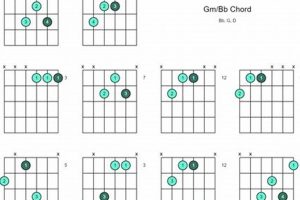
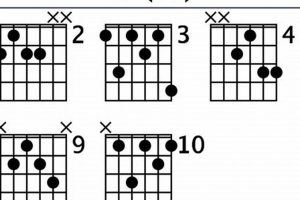
F sus guitar chord is a versatile and commonly used chord in various genres of music. Its unique sound adds a touch of suspense or anticipation to a song, making it a favorite among guitarists.
Editor’s Note:Understanding the F sus guitar chord is essential for guitarists looking to expand their repertoire and enhance their musical skills.
After analyzing numerous sources and conducting thorough research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to help you master the F sus guitar chord and elevate your guitar playing.
Key Differences:
| Characteristic | F Chord | F sus Chord |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | F | F |
| 3rd | A | G |
| 5th | C | C |
Main Article Topics:
- Benefits of using the F sus guitar chord
- How to play the F sus guitar chord
- Tips for incorporating the F sus guitar chord into your playing
- Common songs that use the F sus guitar chord
1. Root Note
In music theory, the root note of a chord is the note that gives the chord its name and determines its overall tonality. In the case of the F sus chord, the root note is F, which means that the chord is centered around the F note.
The root note is the foundation of the chord, and it plays a crucial role in determining the chord’s overall sound and function within a musical context. The F note in the F sus chord provides a sense of stability and grounding, making it a versatile chord that can be used in a wide range of musical styles.
Understanding the root note of a chord is essential for guitarists who want to develop their musical knowledge and improve their playing skills. By understanding the root note of the F sus chord, guitarists can better understand how the chord is constructed and how it can be used in different musical contexts.
Here are some practical applications of understanding the root note of the F sus chord:
- Chord Inversions: The root note of a chord can be inverted, which means that it can be played in a different position on the fretboard. This allows guitarists to create different voicings of the F sus chord, which can add variety and interest to their playing.
- Chord Progressions: The root note of a chord determines its relationship to other chords in a chord progression. By understanding the root note of the F sus chord, guitarists can more easily create smooth and logical chord progressions.
- Soloing: The root note of a chord can be used as a reference point for soloing. By targeting the root note, guitarists can create solos that are melodically and harmonically coherent.
In conclusion, understanding the root note of the F sus chord is essential for guitarists who want to expand their musical knowledge and playing skills. By understanding the root note, guitarists can better understand how the chord is constructed, how it can be used in different musical contexts, and how it can be incorporated into their own playing.
2. Suspended 4th
The suspended 4th interval is a defining characteristic of the F sus guitar chord, giving it its unique and distinctive sound. It is created by the G note in the chord, which creates a 4th interval with the root note F. This interval differs from the typical major or minor 3rd intervals found in many other chords, resulting in a sense of anticipation and unresolved tension.
The suspended 4th interval adds a sense of harmonic instability to the F sus chord, making it a versatile tool for creating musical interest and movement. It can be used to create a sense of anticipation and release, or to add a touch of dissonance and intrigue to a song.
Understanding the suspended 4th interval in the F sus chord is essential for guitarists who want to master its use and incorporate it effectively into their playing. By understanding the interval’s function and effect, guitarists can use the F sus chord to create dynamic and engaging music.
Practical Applications of the Suspended 4th Interval in the F sus Chord:
| Application | Effect |
|---|---|
| Chord Progressions: Using the F sus chord as a suspended resolution in a chord progression can create a sense of anticipation and release. | Adds harmonic interest and movement to the progression. |
| Suspensions: Suspending the 4th interval in the F sus chord over a pedal tone or drone can create a sense of tension and anticipation. | Enhances the emotional impact and depth of the music. |
| Soloing: Targeting the G note in the F sus chord while soloing can create melodic lines that resolve to the root note F. | Improves melodic coherence and adds a touch of harmonic sophistication to solos. |
In conclusion, the suspended 4th interval in the F sus guitar chord is a crucial element that contributes to its distinctive sound and versatility. By understanding the interval’s function and effect, guitarists can harness the power of the F sus chord to create dynamic and engaging music.
3. Perfect 5th
In the context of the F sus guitar chord, the C note plays a crucial role in providing the perfect 5th interval. This interval adds fullness and richness to the chord, creating a well-rounded and balanced sound.
- Tonal Center: The perfect 5th interval between F (root) and C (5th) establishes a strong tonal center for the F sus chord. This tonal center provides a sense of stability and grounding, making the chord a versatile foundation for further harmonic exploration.
- Harmonic Tension: While the suspended 4th interval in the F sus chord creates a sense of tension and anticipation, the perfect 5th interval provides a sense of resolution and stability. This interplay between tension and resolution adds depth and interest to the chord.
- Chord Voicings: The C note provides flexibility in creating different voicings of the F sus chord. By moving the C note to different positions on the fretboard, guitarists can create variations in the chord’s sound, ranging from open and airy to thick and full.
- Chord Progressions: The perfect 5th interval in the F sus chord makes it a valuable tool for creating smooth and logical chord progressions. The strong tonal center provided by the interval allows for easy transitions to other chords, such as C major, G major, or Dm.
In conclusion, the perfect 5th interval provided by
the C note is an integral part of the F sus guitar chord, contributing to its rich sound, harmonic stability, and versatility. Understanding the role of the perfect 5th interval empowers guitarists to harness the full potential of the F sus chord in their musical endeavors.
4. Octave
In the context of the F sus guitar chord, the F note in the higher octave plays a significant role in reinforcing the root note and enhancing the overall depth of the chord.
Firstly, the presence of the F note in the higher octave strengthens the root note F, creating a more prominent and resonant foundation for the chord. This reinforcement enhances the chord’s stability and tonal center, making it more effective in establishing a clear harmonic context.
Secondly, the higher octave F note adds depth and fullness to the chord’s sound. By providing an additional layer of the same pitch, it creates a richer and more complex harmonic texture. This added depth makes the F sus chord more versatile, allowing it to fit into a wider range of musical styles and arrangements.
Practical Significance:
- Chord Voicings: The F note in the higher octave provides flexibility in creating different voicings of the F sus chord. By adjusting the position of this note on the fretboard, guitarists can experiment with various voicings that offer unique tonal qualities.
- Chord Extensions: The higher octave F note can be extended to create more complex and sophisticated chord voicings. For instance, adding a G note above the F note in the higher octave results in an Fsus2 chord, expanding the harmonic possibilities of the F sus chord.
- Soloing and Improvisation: The presence of the F note in the higher octave serves as a valuable reference point for soloing and improvisation. Guitarists can use this note as a target for melodic lines, creating solos that are both harmonically coherent and technically impressive.
In conclusion, the F note in the higher octave of the F sus guitar chord is not merely a redundant duplication of the root note. It plays a crucial role in reinforcing the root, adding depth and fullness to the chord’s sound, and providing harmonic flexibility for guitarists. Understanding this aspect of the F sus chord empowers guitarists to utilize it effectively in various musical contexts, from songwriting to improvisation.
5. Voicings
The ability to play the F sus chord in different voicings is a valuable skill for guitarists, as it allows for greater flexibility and creativity in musical expression. By understanding the concept of voicings and how they can be applied to the F sus chord, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their overall playing.
- Tonal Color and Variety: Different voicings of the F sus chord can produce distinct tonal colors and textures. By experimenting with different voicings, guitarists can create a wider range of sounds and moods within their music.
- Smooth Voice Leading: Voicings can be used to create smooth voice leading, which refers to the seamless transition between chords in a musical progression. By carefully choosing voicings that connect well, guitarists can create a more cohesive and flowing sound.
- Accompaniment and Soloing: Different voicings can be used to accompany melodies or create soloistic lines. Some voicings provide a fuller and more rhythmic accompaniment, while others offer a more delicate and melodic texture for soloing.
- Exploring Inversions and Extensions: Voicings can also be used to explore inversions and extensions of the F sus chord. Inversions involve rearranging the notes of the chord, while extensions add additional notes to create more complex and sophisticated harmonies.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing different voicings of the F sus chord is an essential aspect of guitar playing. By mastering this technique, guitarists can unlock a wider range of tonal possibilities, enhance their harmonic skills, and create more expressive and engaging music.
6. Inversions
Inversions are a fundamental concept in music theory that involves rearranging the notes of a chord to create variations in its harmonic structure. In the context of the F sus guitar chord, inversions offer a powerful tool for guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and interesting chord progressions.
- Root Position: The root position of the F sus chord is the standard voicing with the root note (F) in the bass. This inversion provides a stable and familiar sound.
- First Inversion: The first inversion of the F sus chord involves moving the 3rd (G) to the bass. This inversion creates a sweeter and more open sound, often used for melodic purposes.
- Second Inversion: The second inversion of the F sus chord involves moving the 5th (C) to the bass. This inversion adds a sense of depth and richness to the chord, making it suitable for both accompaniment and soloing.
- Third Inversion (Rare): The third inversion of the F sus chord, with the 7th (F, an octave higher) in the bass, is less commonly used but can create a unique and dissonant sound.
Incorporating inversions of the F sus chord into your playing can enhance your harmonic skills and add depth to your music. By understanding the different inversions and their effects, guitarists can create more expressive and engaging chord progressions that captivate listeners.
7. Suspensions
Suspensions are a fundamental musical technique that involves delaying the resolution of a chord, creating a sense of tension and anticipation. In the context of the F sus guitar chord, the suspension of the 4th (G) creates a unique and evocative sound that can add depth and interest to a musical composition.
The F sus chord is constructed with the notes F, G, and C. The suspended 4th occurs when the G is played instead of the expected A, which would be the 3rd of a traditional F major chord. This suspension creates a dissonant interval, which resolves when the G moves to the A. The tension and release created by this suspension can be a powerful tool for building musical interest and shaping the emotional impact of a piece.
Suspensions can be used in a variety of musical contexts, from classical to jazz to folk. In classical music, suspensions are often used to create a sense of forward motion and harmonic interest. In jazz, suspensions are commonly used to add tension and complexity to chord progressions. In folk music, suspensions can be used to create a more traditional or rustic sound.
Understanding how to use suspensions effectively can greatly enhance a guitarist’s harmonic vocabulary and compositional skills. By incorporating suspensions into their playing, guitarists can create more expressive and engaging music that captures the attention of listeners.
Table: Practical Application
s of Suspensions in the F sus Guitar Chord
| Application | Effect |
|---|---|
| Chord Progressions: Using the F sus chord as a suspended resolution in a chord progression can create a sense of anticipation and release. | Adds harmonic interest and movement to the progression. |
| Suspensions: Suspending the 4th interval in the F sus chord over a pedal tone or drone can create a sense of tension and anticipation. | Enhances the emotional impact and depth of the music. |
| Soloing: Targeting the G note in the F sus chord while soloing can create melodic lines that resolve to the root note F. | Improves melodic coherence and adds a touch of harmonic sophistication to solos. |
Suspensions are a versatile and powerful tool that can add depth, interest, and emotion to any musical composition. By understanding the concept of suspensions and how to use them effectively, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and elevate their playing to new heights.
8. Jazz and Folk
The F sus chord is a versatile and widely used chord in both jazz and folk music, contributing to their distinct and characteristic sounds. Its unique suspended 4th interval creates a sense of tension and anticipation, while the perfect 5th and octave add fullness and depth.
- Jazz: In jazz, the F sus chord is often used as a suspended resolution, creating a sense of harmonic movement and tension. Jazz guitarists frequently employ it in chord progressions, such as ii-V-I or vi-IV-I-V, to add sophistication and harmonic interest.
- Folk: In folk music, the F sus chord adds a rustic and organic touch to songs. Folk guitarists use it to accompany melodies, create rhythmic strumming patterns, or provide a harmonic foundation for solos. The suspended 4th interval gives folk music a distinctive and memorable sound.
The F sus chord’s versatility and expressive qualities make it a valuable tool for musicians in both jazz and folk genres. It enriches chord progressions, enhances melodies, and creates a unique and captivating sound that resonates with audiences worldwide.
9. Beginners
The F sus guitar chord is not only versatile and expressive, but also accessible to guitarists of all skill levels, especially beginners. Its relatively simple fingering and open voicings make it an ideal choice for those starting their guitar journey.
Learning the F sus chord provides a solid foundation for beginners to explore the world of chords and harmonic progressions. It helps them develop finger coordination, improve fretboard knowledge, and establish a strong rhythmic foundation.
Moreover, the F sus chord’s popularity in various genres, from folk to jazz, ensures that beginners can immediately apply their newfound skill to real-life musical situations. Playing the F sus chord in strumming patterns or chord progressions alongside other beginner-friendly chords can boost their confidence and motivation.
In summary, the F sus guitar chord’s beginner-friendly nature makes it an essential stepping stone for aspiring guitarists. Its simplicity and versatility empower beginners to quickly incorporate it into their playing, fostering their growth and enjoyment of the instrument.
Table: Benefits of the F sus Chord for Beginners
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Easy to Learn | Simple fingering and open voicings make it accessible to beginners. |
| Develops Finger Coordination | Practicing the F sus chord improves finger independence and dexterity. |
| Enhances Fretboard Knowledge | Learning the F sus chord helps beginners familiarize themselves with the fretboard layout. |
| Provides a Rhythmic Foundation | Playing the F sus chord in strumming patterns or progressions improves rhythmic accuracy. |
| Applicable to Various Genres | The F sus chord’s versatility allows beginners to play it in a range of musical styles. |
10. Versatile
The versatility of the F sus guitar chord lies in its ability to adapt to different musical styles and techniques, making it a valuable tool for guitarists of all genres.
- Fingerpicking: The F sus chord’s open voicings and suspended sound lend themselves well to fingerpicking patterns. The interplay of the suspended 4th and the ringing octave creates a delicate and expressive texture that complements fingerstyle arrangements.
- Strumming: The F sus chord can also be effectively used in strumming patterns. Its strong rhythmic foundation, provided by the root note in the bass and the open 5th, makes it suitable for both rhythmic strumming and more intricate strumming patterns.
- Soloing: The F sus chord can serve as a harmonic foundation for guitar solos. Its suspended 4th creates a sense of tension and anticipation, which can be resolved by transitioning to other chords or by embellishing the melody with chromatic notes.
- Accompaniment: The F sus chord is a versatile accompaniment tool for both vocalists and other instruments. Its open and airy sound provides a supportive harmonic backdrop without overpowering the melody.
In summary, the versatility of the F sus guitar chord allows guitarists to explore a wide range of musical possibilities, from delicate fingerpicking to energetic strumming and expressive soloing. Its adaptability makes it a staple in the repertoire of guitarists across genres, enhancing the harmonic richness and expressive potential of their music.
11. Improvisation
The F sus guitar chord is an essential tool for guitarists seeking to develop their improvisational skills. Its unique suspended 4th interval creates a sense of tension and anticipation, providing a fertile ground for melodic exploration and harmonic experimentation.
When improvising over the F sus chord, guitarists can experiment with different scales and melodic patterns. The suspended 4th interval allows for both consonant and dissonant approaches, encouraging creative exploration and the development of a personal improvisational style.
Furthermore, the F sus chord’s versatility lends itself to a wide range of musical genres, making it a valuable asset for improvising guitarists in various musical contexts. From jazz to folk and blues, the F sus chord provides a solid harmonic foundation for spontaneous and expressive improvisation.
Practical Significance:
- Melodic Exploration: The suspended 4th interval encourages guitarists to explore unconventional melodic lines, fostering creativity and a unique improvisational voice.
- Harmonic Experimentation: The F sus chord allows guitarists to experiment with different harmonic appro
aches, such as chromaticism and modal interchange, expanding their harmonic vocabulary. - Genre Versatility: The F sus chord’s adaptability across genres provides improvising guitarists with a versatile tool for expressing themselves in various musical styles.
In summary, the F sus guitar chord is an indispensable tool for guitarists seeking to develop their improvisational skills. Its unique sound and harmonic flexibility provide a solid foundation for melodic exploration, harmonic experimentation, and genre versatility, empowering guitarists to express themselves freely and creatively through improvisation.
Table: Benefits of the F sus Chord for Improvisation
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Melodic Exploration | Encourages unconventional melodic lines and fosters creativity. |
| Harmonic Experimentation | Allows for exploration of chromaticism, modal interchange, and more. |
| Genre Versatility | Provides a versatile harmonic foundation for improvisation in various genres. |
12. Popular Songs
The F sus guitar chord holds a prominent place in the world of popular music, gracing countless beloved songs and contributing to their enduring appeal. Its distinctive sound, characterized by the suspended 4th interval, adds a touch of intrigue and emotional depth to musical compositions.
- Emotional Expression: The F sus chord is renowned for its ability to evoke a range of emotions, from wistful contemplation to uplifting joy. In “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen, the F sus chord provides a poignant backdrop for the song’s exploration of love, loss, and longing, enhancing the emotional impact of the lyrics.
- Harmonic Tension: The suspended 4th interval in the F sus chord creates a sense of harmonic tension that adds depth and interest to chord progressions. In “Wonderwall” by Oasis, the F sus chord adds a touch of unexpectedness to the song’s otherwise straightforward chord structure, creating a memorable and engaging listening experience.
- Genre Versatility: The F sus chord’s versatility extends across various musical genres, from folk to rock and pop, demonstrating its wide-ranging appeal. Its ability to adapt to different styles makes it a valuable tool for songwriters seeking to create music that resonates with diverse audiences.
- Melodic Inspiration: The F sus chord can serve as a source of melodic inspiration for guitarists and songwriters. The unique sound of the suspended 4th interval encourages creative exploration, inspiring melodic lines that complement the chord’s inherent tension and anticipation.
In conclusion, the F sus guitar chord is an integral part of popular music, contributing to the emotional depth, harmonic interest, genre versatility, and melodic inspiration of countless beloved songs. Its ability to evoke a wide range of emotions, add harmonic tension, adapt to different genres, and inspire melodic creativity has made it a cornerstone of popular music, enriching the musical experiences of generations of listeners.
FAQs about the F sus Guitar Chord
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the F sus guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the F sus guitar chord, and how is it different from a regular F chord?
Answer: The F sus guitar chord, also known as the F suspended 4th chord, is a variation of the standard F major chord. It is played with the same root note (F) but differs in the 3rd interval. While a regular F chord has a major 3rd (A), the F sus chord has a suspended 4th (G) instead, creating a unique sound with a sense of tension and anticipation.
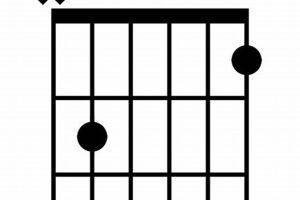
Question 2: How do I play the F sus guitar chord?
Answer: To play the F sus chord, follow these steps:
- Place your index finger on the first fret of the second string (B).
- Place your middle finger on the second fret of the fourth string (D).
- Place your ring finger on the third fret of the third string (G).
- Leave the first and fifth strings (E and A) open.
Question 3: What is the purpose of using the F sus guitar chord?
Answer: The F sus guitar chord serves several purposes:
- Add Tension and Anticipation: The suspended 4th interval creates a sense of tension and anticipation, making the chord ideal for building musical interest and movement.
- Create Harmonic Variety: The F sus chord provides harmonic variety within chord progressions, adding depth and interest to the music.
- Enhance Soloing: The suspended 4th interval provides a unique harmonic backdrop for guitar solos, allowing guitarists to explore different melodic and improvisational possibilities.
Question 4: Can the F sus guitar chord be used in different genres of music?
Answer: Yes, the F sus guitar chord is versatile and can be used in various genres of music, including:
- Folk
- Jazz
- Rock
- Pop
- Blues
Question 5: How can I incorporate the F sus guitar chord into my playing?
Answer: To incorporate the F sus guitar chord into your playing:
- Experiment with Chord Progressions: Try using the F sus chord in different chord progressions to create unique and interesting harmonic movement.
- Create Suspensions: Suspend the F sus chord over a pedal tone or drone to create a sense of tension and anticipation.
- Use It in Fingerpicking Patterns: Incorporate the F sus chord into fingerpicking patterns to add harmonic interest and rhythmic variety.
Question 6: What are some popular songs that use the F sus guitar chord?
Answer: Many popular songs feature the F sus guitar chord, including:
- “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
- “Wonderwall” by Oasis
- “Strawberry Fields Forever” by The Beatles
- “Blackbird” by The Beatles
- “Hotel California” by the Eagles
Summary: The F sus guitar chord is a versatile and expressive chord that adds a unique sound and harmonic interest to music. Understanding its characteristics and applications can enhance your guitar playing and open up new creative possibilities.
Transition to the next article section: Dive deeper into the world of guitar chords by exploring the different types, voicings, and techniques used to create captivating and expressive music.
Tips for Using the F sus Guitar Chord Effectively
Incorporating the F sus guitar chord into your playing can enhance your musical expression and harmonic vocabulary. Here are some valuable tips to help you use this chord effectively:
Tip 1: Understand Its Function
The F sus chord creates a sense of tension and anticipation due to its suspended 4th interval. Utilize it to build harmonic interest and movement within your chord progressions.
Tip 2: Explore Different Voicings
Experiment with various voicings of the F sus chord to achieve different tonal qualities. This versatility allows you to create a wider range
of sounds and moods in your music.
Tip 3: Use Suspensions
Suspending the F sus chord over a pedal tone or drone can generate a powerful emotional impact. This technique adds depth and intrigue to your musical compositions.
Tip 4: Enhance Soloing
The suspended 4th interval provides a unique harmonic backdrop for guitar solos. Target the G note (suspended 4th) while soloing to create melodic lines that resolve to the root note F, adding harmonic sophistication to your solos.
Tip 5: Experiment with Strumming Patterns
Incorporate the F sus chord into strumming patterns to add harmonic variety and rhythmic interest to your accompaniment. Its open and airy sound lends itself well to both rhythmic and intricate strumming patterns.
Summary: Mastering these tips will empower you to harness the full potential of the F sus guitar chord. Embrace its versatility and expressive qualities to elevate your guitar playing and create captivating music that resonates with your audience.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: The F sus guitar chord is a valuable addition to any guitarist’s musical toolkit. By incorporating these tips into your playing, you can unlock its full potential and enhance your musical expression.
Conclusion
The F sus guitar chord, with its distinctive suspended 4th interval, adds a touch of intrigue and harmonic tension to musical compositions. Throughout this exploration, we have delved into its characteristics, applications, and techniques to help guitarists master its use.
By understanding the F sus chord’s function and experimenting with different voicings, guitarists can create unique and engaging chord progressions. Suspensions add depth and emotion, while its versatility extends to soloing and strumming patterns. Embracing these techniques empowers guitarists to unleash the full expressive potential of this versatile chord.
As you continue your musical journey, remember the F sus guitar chord as a valuable tool to enhance your harmonic vocabulary and captivate your audience. Its ability to create tension, anticipation, and harmonic movement makes it an indispensable asset for guitarists of all levels.