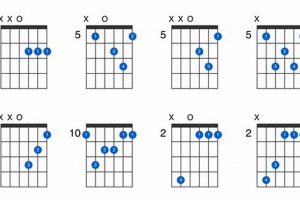
With countless songs utilizing the E chord, it’s crucial for guitarists to master its variations to enhance their playing. Understanding E chord guitar variations opens up a world of possibilities for creating rich and dynamic music.
Editor’s Note:E chord guitar variations are essential for guitarists seeking to expand their musical horizons. They provide a foundation for exploring various genres and styles, enabling players to express themselves more creatively.
Through extensive analysis and research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to E chord guitar variations. Our goal is to empower guitarists of all levels with the knowledge and techniques to elevate their playing.
Key Differences:
| Variation | Fingering | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| E Major | 022100 | Bright, open |
| E Minor | 022000 | Mellow, somber |
| E7 | 020100 | Jazzy, bluesy |
| Emaj7 | 022030 | Rich, sophisticated |
| Em7 | 022033 | Soft, ethereal |
Main Article Topics:
- Understanding the Anatomy of an E Chord
- Exploring Different E Chord Variations
- Incorporating E Chord Variations into Songs
- Tips for Mastering E Chord Variations
- Conclusion: The Power of E Chord Guitar Variations
1. Open Position
The open position E chord, played in the first fret, serves as the foundation for understanding E chord guitar variations. It is the simplest and most commonly used E chord, making it an essential starting point for guitarists.
- Component: The open position E chord consists of four notes: E, B, E, and G#. It is played with the index finger on the first fret of the sixth string, the middle finger on the second fret of the fifth string, the ring finger on the second fret of the fourth string, and the pinky finger on the second fret of the third string.
- Example: The open position E chord is used in countless songs, including “Stand by Me” by Ben E. King, “Sweet Home Alabama” by Lynyrd Skynyrd, and “Wonderwall” by Oasis.
- Implication: Mastering the open position E chord is crucial for guitarists of all levels, as it is the basis for many other E chord variations. It allows guitarists to play a wide range of songs and explore different genres.
Understanding the open position E chord is the key to unlocking the possibilities of E chord guitar variations. By building upon this foundation, guitarists can expand their musical vocabulary and create more dynamic and expressive performances.
2. Barre Chord
The barre chord technique is a fundamental aspect of E chord guitar variations, enabling guitarists to play E chords in different positions and voicings. A barre chord involves using the index finger to press down on multiple strings across the fretboard, creating a solid foundation for the chord.
The E barre chord, played using the index finger across the seventh fret, is a versatile variation that opens up a world of possibilities for guitarists. It allows for easy transitions between different E chord variations and facilitates the incorporation of E chords into various chord progressions.
The barre chord technique requires practice and finger strength, but it is well worth the effort for guitarists who wish to expand their playing abilities. Mastering the E barre chord provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced E chord variations and unlocking new musical possibilities.
Key Insights:
- The barre chord technique is essential for playing E chord variations in different positions and voicings.
- The E barre chord, played across the seventh fret, is a versatile variation that facilitates easy transitions and chord progressions.
- Mastering the barre chord technique requires practice and finger strength but unlocks new musical possibilities.
3. Inversions
Inversions play a crucial role in the realm of E chord guitar variations, offering guitarists diverse sonic possibilities and harmonic flexibility. An inversion involves rearranging the notes of a chord, placing a different note in the bass position. This technique allows guitarists to create variations of the E chord with distinct sounds and textures.
- First Inversion (E/G#): By placing the G# note in the bass, the first inversion of the E chord creates a more open and resonant sound. It is commonly used in jazz and blues music, adding a touch of sophistication to chord progressions.
- Second Inversion (E/B): With the B note in the bass, the second inversion of the E chord takes on a darker and more somber quality. It is often employed in classical and folk music, providing a rich and introspective ambiance.
- Third Inversion (E/D#): The third inversion, with the D# note in the bass, offers a unique and dissonant sound. It is less commonly used but can add a touch of intrigue and tension to chord progressions.
- Hybrid Inversions: Guitarists can also explore hybrid inversions, which combine elements of different inversions. For instance, an E/G#/D# inversion incorporates the bass notes of both the first and third inversions, resulting in a complex and harmonically rich sound.
Incorporating inversions into E chord guitar variations allows guitarists to create more dynamic and interesting chord progressions. By experimenting with different voicings, guitarists can add depth, color, and texture to their playing, enhancing their overall musical expression.
4. Extensions
Extensions play a significant role in expanding the harmonic possibilities of E chord guitar variations. By adding notes beyond the basic triad structure, guitarists can create richer and more complex sounds.
One common extension is the major 7th, denoted as Emaj7. This variation adds a major 7th interval to the basic E chord, resulting in a brighter and more sophisticated sound. The Emaj7 is commonly used in jazz, blues, and pop music, adding a touch of elegance and sophistication to chord progressions.
Incorporating extensions into E chord guitar variations allows guitarists to cre
ate more dynamic and expressive music. By experimenting with different extensions, guitarists can add depth, color, and texture to their playing, enhancing their overall musical expression.
Key Insights:
- Extensions expand the harmonic possibilities of E chord guitar variations.
- The Emaj7 is a common extension that adds a major 7th interval to the basic E chord.
- Incorporating extensions into E chord guitar variations allows guitarists to create more dynamic and expressive music.
Table: E Chord Extensions
| Extension | Formula | Sound | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emaj7 | 1, 3, 5, 7 | Bright, sophisticated | Jazz, blues, pop |
| Em7 | 1, 3, 5, 7 | Soft, ethereal | Jazz, folk, classical |
| E7 | 1, 3, 5, 7 | Jazzy, bluesy | Jazz, blues, rock |
| E9 | 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 | Rich, complex | Jazz, fusion |
| E11 | 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 | Dissonant, modern | Jazz, contemporary music |
5. Suspensions
Suspensions are a type of E chord guitar variation that creates a sense of tension and release. They are created by replacing a chord tone with a note that is a step above or below it. The most common suspension is the suspended 4th, denoted as Esus4.
The Esus4 is created by replacing the 3rd of the E chord (G#) with a suspended 4th (A). This creates a dissonant sound that resolves when the 3rd is played again. Suspensions are often used to add interest and movement to chord progressions.
Here are some examples of how suspensions can be used in e chord guitar variations:
- In the song “Strawberry Fields Forever” by The Beatles, the Esus4 is used to create a sense of tension and release in the intro.
- In the song “Hotel California” by The Eagles, the Esus4 is used to add interest to the chord progression in the verse.
- In the song “Blackbird” by The Beatles, the Esus4 is used to create a sense of movement in the chord progression in the chorus.
Suspensions are a versatile tool that can be used to add interest, movement, and tension to e chord guitar variations. By understanding how suspensions work, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more expressive and dynamic music.
Table: E Chord Suspensions
| Suspension | Formula | Sound | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Esus4 | 1, 4, 5 | Dissonant, resolving | Jazz, folk, pop |
| Esus2 | 1, 2, 5 | Soft, ethereal | Jazz, classical, folk |
6. Slash Chords
Slash chords, denoted as E/G#, introduce a unique variation to the E chord guitar variations landscape. They consist of an E chord with an added bass note in the denominator, such as G#. This technique allows guitarists to emphasize specific bass notes and create richer harmonic textures.
- Function and Role: Slash chords serve multiple functions. They can be used to strengthen the bassline, add harmonic interest, or create a sense of movement in chord progressions. By highlighting a particular bass note, slash chords provide a solid foundation for melodies and solos.
- Examples and Usage: The E/G# slash chord is commonly employed in jazz, blues, and rock music. It can be found in iconic songs such as “Sweet Child O’ Mine” by Guns N’ Roses and “Superstition” by Stevie Wonder.
- Implications for E Chord Guitar Variations: Slash chords expand the harmonic possibilities of E chord guitar variations. They allow guitarists to experiment with different bass notes, creating variations that range from subtle shifts to more dramatic changes in the overall sound. This versatility makes slash chords an essential tool for guitarists seeking to enhance their harmonic vocabulary.
- Additional Examples: Other common slash chord variations include E/B, E/D, and E/A. Each variation imparts a distinct harmonic flavor, allowing guitarists to tailor their chord progressions to specific musical contexts.
In conclusion, slash chords play a significant role in the realm of E chord guitar variations. They offer a powerful means of adding harmonic interest, emphasizing bass notes, and creating dynamic chord progressions. By incorporating slash chords into their playing, guitarists can unlock a world of harmonic possibilities and expand their musical expression.
7. Drop 2 and Drop 3 Voicings
Drop 2 and drop 3 voicings are essential components of e chord guitar variations, offering unique harmonic and melodic possibilities. These variations involve rearranging the notes of the E chord, placing either the 3rd (G#) or 2nd (F#) scale degree in the bass.
Drop 2 voicings, with the 3rd in the bass, create a warmer, fuller sound compared to the root position E chord. They are commonly used in jazz and blues, providing a rich and sophisticated foundation for improvisation. Drop 3 voicings, with the 2nd in the bass, offer a brighter, more open sound. They are often employed in pop and rock music, adding a touch of sparkle and energy to chord progressions.
These variations expand the harmonic vocabulary of e chord guitar variations, allowing guitarists to create more dynamic and expressive music. By incorporating drop 2 and drop 3 voicings into their playing, guitarists can add depth, color, and texture to their chords, enhancing their overall musical expression.
Real-Life Examples:
- In the song “Autumn Leaves” by Miles Davis, the drop 2 E chord voicing is used extensively, creating a warm and mellow atmosphere.
- In the song “Hotel California” by The Eagles, the drop 3 E chord voicing is used in the intro, adding a bright and energetic touch to the chord progression.
Practical Significance:
Understanding drop 2 and drop 3 voicings is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic knowledge and create more sophisticated music. These variations provide a powerful tool for adding harmonic interest, melodic movement, and rhythmic drive to e chord guitar variations.
Table: Comparison of Drop 2 and Drop 3 Voicings
| Voicing | Bass Note | Sound | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drop 2 | 3rd (G#) | Warm, full | Jazz, blues |
| Drop 3 | 2nd (F#) | Bright, open | Pop, rock |
8. Hybrid Picking
Hybrid picking is a technique that combines the use of a pick with fingerpicking techni
ques to play the guitar. This technique offers a unique approach to playing E chord variations, allowing guitarists to create a wider range of sounds and textures.
Hybrid picking is particularly effective for playing E chord variations that require a combination of strumming and fingerpicking patterns. For instance, in the song “Blackbird” by The Beatles, the intro features a hybrid picking pattern that combines strumming with fingerpicked bass notes. This technique adds a rhythmic and melodic interest to the E chord, creating a more dynamic and engaging sound.
Hybrid picking also allows guitarists to play E chord variations with greater control and precision. By using a pick for the strumming and fingers for the individual notes, guitarists can achieve a more nuanced and articulate sound. This technique is particularly useful for playing complex E chord variations that require a high level of accuracy.
Understanding hybrid picking is crucial for guitarists who wish to expand their technical abilities and explore new ways of playing E chord variations. This technique offers a powerful tool for creating unique and expressive sounds, enhancing the overall musicality of guitar playing.
Table: Advantages of Hybrid Picking for E Chord Variations
| Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Allows for a wider range of sounds and textures |
| Control and precision | Enables more nuanced and articulate playing |
| Rhythmic and melodic possibilities | Facilitates the creation of more dynamic and engaging chord variations |
9. Strumming Patterns
Strumming patterns play an integral role in the realm of E chord guitar variations, shaping the rhythmic and dynamic character of the music. By exploring different strumming patterns, guitarists can add depth, interest, and movement to their E chord variations.
- Foundation and Embellishment: Basic strumming patterns provide the rhythmic foundation for E chord variations, while more intricate patterns add embellishments and enhance the overall texture. Simple downstrokes and upstrokes can be combined to create a variety of rhythms, while techniques like palm muting and ghost notes can add rhythmic interest and percussive elements.
- Genre Influences: Strumming patterns are heavily influenced by different musical genres. Reggae, for instance, features a relaxed, laid-back strumming style, while rock music often employs more aggressive and syncopated patterns. Understanding the strumming patterns associated with different genres can help guitarists create authentic and stylistically appropriate E chord variations.
- Tempo and Dynamics: Strumming patterns can be adapted to suit the tempo and dynamics of the music. Faster tempos may call for simpler patterns, while slower tempos allow for more intricate and nuanced strumming. Additionally, varying the intensity of the strumming can create dynamic contrasts and add emotional depth to the performance.
- Creating Movement and Contrast: Strumming patterns can be used to create a sense of movement and contrast within a song. Alternating between different patterns, such as a driving eighth-note strumming pattern followed by a more relaxed quarter-note pattern, can create a dynamic and engaging musical experience. This technique can also be used to highlight specific sections of a song or to transition smoothly between different parts.
In conclusion, strumming patterns are an essential aspect of E chord guitar variations, offering a powerful tool for shaping the rhythmic and dynamic character of the music. By understanding the different facets of strumming patterns, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary, enhance their technical abilities, and create more expressive and nuanced performances.
10. Chord Progressions
Chord progressions are a fundamental aspect of e chord guitar variations, providing a framework for creating harmonic movement and musical structure. By incorporating E chord variations into chord progressions, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing.
E chord variations offer a wide range of harmonic possibilities, allowing guitarists to create progressions that are both pleasing to the ear and effective in supporting the melody. For instance, a progression that moves from E major to E minor to E7 can create a sense of tension and release, while a progression that uses Emaj7 and Em7 can add a touch of jazz or folk flavor.Understanding how to use E chord variations in chord progressions is essential for guitarists who wish to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more expressive and dynamic music. By experimenting with different variations and combinations, guitarists can unlock a world of musical possibilities and enhance their overall playing abilities.
Real-Life Example: The song “Yesterday” by The Beatles features a simple yet effective chord progression that utilizes E chord variations. The progression, which moves from E major to E7 and back to E major, provides a solid harmonic foundation for the melody and creates a sense of emotional depth.
Practical Significance: Understanding how to use E chord variations in chord progressions is a crucial skill for guitarists of all levels. By incorporating these variations into their playing, guitarists can create more sophisticated and engaging music and expand their harmonic knowledge.
Table: Benefits of Using E Chord Variations in Chord Progressions
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Interest | Adds depth and variety to chord progressions |
| Emotional Impact | Can evoke specific emotions or moods |
| Melodic Support | Provides a strong harmonic foundation for melodies |
| Genre Versatility | Allows guitarists to explore different musical styles |
11. Genre Applications
E chord variations serve as a versatile foundation for a wide range of musical genres, allowing guitarists to create diverse and stylistically appropriate music. By understanding the unique applications of E chord variations in different genres, guitarists can expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their ability to connect with audiences.
- Rock:
In rock music, E chord variations are frequently employed to create a powerful and energetic sound. The use of power chords, which are variations of the E chord that omit the 3rd, adds a raw and distorted edge to rock music. Additionally, palm muting techniques, combined with E chord variations, create a percussive and rhythmic foundation for rock songs.
- Pop:
E chord variations play a central role in pop music, providing a bright and catchy sound. Arpeggiated E chord variations, where the notes of the chord are played individually, add a sense of movement and melodic interest. Additi
onally, sus4 variations of the E chord, such as E7sus4, add a touch of sophistication and intrigue to pop songs. - Jazz:
In jazz music, E chord variations are used to create a sophisticated and harmonic sound. Jazz guitarists frequently employ extended E chord variations, such as Emaj7 or E9, to add harmonic richness and complexity to their playing. Additionally, drop 2 and drop 3 voicings of the E chord provide a warm and mellow sound that is commonly found in jazz.
Understanding the genre-specific applications of E chord variations empowers guitarists to tailor their playing to the desired musical style. By incorporating these variations into their playing, guitarists can create music that resonates with the unique characteristics and expressive qualities of different genres.
12. Improvisation
Improvisation, the art of creating spontaneous music, finds a fertile ground in the realm of E chord guitar variations. By mastering these variations, guitarists unlock a vast harmonic landscape that fuels their improvisational journeys.
E chord variations provide a solid foundation for improvisation, offering a diverse palette of sounds and textures. The open E chord, with its bright and resonant sound, serves as a starting point, while barre chord variations extend the harmonic possibilities, allowing guitarists to explore higher registers and create more complex chord voicings.
Inversions and extensions further enhance the improviser’s toolkit. Inversions rearrange the notes of the chord, providing fresh perspectives and harmonic colors. Extensions, such as the Emaj7 or E7, add dissonant intervals, creating tension and release that can fuel improvisational ideas.
Real-life examples abound. Jazz guitarists like George Benson and Pat Metheny have built their reputations on their mastery of E chord variations in improvisation. Their solos are characterized by fluid movement across the fretboard, incorporating a wide range of E chord variations to create melodic lines that are both harmonically rich and emotionally expressive.
Understanding the connection between E chord variations and improvisation is of paramount importance for guitarists seeking to expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their improvisational skills. By incorporating these variations into their playing, guitarists can break free from predefined patterns and embrace the boundless possibilities of spontaneous music-making.
Table: Benefits of Using E Chord Variations for Improvisation
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Diversity | Access to a wide range of sounds and textures |
| Melodic Inspiration | Chord variations provide a framework for creating melodic lines |
| Emotional Expression | Dissonant intervals and extended chords add depth and emotion |
| Technical Development | Improvisation with E chord variations improves finger dexterity and fretboard knowledge |
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses frequently asked questions related to e chord guitar variations, providing clear and informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the most common E chord variations?
The most common E chord variations include the open E chord, barre chord variations, inversions, and extensions. These variations provide a diverse range of sounds and textures, allowing guitarists to explore different harmonic possibilities.
Question 2: How can I incorporate E chord variations into my playing?
To incorporate E chord variations into your playing, start by practicing the basic open E chord. Once you are comfortable with the open E chord, you can begin to explore barre chord variations, inversions, and extensions. Experiment with different variations to find the sounds that best suit your musical style.
Question 3: Are E chord variations difficult to learn?
The difficulty of learning E chord variations depends on your current skill level. Barre chord variations, inversions, and extensions can be more challenging than the open E chord. However, with practice and dedication, you can master these variations and expand your harmonic vocabulary.
Question 4: How can I use E chord variations to improve my improvisation?
E chord variations provide a solid foundation for improvisation. By understanding the different variations and how to use them, you can create more melodic and harmonically interesting solos. Experiment with different variations and see how they inspire your improvisational ideas.
Question 5: What are some tips for mastering E chord variations?
To master E chord variations, practice regularly, experiment with different variations, and listen to how professional guitarists use them in their playing. Focus on developing your finger dexterity and fretboard knowledge, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes. With consistent effort, you can master E chord variations and enhance your overall guitar playing.
Question 6: How can E chord variations enhance my songwriting?
E chord variations can greatly enhance your songwriting by providing a wider range of harmonic possibilities. By incorporating different variations into your chord progressions, you can create more depth, interest, and sophistication in your compositions. Experiment with different variations to find the sounds that best express your musical ideas.
In summary, E chord guitar variations are a powerful tool for guitarists of all levels. By understanding the different variations and how to use them, you can expand your harmonic vocabulary, improve your improvisation skills, and enhance your overall playing. Embrace the journey of learning and experimenting with E chord variations, and you will unlock a world of musical possibilities.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the Anatomy of an E Chord
Tips for Mastering E Chord Guitar Variations
To master e chord guitar variations and unlock their full potential, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Dedicate time to practice.
Regular practice is crucial for developing muscle memory and improving finger dexterity. Set aside dedicated practice time each day to work on E chord variations.
Tip 2: Explore different variations.
Don’t limit yourself to one or two variations. Experiment with open chords, barre chords, inversions, and extensions to expand your harmonic vocabulary.
Tip 3: Listen to professional guitarists.
Pay attention to how professional guitarists utilize E chord variations in their playing. Analyze their techniques, voicings, and progressions to gain valuable insights.
Tip 4: Apply variations to improvisation.
Incorporate E chord variations into your improvisational solos. Experiment with different variations to create unique and expressive melodic lines.
Tip 5: Focus on developing finger dexterity.
Mastering E chord variations requires strong finger dexterity. Practice finger exercises and scales to improve your finger coordination and accuracy.
By following these tips and dedicating yourself to consistent practice, you will enhance your command of E chord guitar variations and unlock a world of harmonic possibilities.
Transition to the
article’s conclusion:
E chord guitar variations are a gateway to harmonic exploration and musical expression. Embrace these variations, practice diligently, and let them elevate your guitar playing to new heights.
E Chord Guitar Variations
Our exploration of e chord guitar variations has unveiled a vast and versatile harmonic landscape. From the open E chord to barre chord variations, inversions, and extensions, each variation offers a unique sonic character and harmonic possibilities.
Mastering these variations empowers guitarists to transcend the boundaries of traditional E chord voicings and embark on a journey of harmonic exploration. The ability to incorporate these variations into your playing opens up a world of creative possibilities, allowing you to craft rich and expressive chord progressions, enhance improvisational solos, and compose captivating songs.
Remember, the key to mastering e chord guitar variations lies in consistent practice, experimentation, and a deep understanding of music theory. Embrace the challenge, dedicate yourself to the learning process, and unlock the full potential of this harmonic treasure.