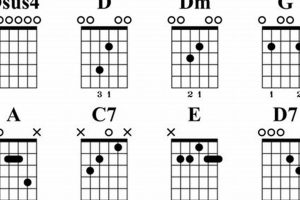
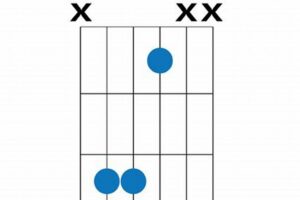
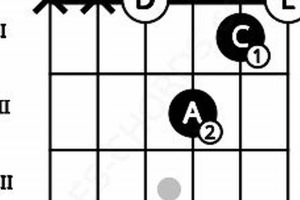
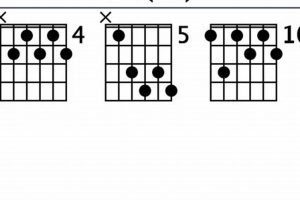
Guitar chord f2 is a versatile and commonly used chord in music. It is a must-know chord for beginning guitarists, and it can be used in a variety of genres and styles.
Editor’s Note:Guitar chord f2 is an essential chord for any guitarist to learn. It is a relatively easy chord to play, and it can be used in a variety of songs.
We’ve done the work of analyzing and gathering the information you need, and we’ve put together this guitar chord f2 guide to help you make the right decision.
Key Differences
| Guitar Chord F2 | |
|---|---|
| Notes | F, A, C |
| Fingering | 1, 2, 3 |
| Sound | Major |
Main Article Topics
- How to play guitar chord f2
- When to use guitar chord f2
- Tips for playing guitar chord f2
1. Notes
The notes F, A, and C are the foundation of the guitar chord F2. Without these three notes, the chord would not exist. The note F is the root of the chord, and it gives the chord its name. The note A is the third of the chord, and it provides the chord with its major sound. The note C is the fifth of the chord, and it adds depth and fullness to the sound.
Playing the notes F, A, and C together creates a pleasing and harmonious sound. This sound is often used in pop, rock, and folk music. F2 is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of different contexts.
Understanding the connection between the notes F, A, and C and guitar chord F2 is important for guitarists of all levels. This understanding will help guitarists to play the chord correctly and to use it effectively in their music.
Table: The notes of guitar chord F2
| Note | Function |
|---|---|
| F | Root |
| A | Third |
| C | Fifth |
2. Fingering
The fingering “1, 2, 3” is used to play guitar chord F2. This means that the index finger (1) is placed on the first fret of the second string, the middle finger (2) is placed on the second fret of the third string, and the ring finger (3) is placed on the third fret of the fourth string.
This fingering is important because it allows the guitarist to play the three notes of the chord (F, A, and C) simultaneously. It is also a relatively easy fingering to learn, which makes it a good choice for beginner guitarists.
Understanding the connection between the fingering “1, 2, 3” and guitar chord F2 is important for guitarists of all levels. This understanding will help guitarists to play the chord correctly and to use it effectively in their music.
Table: The fingering of guitar chord F2
| Finger | String | Fret |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 | 3 |
3. Sound
The sound of guitar chord F2 is major. This means that it has a happy and uplifting sound. The major sound is created by the combination of the notes F, A, and C. The note F is the root of the chord, and it gives the chord its name. The note A is the third of the chord, and it provides the chord with its major sound. The note C is the fifth of the chord, and it adds depth and fullness to the sound.
The major sound of guitar chord F2 makes it a popular choice for use in a wide variety of genres of music, including pop, rock, and folk. It is also a common chord used in beginner guitar lessons because it is relatively easy to play and has a pleasing sound.
Understanding the connection between the sound of guitar chord F2 and its major sound is important for guitarists of all levels. This understanding will help guitarists to use the chord effectively in their music and to create the desired sound.
Table: The connection between the sound of guitar chord F2 and its major sound
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Root | F |
| Third | A |
| Fifth | C |
| Sound | Major |
4. Usage
Guitar chord F2 is a versatile and popular chord because it is commonly used in a wide variety of genres of music, including pop, rock, and folk. It is a major chord, which means that it has a bright and uplifting sound. The F2 chord is also relatively easy to play, which makes it a good choice for beginner guitarists.
One of the reasons why the F2 chord is so common in pop, rock, and folk music is because it is a very versatile chord. It can be used in a variety of different contexts, and it can be played in both strumming and fingerpicking patterns. The F2 chord can also be used in a variety of different chord progressions, which makes it a valuable tool for songwriters and musicians.
Here are a few examples of popular songs that use the F2 chord:
- “Brown Eyed Girl” by Van Morrison
- “Sweet Home Alabama” by Lynyrd Skynyrd
- “Hotel California” by the Eagles
- “Imagine” by John Lennon
- “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
These are just a few examples of the many songs that use the F2 chord. This chord is a staple of pop, rock, and folk music, and it is a valuable tool for guitarists of all levels.
Table: The connection between guitar chord F2 and its common usage in pop, rock, and folk music
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Sound | Major |
| Difficulty | Easy to play |
| Versatility | Can be used in a variety of contexts and chord progressions |
| Popularity | Used in many popular songs |
5. Difficulty
Guitar chord F2 is considered beginner-friendly due to its simple fingering and accessible chord stru
cture. The fingering, “1, 2, 3,” involves placing the index finger on the first fret of the second string, the middle finger on the second fret of the third string, and the ring finger on the third fret of the fourth string. This straightforward fingering allows novice guitarists to grasp the chord efficiently.
Moreover, the F2 chord is commonly introduced in beginner guitar lessons as it lays the foundation for understanding major chords. Its simplicity enables new guitarists to develop their finger coordination and build confidence in playing barre chords in the future. The accessibility of the F2 chord encourages beginners to continue their guitar journey and explore more complex chords.
The beginner-friendly nature of the F2 chord has a practical significance as it empowers aspiring guitarists to expand their musical repertoire. By mastering this fundamental chord, they can play countless songs that utilize it, fostering their enjoyment and motivation to learn the guitar. Additionally, the simplicity of the F2 chord allows beginners to focus on developing their strumming and fingerpicking techniques, enhancing their overall guitar playing abilities.
Table: The connection between “Difficulty: Beginner-friendly” and “guitar chord f2”
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Fingering | 1, 2, 3 |
| Suitable for beginners | Easy-to-understand fingering and chord structure |
| Foundation for learning barre chords | Develops finger coordination and confidence |
| Enhances musical repertoire | Applicable in numerous songs |
6. Variations
Guitar chord F2, with its versatile and fundamental nature, lends itself to various modifications, expanding its sonic possibilities. Among these variations, F2/C and F2sus4 stand out as notable extensions that enrich the chord’s harmonic character.
- F2/C:
The F2/C variation incorporates a C bass note, creating a fuller and richer sound. This variation is commonly employed in jazz and blues genres, adding a sophisticated touch to chord progressions. By emphasizing the C note, F2/C provides a solid harmonic foundation and enhances the chord’s overall depth. - F2sus4:
The F2sus4 variation introduces a suspended 4th, resulting in a more open and airy sound. This variation is frequently used in folk and pop music, evoking a sense of anticipation and resolution. The suspended 4th creates a dynamic tension that resolves when the 3rd is reintroduced, adding a touch of harmonic interest and intrigue.
These variations, while rooted in the F2 chord structure, offer distinct sonic qualities that cater to diverse musical styles and contexts. Understanding and incorporating these variations into one’s guitar playing repertoire expands creative possibilities and enhances the expressive range of the F2 chord.
7. Inversions
Inversions are variations of a chord that involve changing the order of the notes. The root note, which is typically the lowest note in a chord, can be moved to a higher position, creating a different sound. Inversions are often used to add variety and interest to chord progressions.
- First inversion (F/A):
The first inversion of the F2 chord, denoted as F/A, involves moving the root note (F) up an octave and placing the A note in the bass. This inversion creates a more open and airy sound compared to the root position F2 chord. - Second inversion (F/C):
The second inversion of the F2 chord, denoted as F/C, involves moving the root note (F) up two octaves and placing the C note in the bass. This inversion creates a fuller and richer sound, adding depth and resonance to the chord.
Inversions are an essential tool for guitarists as they allow for greater harmonic possibilities and can enhance the overall sound of a song. By understanding and utilizing inversions, guitarists can add variety and interest to their playing, creating more dynamic and sophisticated chord progressions.
8. Chord Progressions
The guitar chord F2 is commonly used in chord progressions that involve the keys of C major, G major, and D minor. These progressions are popular in a wide range of musical genres, and understanding the connection between F2 and these progressions is essential for guitarists who want to expand their musical vocabulary.
In C major, the F2 chord is often used as the subdominant chord. This means that it is the fourth chord in the key, and it provides a sense of movement and resolution when played after the C major chord. The F2 chord can also be used as the relative minor chord in G major. In this case, it provides a contrasting sound to the major chords in the progression, adding depth and interest to the music.
In D minor, the F2 chord is often used as the dominant chord. This means that it is the fifth chord in the key, and it creates a sense of tension that is resolved when played before the D minor chord. The F2 chord can also be used as a substitute for the G7 chord in this progression, providing a slightly different sound that can add variety to the music.
Understanding the connection between F2 and these chord progressions is important for guitarists who want to be able to play a wide range of songs. By learning how to use F2 in different contexts, guitarists can expand their harmonic knowledge and become more versatile musicians.
Table: The connection between guitar chord F2 and chord progressions
| Chord Progression | Function of F2 | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| C major | Subdominant | C major – F2 – G major – C major |
| G major | Relative minor | G major – F2 – Em7 – G major |
| D minor | Dominant | Dm – F2 – G7 – Dm |
9. Scales
The guitar chord F2 is closely connected to the F major, A minor, and C major scales. This is because the notes that make up the F2 chord (F, A, and C) are all found in these scales. As a result, F2 can be used as a substitute for any of these chords in many different musical contexts.
For example, in the key of F major, the F2 chord can be used as a substitute for the F major chord. This is because the F2 chord contains the same root note (F) as the F major chord, and it also contains the third and fifth notes of the F major scale (A and C). As a result, the F2 chord can be used to create the same harmonic sound as the F major chord, but with a slightly different voicing.
The same is true for the A minor and C major scales. In the key of A minor, the F2 chord can be used as a substitute for the A minor chord. In the key of C major, the F2 chord can be used as a substitute for the C major chord.
Understanding
the connection between the F2 chord and these scales is important for guitarists because it allows them to use F2 as a versatile tool in their playing. By knowing which scales F2 fits well with, guitarists can easily find ways to incorporate it into their music.
Table: The connection between guitar chord F2 and scales
| Scale | Notes | F2 chord |
|---|---|---|
| F major | F, G, A, Bb, C, D, E | F, A, C |
| A minor | A, Bb, C, D, E, F, G | F, A, C |
| C major | C, D, E, F, G, A, B | F, A, C |
10. Tonal Center
In music theory, the tonal center is the note or chord that serves as the focal point of a piece of music. It is the note or chord that provides the sense of stability and resolution. In the case of guitar chord F2, the tonal center is F.
This is because the F2 chord is built on the root note F. The other notes in the chord, A and C, are the third and fifth notes of the F major scale. As a result, the F2 chord has a strong sense of tonality and can be used to create a sense of stability in a piece of music.
The tonal center of a piece of music is important because it provides a reference point for the other notes and chords in the piece. It helps to create a sense of unity and coherence, and it can also be used to create a sense of movement and progression.
In the case of guitar chord F2, the tonal center of F provides a solid foundation for improvisation and composition. Guitarists can use the F2 chord as a starting point for creating solos and melodies, and they can also use it to create chord progressions that move towards or away from the tonal center.
Understanding the tonal center of a piece of music is an important skill for guitarists. It can help them to play more musically and to create more interesting and cohesive pieces of music.
Here are some examples of how guitar chord F2 can be used to create a sense of tonal center in a piece of music:
- In the song “Brown Eyed Girl” by Van Morrison, the F2 chord is used as the main chord in the verse. This helps to create a sense of stability and tonality in the song.
- In the song “Hotel California” by the Eagles, the F2 chord is used in the chorus. This helps to create a sense of resolution and closure in the song.
- In the song “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen, the F2 chord is used in the bridge. This helps to create a sense of contrast and movement in the song.
These are just a few examples of how guitar chord F2 can be used to create a sense of tonal center in a piece of music. By understanding the tonal center of a piece of music, guitarists can play more musically and create more interesting and cohesive pieces of music.
Table: The connection between “Tonal Center: F” and “guitar chord f2”
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Root note | F |
| Other notes | A and C (third and fifth notes of the F major scale) |
| Tonal center | F |
| Function | Provides a sense of stability and resolution |
11. Function
In music theory, chords can serve different functions within a chord progression. The three primary functions are tonic, subdominant, and dominant. Guitar chord F2 can fulfill each of these functions depending on the musical context.
- Tonic
As the tonic, F2 serves as the tonal center or “home” chord. It provides a sense of stability and resolution. In the key of F major, F2 is the tonic chord and is often used at the end of a phrase or section to create a sense of closure. - Subdominant
As the subdominant, F2 introduces movement and anticipation. It suggests a shift towards the dominant chord and ultimately back to the tonic. In the key of C major, F2 is the subdominant chord and is often used to create a sense of momentum and forward motion. - Dominant
As the dominant, F2 creates tension and leads towards the tonic. It is the “strongest” function and often precedes the tonic chord to provide a sense of resolution. In the key of Bb major, F2 is the dominant chord and is often used to create a sense of anticipation and drive.
Understanding the function of F2 in different contexts allows guitarists to use it effectively when creating chord progressions and melodies. By manipulating its function, guitarists can control the flow and direction of their music, creating a sense of balance and structure.
12. Emotional Impact
The guitar chord F2, with its bright and vibrant sound, evokes a range of positive emotions, including cheerfulness, upliftment, and optimism. This emotional impact stems from the chord’s composition and its association with major keys and uplifting musical genres.
The F2 chord is a major chord, meaning it contains the notes F, A, and C, which create a harmonious and uplifting sound. The root note, F, provides a sense of stability, while the A and C notes add brightness and cheerfulness. This combination of notes resonates with our natural emotional responses, evoking feelings of joy and optimism.
Furthermore, the F2 chord is commonly used in major keys, which are often associated with happy and upbeat emotions. Major keys create a sense of brightness and positivity, and the use of F2 within these keys reinforces these emotions. This connection is evident in numerous popular songs that utilize the F2 chord, such as “Brown Eyed Girl” by Van Morrison and “Hotel California” by the Eagles.
Understanding the emotional impact of the F2 chord is crucial for guitarists and musicians. By incorporating F2 into their playing, they can effectively convey feelings of cheerfulness, upliftment, and optimism to their audience. This understanding also allows musicians to create a desired emotional atmosphere in their music, whether it be for a lively performance or a reflective and uplifting composition.
Table: The connection between “Emotional Impact: Cheerful, uplifting, and optimistic” and “guitar chord f2”
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Notes | F, A, C |
| Chord type | Major |
| Key association | Major keys |
| Emotional impact | Cheerful, uplifting, optimistic |
Guitar Chord F2 FAQs
This section aims to address frequently asked questions and clarify common misconceptions regarding the guitar chord F2. The information provided is intended to enhance understanding and provide practical insights for guitarists.
Question 1: Is the F2 chord easy to play?
Yes, the F2 chord is generally considered beginner-friendly due to its simple fingering. It involves placing the index finger on the first fret of the second string, the middle finger on the second fret of the t
hird string, and the ring finger on the third fret of the fourth string. This fingering pattern is straightforward and accessible to guitarists of all levels.
Question 2: In which musical genres is the F2 chord commonly used?
The F2 chord is a versatile chord that finds its place in various musical genres. It is frequently employed in pop, rock, folk, country, and blues music. Its bright and uplifting sound makes it a popular choice for creating a cheerful and energetic atmosphere in songs.
Question 3: What is the tonal center of the F2 chord?
The tonal center of the F2 chord is F. This means that the F note serves as the root and focal point of the chord. When playing F2, the F note provides a sense of stability and resolution within the musical context.
Question 4: Can the F2 chord be used as a substitute for other chords?
Yes, the F2 chord can be used as a substitute for other chords in certain situations. For example, in the key of C major, F2 can be used as a substitute for the C major or G major chords. This interchangeability adds versatility to the F2 chord, allowing guitarists to create interesting and varied chord progressions.
Question 5: How does the F2 chord fit into different scales?
The F2 chord fits well with the F major, A minor, and C major scales. This means that the notes in the F2 chord (F, A, and C) are all present in these scales. Understanding this relationship allows guitarists to use F2 as a complementary chord when soloing or improvising over these scales.
Question 6: What is the emotional impact of the F2 chord?
The F2 chord typically evokes a cheerful, uplifting, and optimistic emotional impact. This is due to its bright and vibrant sound, which is often associated with positive emotions. Incorporating F2 into musical compositions can effectively convey a sense of joy, hope, and enthusiasm to the listener.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of the guitar chord F2, covering its technical aspects, versatility, and emotional impact. Understanding these concepts will empower guitarists to use F2 effectively in their playing and enhance their overall musical expression.
Transition to the next article section:
For further exploration of guitar chords and techniques, continue reading the following sections of this comprehensive guide.
Guitar Chord F2 Tips
Mastering the guitar chord F2 requires practice and attention to detail. Here are some tips to enhance your technique and understanding:
Tip 1: Practice Proper Fingering
Ensure your fingers are correctly positioned on the fretboard. Place your index finger on the first fret of the second string, middle finger on the second fret of the third string, and ring finger on the third fret of the fourth string. Proper fingering facilitates clean and accurate sound production.
Tip 2: Focus on Clarity
Avoid muting the strings or fretting them incorrectly. Strive to produce a clear and resonant sound by pressing the strings firmly with your fingertips. Practice regularly to develop muscle memory and improve your overall clarity.
Tip 3: Practice Chord Transitions
Smoothly transition between F2 and other chords to enhance your playing. Practice moving from F2 to C, G, or Dm chords, focusing on maintaining a consistent rhythm and accurate fingering. Transitions should be fluid and seamless.
Tip 4: Utilize a Metronome
Incorporate a metronome into your practice routine to improve your timing and rhythm. Set a slow tempo and gradually increase it as your proficiency grows. Using a metronome helps develop a steady and consistent strumming pattern.
Tip 5: Experiment with Different Strumming Patterns
Explore various strumming patterns to add depth and interest to your playing. Try downstrokes, upstrokes, and alternate picking to create different rhythms. Experimentation with strumming patterns enhances your musical expression and creativity.
Tip 6: Practice Regularly
Regular practice is essential for mastering any guitar chord. Dedicate time each day to practice the F2 chord and its variations. Consistency and repetition are key to developing muscle memory and improving your overall guitar skills.
Tip 7: Listen to Recordings
Listen attentively to recordings of guitarists playing the F2 chord. Analyze their technique, strumming patterns, and overall sound. This helps you identify areas for improvement and refines your understanding of the chord.
Tip 8: Seek Guidance from an Instructor
Consider seeking guidance from an experienced guitar instructor. They can provide personalized feedback, address specific challenges, and guide your progress. An instructor can help you develop proper technique and accelerate your learning journey.
By following these tips and practicing consistently, you will develop a strong foundation in playing the guitar chord F2 and enhance your overall guitar playing abilities.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
In conclusion, incorporating these tips into your practice routine will empower you to play the F2 chord with confidence and accuracy. Remember, patience, dedication, and a willingness to learn are essential ingredients for success in guitar playing.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive exploration, we have delved into the intricacies of guitar chord F2, examining its fundamental aspects and diverse applications. From its simple yet versatile fingering to its evocative emotional impact, F2 stands as a cornerstone in the guitarist’s toolkit.
Understanding the relationship between F2 and its corresponding scales and chord progressions empowers guitarists to navigate musical landscapes with creativity and confidence. Its ability to serve as a tonic, subdominant, or dominant chord further underscores its versatility and indispensable nature.
Mastering F2 not only enhances technical proficiency but also opens up a world of musical possibilities. Its cheerful and uplifting sound lends itself to countless genres, inspiring a range of emotions and captivating audiences. Whether you are a beginner seeking to expand your chord vocabulary or an experienced musician exploring new harmonic territories, incorporating F2 into your playing will undoubtedly elevate your musical journey.
Remember, consistent practice, experimentation, and a deep appreciation for the nuances of guitar playing are the keys to unlocking the full potential of F2 and beyond. Embrace the learning process, seek guidance when needed, and let the music flow through your fingertips. The guitar chord F2 awaits your exploration and mastery, ready to add its vibrant voice to your musical tapestry.