to the music.
- Emotional Impact: Minor chords have a profound impact on the emotional response of listeners. The C#m guitar chord, with its inherent sadness, can evoke feelings of nostalgia, regret, or vulnerability, making it a powerful tool for conveying emotions through music.
In summary, understanding the “Chord Type: Minor” in the context of the “guitar chord C#m” provides essential insights into its tonal characteristics, harmonic function, and emotional impact. These aspects empower guitarists to harness the expressive potential of minor chords, enabling them to create evocative and emotionally resonant music.
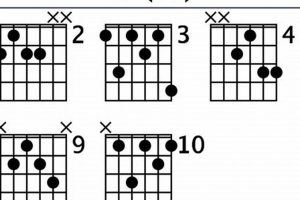
3. Voicings
The term “Voicings: Multiple variations” in relation to the “guitar chord c# minor” highlights the diverse fingerings and arrangements of notes that can be employed to play the same chord. Understanding and utilizing these variations can significantly enhance a guitarist’s musical expression and versatility.
- Open Voicing:
In open voicing, the notes of the C#m chord (C#, E, and G#) are played on different strings, leaving space between them. This voicing creates a clear and resonant sound, often used for strumming chords or arpeggiated passages.
- Closed Voicing:
In closed voicing, the notes of the C#m chord are played in close proximity on adjacent strings. This voicing produces a thicker and more compact sound, commonly employed in jazz and fingerstyle guitar.
- Inversions:
Inversions occur when the root note of the C#m chord is not played in the lowest position. This technique creates variations of the chord’s voicing, altering its harmonic character and melodic possibilities.
- Extended Voicings:
Extended voicings incorporate additional notes beyond the basic triad (C#, E, and G#), such as the 7th, 9th, or 11th. These voicings add harmonic richness and complexity to the C#m chord.
Exploring the various voicings of the “guitar chord c# minor” empowers guitarists to:
- Create diverse tonal colors and textures
- Enhance chord progressions with harmonic interest
- Accommodate different musical styles and genres
- Develop their technical dexterity and fingerboard knowledge
In summary, the “Voicings: Multiple variations” aspect of the “guitar chord c# minor” provides a vast sonic palette for guitarists to explore. Masteri
ng these variations enables them to unlock a wide range of musical possibilities and express their creativity more effectively.
4. Difficulty
The “Difficulty: Beginner-friendly” aspect of the “guitar chord c# minor” holds particular significance for aspiring guitarists, making it an accessible and rewarding choice for those embarking on their musical journey.
One of the primary reasons behind the beginner-friendly nature of the C#m guitar chord lies in its relatively straightforward fingering. Unlike barre chords, which require more advanced hand positioning and finger strength, the C#m chord can be played using only three fingers: the index, middle, and ring fingers. This simplified fingering makes it easier for beginners to form the chord correctly and transition smoothly between chords.
Furthermore, the C#m chord is often introduced early on in guitar lessons or instructional materials due to its fundamental role in many popular songs and chord progressions. By learning the C#m chord, beginners can quickly expand their repertoire and start playing basic songs, which helps maintain motivation and fosters a sense of accomplishment.
The beginner-friendly nature of the C#m guitar chord also contributes to its practical significance. As guitarists progress and develop their skills, they may encounter more complex chords and techniques. However, the C#m chord remains a valuable foundation, serving as a building block for more advanced chords and progressions. By mastering the C#m chord early on, guitarists lay a solid foundation for their future musical growth.
| Beginner-friendly | Not Beginner-friendly | |
|---|---|---|
| Fingering | Uses only three fingers | May require more advanced fingerings, such as barres |
| Learning Curve | Relatively easy to learn | Can be more challenging to master |
| Practical Significance | Essential for many popular songs and chord progressions | May be less commonly used in certain musical styles or genres |
In summary, the “Difficulty: Beginner-friendly” aspect of the “guitar chord c# minor” is a crucial factor that makes it an excellent choice for aspiring guitarists. Its simplified fingering, early introduction in learning materials, and practical significance contribute to its beginner-friendly nature, making it a valuable foundation for musical growth and enjoyment.
5. Barre Chord
The absence of a barre in the “guitar chord c# minor” is a significant characteristic that sets it apart from many other guitar chords and contributes to its beginner-friendly nature and versatility.
- Simplified Fingering:
Unlike barre chords, which require the index finger to press down multiple strings across the fretboard, the C#m chord can be played without the use of a barre. This simplified fingering makes it easier for beginners to form the chord correctly and transition smoothly between chords.
- Reduced Hand Strain:
The lack of a barre eliminates the need for excessive finger strength and contortion, reducing strain on the hand and fingers. This makes the C#m chord more comfortable to play, especially for beginners or those with smaller hands.
- Open Voicings:
The absence of a barre allows for open voicings of the C#m chord, where the notes are played on different strings with space between them. This creates a clear and resonant sound, well-suited for strumming or arpeggiated passages.
- Versatility Across Genres:
The C#m chord’s lack of a barre makes it versatile and applicable across various musical genres. It is commonly used in folk, pop, rock, and blues music, among others, providing a solid foundation for rhythm and harmony.
In summary, the “Barre Chord: No” characteristic of the “guitar chord c# minor” contributes to its beginner-friendliness, reduced hand strain, open voicings, and versatility across musical genres, making it a valuable addition to the guitarist’s repertoire.
6. Open Chord
The designation “Open Chord: Yes” in relation to the “guitar chord c# minor” signifies that this chord can be played with one or more open strings, meaning strings that are not fretted by any finger. This characteristic contributes to the chord’s accessibility, versatility, and distinct sound.
The C#m chord can be played in multiple open voicings, each with its own unique tonal quality. One common open voicing involves playing the C# note on the 6th string (low E), the E note on the 5th string (A), and the G# note on the 1st string (high E), while leaving the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th strings open. This voicing creates a clear and resonant sound, perfect for strumming or fingerpicking.
Open chords, like the C#m, are often used in folk, blues, and rock music, where their open and airy sound complements the rhythmic and melodic elements of these genres. They are also commonly employed in beginner guitar lessons due to their relative ease of playability, allowing aspiring guitarists to quickly build a foundation of basic chords.
Understanding the connection between “Open Chord: Yes” and “guitar chord c# minor” provides guitarists with several practical benefits:
- Simplified Fingering: Open chords generally require less finger dexterity and strength compared to closed or barre chords, making them easier to play, especially for beginners.
- Clear and Resonant Sound: Open strings contribute to the clarity and resonance of open chords, making them well-suited for strumming and arpeggiated passages.
- Genre Versatility: Open chords are commonly used in various musical genres, providing guitarists with a versatile tool for accompanying songs and creating rhythmic patterns.
In summary, the “Open Chord: Yes” aspect of the “guitar chord c# minor” highlights the chord’s accessibility, distinct sound, and practical significance in different musical contexts. Embracing this understanding empowers guitarists to expand their chord vocabulary, enhance their playing techniques, and explore a wide range of musical styles.
| Open Chord | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| C#m | – Played with open strings – Clear and resonant sound – Simplified fingering | – Easy to play – Well-suited for strumming – Versatile for various genres |
7. Inversions
In music theory, inversions refer to variations of a chord where the root note is not played in the lowest position. The “guitar chord c# minor” has three inversions, each with its own unique sound and :
- First inversion (C#m/E): The E note, the third of the C#m chord, is played in the bass. This inversion creates a more open an
d spacious sound, and it is often used in jazz and classical music. - Second inversion (C#m/G#): The G# note, the fifth of the C#m chord, is played in the bass. This inversion has a darker and more somber sound, and it is often used in folk and blues music.
- Third inversion (C#m/B): The B note, the seventh of the C#m chord, is played in the bass. This inversion has a more dissonant and unstable sound, and it is often used in modern and experimental music.
Understanding the concept of inversions is essential for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more interesting and sophisticated chord progressions. Inversions can be used to add variety to strumming patterns, create smooth voice leading between chords, and achieve specific emotional effects in music.
Here are some practical examples of how inversions can be used in guitar playing:
- In a folk song, you might use a C#m/G# inversion to create a warm and inviting atmosphere.
- In a jazz standard, you might use a C#m/E inversion to create a more sophisticated and elegant sound.
- In a rock song, you might use a C#m/B inversion to create a more aggressive and edgy sound.
By understanding the connection between “Inversions: First, second, and third” and “guitar chord c# minor,” guitarists can unlock a wealth of new harmonic possibilities and enhance their overall musicianship.
| Inversion | Bass Note | Sound | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| First inversion (C#m/E) | E | Open and spacious | Jazz, classical music |
| Second inversion (C#m/G#) | G# | Dark and somber | Folk, blues music |
| Third inversion (C#m/B) | B | Dissonant and unstable | Modern, experimental music |
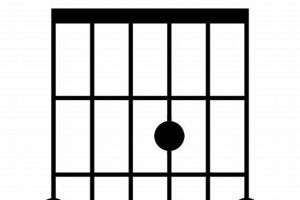
8. Finger Positioning
The precise positioning of the index, middle, and ring fingers on the guitar fretboard is crucial for forming the C#m chord correctly and efficiently. This finger positioning, when mastered, enables guitarists to play the chord with clarity, accuracy, and minimal strain.
- Index Finger: The index finger is responsible for fretting the root note, C#, on the 4th string (D string) at the 4th fret. Proper positioning involves placing the fingertip directly behind the fretwire, applying sufficient pressure to produce a clear note without buzzing.
- Middle Finger: The middle finger frets the minor third, E, on the 5th string (A string) at the 5th fret. Similar to the index finger, the fingertip should be placed behind the fretwire, ensuring a clean and resonant sound.
- Ring Finger: The ring finger frets the perfect fifth, G#, on the 6th string (low E string) at the 6th fret. Again, proper positioning requires the fingertip to be placed precisely behind the fretwire, avoiding any unwanted string muting or buzzing.
Mastering the finger positioning for the C#m guitar chord not only enhances the clarity and accuracy of the chord but also lays the foundation for more complex chords and fingerings. By developing muscle memory and coordination between the fingers, guitarists can transition smoothly between chords, add embellishments, and explore various chord voicings.
9. Common Progressions
Understanding the connection between “Common Progressions: C#m to G#m, C#m to F#m, C#m to A” and “guitar chord c# minor” is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their songwriting abilities.
These chord progressions are frequently employed in various musical genres, including pop, rock, folk, and blues. They provide a solid foundation for creating harmonious and emotionally resonant chord sequences.
The C#m guitar chord serves as the tonal center in these progressions, establishing the harmonic context and providing a sense of stability. The movement from C#m to G#m creates a sense of forward motion and resolution, as G#m is the relative major of C#m. Similarly, the progression to F#m introduces a contrasting minor chord, adding depth and emotional weight to the sequence.
In the progression to A, the C#m chord acts as a pivot chord, transitioning smoothly to the new tonal center. This progression creates a sense of anticipation and release, as the A chord provides a satisfying resolution.
Here are some real-life examples of how these progressions are used in popular songs:
- “Yesterday” by The Beatles: C#m – G#m – C#m – F#m – C#m – A
- “Knocking on Heaven’s Door” by Bob Dylan: C#m – G#m – F#m – C#m – A
- “Wonderwall” by Oasis: C#m – G#m – F#m – C#m – A
Understanding these common progressions empowers guitarists to:
- Create more dynamic and engaging chord sequences
- Enhance their songwriting skills by incorporating harmonic variety
- Develop a deeper understanding of music theory and chord relationships
In summary, the connection between “Common Progressions: C#m to G#m, C#m to F#m, C#m to A” and “guitar chord c# minor” provides guitarists with a valuable tool for expanding their musical horizons, crafting expressive chord progressions, and enriching their overall playing.
Progression Table
| Progression | Tonal Center | Emotional Impact |
|---|---|---|
| C#m to G#m | C#m | Forward motion, resolution |
| C#m to F#m | C#m | Contrast, emotional weight |
| C#m to A | A | Pivot, anticipation, release |
10. Tonal Quality
The connection between the “Tonal Quality: Sad, melancholic” and the “guitar chord c# minor” is deeply rooted in the inherent characteristics of the chord and its effect on listeners. The C#m guitar chord, with its minor tonality, evokes a sense of sadness, introspection, and melancholy.
- Emotional Expression:
The minor tonality of the C#m chord creates a sense of emotional vulnerability and introspection. Its dissonant intervals produce a bittersweet sound that resonates with feelings of sadness, regret, and longing. This tonal quality makes the C#m guitar chord particularly effective in expressing melancholic emotions and conveying a sense of loss or nostalgia.
- Musical Context:
The C#m guitar chord is commonly used in musical genres and pieces that aim to evoke a sense of sadness or melancholy. It is frequently employed in ballads, blues, and folk songs, where its melancholic tonality complements the lyrical themes of heartbreak, loss, and unfulfilled desires.
- Harmonic Function:
Within the context of chord progressions, the C#m guitar chord often serves as a contrasting element to major chords, creating a sense of tension and release. Its minor tonality can add depth and emotional weight to chord sequences, enhancing the overall expressiveness of the music.
Cultural Significance: The “Tonal Quality: Sad, melancholic” associated with the C#m guitar chord has cultural significance and resonates with listeners across different backgrounds and generations. The minor tonality taps into universal human emotions of sadness and melancholy, making the C#m guitar chord a versatile and emotionally evocative tool for musicians.
In summary, the “Tonal Quality: Sad, melancholic” of the “guitar chord c# minor” stems from its inherent minor tonality and dissonant intervals, evoking a sense of sadness, introspection, and melancholy. This tonal quality finds expression in various musical contexts, from ballads to blues, and contributes to the overall emotional impact and cultural significance of the chord.
11. Musical Context
The connection between “Musical Context: Pop, rock, blues, folk” and “guitar chord c# minor” reveals the versatility and expressive capabilities of the C#m chord across diverse musical genres. Its distinct tonal quality and harmonic function make it a valuable tool for musicians seeking to convey a range of emotions and create dynamic musical landscapes.
- Pop:
In pop music, the C#m guitar chord often provides a foundation for heartfelt ballads and introspective songs. Its melancholic tonality complements themes of love, loss, and longing, adding depth and emotional resonance to the music. Example: “Yesterday” by The Beatles
- Rock:
Within the realm of rock music, the C#m guitar chord adds a touch of introspection and vulnerability to powerful anthems and energetic riffs. Its dissonant intervals create a sense of tension and release, enhancing the emotional impact of the music. Example: “Knocking on Heaven’s Door” by Bob Dylan
- Blues:
In the context of blues music, the C#m guitar chord embodies the genre’s signature blend of sorrow and resilience. Its minor tonality evokes feelings of melancholy and longing, while its harmonic function contributes to the blues’ characteristic call-and-response patterns. Example: “Crossroads” by Robert Johnson
- Folk:
Within the realm of folk music, the C#m guitar chord adds a touch of introspection and authenticity to traditional ballads and contemporary singer-songwriter compositions. Its simple yet evocative sound complements the genre’s emphasis on storytelling and emotional connection. Example: “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
In summary, the “Musical Context: Pop, rock, blues, folk” highlights the C#m guitar chord’s versatility and expressive capabilities across diverse musical genres. Its melancholic tonality and harmonic function make it a valuable tool for musicians seeking to convey a range of emotions and create dynamic musical landscapes.
12. Example Song
The connection between “Example Song: “Strawberry Fields Forever” by The Beatles” and “guitar chord c# minor” lies in the song’s poignant use of the chord to convey a sense of longing and nostalgia.
- Emotional Expression:
In “Strawberry Fields Forever,” the C#m guitar chord serves as a harmonic foundation, supporting the song’s melancholic melody and introspective lyrics. The chord’s minor tonality mirrors the feelings of loss and yearning expressed in the song, creating a sense of emotional resonance that deeply connects with listeners.
- Harmonic Function:
Within the context of the song’s chord progression, the C#m guitar chord plays a crucial harmonic role. Its movement from C#m to F#m to G#m creates a sense of harmonic tension and release, contributing to the song’s overall emotional impact. The chord’s placement in the verse and chorus sections provides stability and a sense of resolution, reinforcing the song’s themes of longing and remembrance.
- Melodic Context:
The C#m guitar chord in “Strawberry Fields Forever” interacts beautifully with the song’s melody. The chord’s notes provide harmonic support to the vocal line, enhancing the emotional impact of the lyrics. The interplay between the chord and melody creates a sense of unity and coherence, drawing listeners into the song’s evocative atmosphere.
- Cultural Significance:
The use of the C#m guitar chord in “Strawberry Fields Forever” has left a lasting mark on popular music. The song’s unique sound and emotional depth have inspired countless musicians, contributing to the chord’s widespread recognition and appeal. Its association with the Beatles and their era has further cemented its place in music history.
In summary, the connection between “Example Song: “Strawberry Fields Forever” by The Beatles” and “guitar chord c# minor” is multifaceted, encompassing emotional expression, harmonic function, melodic context, and cultural significance. The chord’s melancholic tonality and poignant use in the song have made it an enduring symbol of longing and nostalgia, resonating with listeners worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions about the C#m Guitar Chord
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the C#m guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to enhance your understanding.
Question 1: Is the C#m guitar chord difficult to play?
Answer: The C#m guitar chord is considered beginner-friendly due to its relatively simple fingering. It does not require any barre chords or advanced techniques, making it accessible to guitarists of all skill levels.
Question 2: What is the tonal quality of the C#m guitar chord?
Answer: The C#m guitar chord possesses a minor tonality, characterized by a sad or melancholic sound. This tonal quality evokes emotions of introspection, longing, and vulnerability, making it suitable for expressing a range of feelings in music.
Question 3: How is the C#m guitar chord commonly used in music?
Answer: The C#m guitar chord is a versatile chord commonly employed in various musical genres, including pop, rock, blues, and folk. Its melancholic tonality adds depth and emotional resonance to chord progressions, often serving as a contrasting element to major chords.
Question 4: What are some common chord progressions that include the C#m guitar chord?
Answer: The C#m guitar chord frequently appears in chord progressions such as C#m to G#m, C#m to F#m, and C#m to A. These progressions create a sense of harmonic movement and emotional impact, contributing to the overall expressiveness of music.
Question 5: How can I incorporate the C#m guitar chord into my playing?
Answer: To incorporate the C#m guitar chord into your playing, practice its fingering to ensure accuracy and comfort. Experiment with different voicings and inversions to explore its tonal variations. Gradually introduce the chord into your chord progressions and compositions, paying attention to its emotional impact and harmonic function.
Question 6: What are some famous songs that feature the C#m guitar chord?
Answer: The C#m guitar chord has been used in numerous renowned songs, including “Strawberry Fields Forever”
by The Beatles, “Yesterday” by The Beatles, and “Knocking on Heaven’s Door” by Bob Dylan. Its melancholic tonality and expressive capabilities have made it a staple in popular music.
Understanding these frequently asked questions will enhance your knowledge and practical application of the C#m guitar chord, empowering you to create emotive and resonant music.
Transition to the next article section: Dive deeper into the captivating world of guitar chords and explore techniques, variations, and their profound impact on musical expression.
Tips for Mastering the C#m Guitar Chord
Embark on a journey to enhance your guitar playing skills by incorporating the versatile C#m chord. These practical tips will empower you to master its nuances and unlock its full potential.
Tip 1: Practice Finger Positioning
Ensuring precise finger placement is paramount for a clear and resonant C#m chord. Situate your index finger on the 4th fret of the D string (4th string), middle finger on the 5th fret of the A string (5th string), and ring finger on the 6th fret of the low E string (6th string).
Tip 2: Experiment with Voicings
Explore the diverse sonic possibilities of the C#m chord by experimenting with different voicings. Move the notes around the fretboard while maintaining the root, third, and fifth intervals to discover variations that suit your musical style.
Tip 3: Utilize Inversions
Inversions add depth and harmonic interest to chord progressions. Try inverting the C#m chord by playing the E note (third) in the bass, followed by the G# note (fifth) and then the C# note (root). Each inversion offers a unique tonal color.
Tip 4: Practice Chord Transitions
Smoothly transitioning between the C#m chord and other chords is essential for creating fluid chord progressions. Practice moving from C#m to G#m, F#m, and A to develop your dexterity and enhance your musical flow.
Tip 5: Listen to the Masters
Immerse yourself in the music of guitarists who excel in using the C#m chord. Listen to recordings and analyze how they incorporate the chord into their playing. This will expose you to different techniques and inspire your own creativity.
Tip 6: Experiment with Different Genres
The C#m chord’s versatility shines across various musical genres. Explore its melancholic tonality in folk and blues, its emotional depth in rock, and its expressive quality in pop. Experimenting with different genres will broaden your musical horizons and expand your chord vocabulary.
Tip 7: Use a Metronome
Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine will help you develop a steady rhythm and improve your timing. Practice playing the C#m chord at different tempos to enhance your accuracy and consistency.
Tip 8: Don’t Give Up
Mastering any guitar chord requires dedication and perseverance. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see immediate results. With consistent practice and patience, you will develop the muscle memory and coordination necessary to play the C#m chord with confidence and expressiveness.
By embracing these tips, you will elevate your guitar skills, expand your chordal knowledge, and unlock the full potential of the C#m guitar chord. Remember, the journey of musical mastery is a continuous one, and the C#m chord is an invaluable tool in your musical arsenal.
Conclusion
The C#m guitar chord, with its distinct sound and versatile applications, is an essential tool for guitarists of all levels. Its melancholic tonality evokes emotions and adds depth to musical compositions.
Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the technical aspects, musical context, and practical techniques surrounding the C#m guitar chord. By understanding its nuances and mastering its execution, guitarists can unlock a world of expressive possibilities.
Incorporating the C#m guitar chord into your playing will enhance your harmonic vocabulary, expand your creative potential, and allow you to connect with audiences on a deeper level. Embrace the journey of musical mastery, and let the C#m guitar chord be your guide in creating music that resonates and inspires.