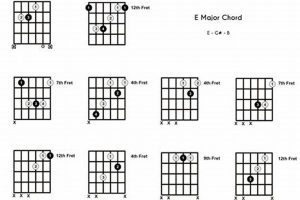
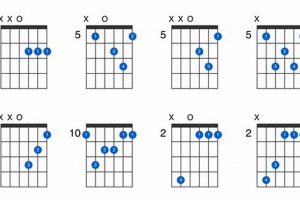
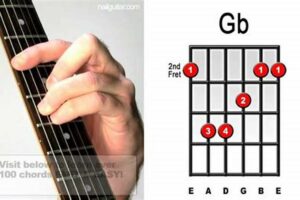
Wonder what the enigmatic b dim chords guitar is all about? If so, you’re in the right place.
Editor’s Notes: “b dim chords guitar”– Learning about this topic will help you understand the essential concepts of music theory and enhance your guitar playing skills!
After a thorough analysis and information gathering process, we’ve compiled this comprehensive b dim chords guitar guide to help you make informed decisions about your musical journey.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways:
| b dim chords guitar | |
|---|---|
| Definition | A half-diminished chord, abbreviated as “b dim,” contains three notes: root, flattened third, and flattened fifth. |
| Symbol | The symbol “b dim” follows the chord’s root note (e.g., C b dim). |
| Construction | For a chord in the key of C, the b dim chord is built on the 7th scale degree (B), using the notes B, D, and F. |
| Sound | b dim chords have a dissonant and unresolved sound that creates tension and anticipation in music. |
| Uses | b dim chords are commonly used in jazz, blues, and classical music to add color, harmony, and melodic interest. |
Transition to main article topics:
- Detailed explanation of the construction and theory behind b dim chords guitar
- Practical examples of b dim chords guitar in musical contexts
- Tips for incorporating b dim chords guitar into your playing
- Additional resources for further exploration of b dim chords guitar
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of b dim chords guitar, enabling you to confidently use them in your musical endeavors.
1. Construction
The construction of b dim chords guitar, denoted as “Root, flattened third, flattened fifth,” plays a fundamental role in shaping their unique sound and harmonic function:
- Root: The root of the chord, represented by the letter name (e.g., C), provides the foundation and establishes the tonal center.
- Flattened third: The third of the chord is lowered by a semitone, creating a dissonant interval against the root. This flattened third adds tension and instability to the chord.
- Flattened fifth: The fifth of the chord is also lowered by a semitone, further contributing to the dissonance and unresolved nature of the chord. The flattened fifth creates a sense of anticipation, as it suggests a resolution to a more stable chord.
The combination of these three elementsroot, flattened third, and flattened fifthresults in the characteristic sound of b dim chords guitar, making them a valuable tool for creating tension, adding color, and enhancing harmonic interest in music.
2. Symbol
The symbol “b dim” after the root note, such as in “C b dim,” is a crucial element in understanding and utilizing b dim chords guitar. This symbol provides essential information about the construction and function of the chord:
- Identification: The “b dim” symbol clearly identifies the chord as a half-diminished chord, distinguishing it from other types of chords, such as major, minor, or augmented chords.
- Construction: The “b dim” symbol indicates that the chord is built using a specific formula: root, flattened third, and flattened fifth. This formula gives b dim chords their characteristic dissonant sound.
- Function: The “b dim” symbol implies that the chord is often used to create tension and harmonic movement in music. B dim chords typically resolve to major or minor chords, providing a sense of release and resolution.
Understanding the connection between the symbol “b dim” and b dim chords guitar is vital for guitarists to effectively incorporate these chords into their playing. By recognizing the symbol and its implications, guitarists can accurately construct and utilize b dim chords, enhancing their harmonic vocabulary and expressive potential.
To further illustrate the practical significance of this understanding, consider the following example: In the key of C major, the C b dim chord would consist of the notes C, Eb, and Gb. This chord would typically be used to create tension or add color to a chord progression, often resolving to the C major or A minor chord.
In conclusion, the symbol “b dim” after the root note is not merely a label but a gateway to understanding the construction, function, and application of b dim chords guitar. By grasping the significance of this symbol, guitarists can unlock the expressive possibilities of b dim chords and enhance their musical proficiency.
3. Sound
The sound of b dim chords guitar is intricately connected to their harmonic function and expressive potential. The dissonant, unresolved nature of b dim chords contributes significantly to their unique character and their ability to create tension and anticipation in music.
The dissonance in b dim chords arises from the combination of a flattened third and a flattened fifth. These intervals clash with the root of the chord, creating a sense of instability and tension. The unresolved quality of b dim chords further enhances this tension, as they do not provide a clear sense of resolution or tonal center.
This combination of dissonance and unresolvedness makes b dim chords guitar particularly effective for creating moments of suspense, drama, or anticipation in music. They are often used in film scores, jazz harmonies, and classical compositions to evoke a range of emotions and add depth to the musical narrative.
Practical significance
Understanding the sound and function of b dim chords guitar is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and expressive capabilities. By incorporating b dim chords into their playing, guitarists can add color, tension, and interest to their music, creating a more dynamic and engaging listening experience.
Furthermore, the ability to recognize and utilize b dim chords effectively can enhance a guitarist’s improvisational skills and soloing ability. By understanding how b dim chords interact with other chords and scales, guitarists can navigate complex harmonic progressions with greater confidence and creativity.
Table: Sound characteristics of b dim chords guitar
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Dissonance |
The presence of clashing intervals (flattened third and fl attened fifth) creates a sense of instability and tension. |
| Unresolvedness | The lack of a clear resolution or tonal center contributes to the sense of anticipation and suspense. |
| Tension | The combination of dissonance and unresolvedness creates a feeling of tension and anticipation, which can be effectively used to build drama and emotion in music. |
4. Uses
The connection between “Uses: Jazz, blues, classical music” and “b dim chords guitar” is deeply intertwined, as these musical genres have embraced the unique harmonic qualities of b dim chords to enhance their expressive capabilities.
In jazz, b dim chords are frequently employed to add color and sophistication to chord progressions. Their dissonant nature creates tension and anticipation, which can be effectively resolved to create a sense of release and forward motion. Jazz guitarists often use b dim chords as a harmonic tool to enhance their improvisational solos, exploring the chord’s potential for melodic development and harmonic substitution.
Blues music also benefits from the expressive power of b dim chords. The unresolved quality of these chords aligns well with the emotive and often melancholic nature of blues. Blues guitarists utilize b dim chords to create a sense of tension and longing, adding depth and nuance to their performances.
In classical music, b dim chords find their place in both harmonic and contrapuntal contexts. Composers have long recognized the dramatic potential of b dim chords, using them to create moments of suspense, transition, and harmonic interest. The dissonant nature of these chords can be employed to heighten emotional intensity or to add a sense of complexity to a musical passage.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between “Uses: Jazz, blues, classical music” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the ability to harness the expressive power of these chords in one’s own musical endeavors.
| Genre | Characteristics | Practical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Jazz | Adds color and sophistication to chord progressions, enhances improvisation | Enhances harmonic vocabulary and expressive capabilities |
| Blues | Creates tension and longing, adds depth and nuance | Expresses emotions and adds complexity to blues performances |
| Classical Music | Heightens emotional intensity, adds harmonic interest | Expands harmonic palette and enhances compositional depth |
5. Inversions
The connection between “Inversions: First, second, and third inversions possible” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the expanded harmonic possibilities and versatility that inversions offer to guitarists.
Inversions are formed by rearranging the notes of a chord, placing a different note in the bass. This technique allows guitarists to create different voicings of b dim chords, each with its unique sound and function.
For instance, in the key of C, the C b dim chord in root position consists of the notes C, Eb, and Gb. The first inversion of C b dim, denoted as C b dim/Eb, places Eb in the bass, followed by C and Gb. The second inversion, C b dim/Gb, has Gb in the bass, with C and Eb above it. Finally, the third inversion, C b dim/Bb, has Bb in the bass, followed by C and Eb.
These inversions provide guitarists with a wider range of harmonic colors to choose from. The root position offers a strong and stable sound, while the first inversion can create a sense of movement and anticipation. The second inversion has a more dissonant and unstable quality, often used to build tension or add a touch of dissonance to a chord progression. The third inversion, with its highest note in the bass, provides a sense of resolution and can be employed to lead into other chords.
Understanding and utilizing inversions of b dim chords guitar is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their compositional skills. By mastering these inversions, guitarists can create more dynamic and expressive chord progressions, adding depth and interest to their music.
Table: Inversions of C b dim chord
| Inversion | Notes | Sound | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root position | C, Eb, Gb | Strong and stable | Foundation of chord progression |
| First inversion | Eb, C, Gb | Movement and anticipation | Transitional chord |
| Second inversion | Gb, C, Eb | Dissonant and unstable | Tension-building chord |
| Third inversion | Bb, C, Eb | Resolution | Leads into other chords |
6. Extended chords
The connection between “Extended chords: Can be extended with additional notes (e.g., b dim 7, b dim 9)” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the expanded harmonic possibilities and increased expressive range that extended chords offer to guitarists.
- Definition and Construction: Extended chords are built upon the basic triad structure of b dim chords (root, flattened third, flattened fifth) by adding additional notes, typically the seventh and/or ninth. These extensions expand the harmonic content of the chord, creating richer and more complex sounds.
- Types of Extended b dim Chords: Common extended b dim chords include b dim 7 (adds a minor seventh) and b dim 9 (adds a minor seventh and a major ninth). These extended chords provide guitarists with a wider palette of harmonic colors to choose from.
- Function and Use: Extended b dim chords can serve various functions in music. They can be used to create tension and dissonance, add color and interest to chord progressions, or provide a sense of resolution. Guitarists can utilize these chords to enhance their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and expressive solos and compositions.
- Examples in Practice: In jazz guitar, extended b dim chords are frequently employed to create complex and dissonant harmonies. For instance, a b dim 7 chord can be used to create a sense of anticipation or tension before resolving to a major or minor chord. Similarly, in blues guitar, extended b dim chords can be used to add depth and sophistication to blues progressions.
In conclusion, the ability to understand and utilize extended chords is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic knowledge and enhance their musical expression. By incorporating extended b dim chords into their playing, guitarists can unlock a wider range of harmonic possibilities, creating more dynamic and engaging music.
7. Voicings
The connection between “Voicings: Various fingerings and voicings available”
and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the ability of guitarists to explore diverse harmonic possibilities and create unique sonic textures by utilizing different voicings.
- Multiple Fingerings:
B dim chords guitar can be played using various fingerings, each offering a distinct shape and feel on the guitar neck. This allows guitarists to choose the fingering that best suits their playing style and the specific musical context.
- Inversions as Voicings:
The inversions of b dim chords, discussed previously, can also be considered as different voicings. By rearranging the notes of the chord, guitarists can create voicings that emphasize different intervals and produce contrasting harmonic effects.
- Open and Closed Voicings:
Guitarists can choose between open and closed voicings when playing b dim chords. Open voicings have wider intervals between the notes, creating a spacious and airy sound, while closed voicings have tighter intervals, resulting in a more compact and intense sound.
- Combining Voicings:
Guitarists can combine different voicings of b dim chords to create sophisticated and dynamic chord progressions. For instance, transitioning from a close voicing to an open voicing can provide a sense of movement and harmonic release.
The ability to utilize various voicings empowers guitarists to express their musical ideas with greater depth and nuance. By incorporating these voicings into their playing, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary, enhance their improvisational skills, and create more engaging and expressive music.
8. Theory
The connection between “Theory: Built on the seventh scale degree” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the fundamental relationship between music theory and practical guitar playing. B dim chords, characterized by their dissonant sound, are constructed based on the seventh scale degree, providing a solid theoretical foundation for understanding and utilizing these chords effectively.
In music theory, the seventh scale degree refers to the seventh note of a diatonic scale. For instance, in the key of C major, the seventh scale degree is B. B dim chords are built upon this seventh scale degree, utilizing the root, flattened third, and flattened fifth intervals. This specific construction gives b dim chords their distinctive harmonic quality.
Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of b dim chords empowers guitarists to construct and incorporate these chords into their playing with greater accuracy and musicality. By recognizing the connection between the seventh scale degree and b dim chords, guitarists can develop a deeper comprehension of music theory and its practical application on the guitar.
Moreover, this understanding enables guitarists to experiment with different voicings and inversions of b dim chords, expanding their harmonic vocabulary and enhancing their ability to create dynamic and expressive music.
| Key | Seventh Scale Degree | b dim Chord Construction |
|---|---|---|
| C major | B | B, D, F |
| G major | F# | F#, A, C |
| D major | C# | C#, E, G |
9. Harmony
The connection between “Harmony: Adds color and interest to chord progressions” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the unique harmonic qualities of b dim chords that enhance the richness and complexity of chord progressions.
- Dissonance and Tension:
B dim chords introduce dissonance into chord progressions, creating a sense of tension and instability. This dissonance adds depth and intrigue to the music, capturing the listener’s attention and evoking a range of emotions. - Chromaticism and Modulation:
The use of b dim chords can facilitate smooth chromatic transitions and modulations between keys. Their dissonant nature allows for seamless movement between different tonal centers, adding an element of surprise and sophistication to compositions. - Harmonic Embellishment:
B dim chords serve as effective harmonic embellishments, adding color and interest to otherwise predictable chord progressions. Their unexpected and dissonant intervals create a sense of harmonic movement and development, preventing the music from becoming stagnant. - Voice Leading and Resolution:
The careful voice leading of b dim chords can create a strong sense of resolution and harmonic closure. By resolving the dissonance to consonant chords, composers can create a satisfying and emotionally impactful musical experience.
Overall, the incorporation of b dim chords into guitar playing expands harmonic possibilities, adds depth and interest to chord progressions, and enhances the emotional impact of music.
10. Melodic interest
The connection between “Melodic interest: Can be used to create melodic lines” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the unique melodic possibilities that arise from the dissonant and unresolved nature of b dim chords. Guitarists can exploit these characteristics to craft expressive and memorable melodies.
- Dissonance as Melodic Tension:
The dissonance inherent in b dim chords creates a sense of melodic tension that can be effectively utilized to build anticipation and emotional impact. Guitarists can use this tension to create melodies that gradually resolve into consonant intervals, providing a satisfying release and sense of closure. - Chromatic Embellishments:
The chromatic intervals within b dim chords offer opportunities for creating intricate and unexpected melodic embellishments. Guitarists can incorporate chromatic passing tones, neighboring tones, and other melodic devices to add color and interest to their solos and compositions. - Harmonic Implied Melodies:
B dim chords can imply melodic lines through their harmonic structure. By understanding the voice leading and harmonic progressions, guitarists can craft melodies that naturally flow from the chord changes, creating a cohesive and musically satisfying experience. - Dissonant Counterpoint:
The dissonant intervals in b dim chords can be effectively used in contrapuntal melodies. By combining b dim chords with consonant melodies or vice versa, guitarists can create intricate and engaging melodic textures that explore the interplay between dissonance and consonance.
In summary, the melodic interest provided by b dim chords guitar stems from their dissonant nature, chromatic possibilities, harmonic implications, and potential for contrapuntal interplay. By embracing these characteristics, guitarists can expand their melodic vocabulary and create solos and compositions that are both expressive and technically proficient.
11. Improvisation
The connection between “Improvisation: Provides a harmonic framework for improvisation” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the unique harmonic qualities and improvisational possibilities that b dim chords offer guitarists. These chords, with their dissonant and unresolved nature, serve as a fertile ground for spontaneous melodic exploration and harmonic experimentation.
B dim chords provide a harmonic framework that allows improvisers to navigate through complex chord progressions and create cohesive and expressive solos. The dissonant intervals within these chords create a sense of tension and instability, which can be effectively resolved through melodic improvisation. Guitarists can use the chord tones as starting points for their improvisational lines, exploring chromatic approaches, enclosures, and other techniques to create melodies that both embrace and resolve the dissonance.
The improvisational possibilities of b dim chords are further enhanced by their ability to facilitate modulations and key changes. By transitioning through different b dim chords, guitarists can smoothly move between distant keys, creating a sense of harmonic movement and exploration. This technique is particularly useful in jazz improvisation, where soloists often navigate through complex chord changes and modulations.
In summary, the connection between “Improvisation: Provides a harmonic framework for improvisation” and “b dim chords guitar” is rooted in the unique harmonic qualities of these chords. Their dissonant nature, combined with their potential for resolving dissonance and facilitating modulations, makes b dim chords a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to expand their improvisational vocabulary and create expressive and engaging solos.
Table: Key Insights
| Key Insight | Description |
|---|---|
| Dissonant nature provides tension for improvisation | The dissonant intervals in b dim chords create a sense of tension that can be resolved through melodic improvisation. |
| Harmonic framework for exploration | B dim chords provide a harmonic framework that allows guitarists to navigate through complex chord progressions and experiment with different melodic ideas. |
| Facilitates modulations and key changes | By transitioning through different b dim chords, guitarists can smoothly move between distant keys, creating a sense of harmonic movement and exploration. |
12. Practice
The connection between “Practice: Regular practice is essential for mastering b dim chords” and “b dim chords guitar” lies in the fundamental role that consistent practice plays in developing proficiency and enhancing one’s understanding of these chords on the guitar. Regular practice is crucial for internalizing the fingerings, voicings, and harmonic functions of b dim chords, enabling guitarists to utilize them effectively in musical contexts.
- Technical Proficiency
Regular practice is essential for developing the technical proficiency required to play b dim chords cleanly and accurately on the guitar. Through repetitive practice, guitarists can train their fingers to execute the specific fingerings and voicings associated with these chords, ensuring smooth transitions and precise intonation.
- Voicing Exploration
B dim chords offer a diverse range of voicings, each with its unique harmonic qualities. Regular practice allows guitarists to explore these different voicings, experimenting with various fingerings and positions on the fretboard. By doing so, they can expand their harmonic vocabulary and discover new sonic possibilities when using b dim chords.
- Harmonic Understanding
Regular practice fosters a deeper understanding of the harmonic functions of b dim chords within the context of guitar playing. Through practice, guitarists can learn how to identify and utilize b dim chords in different chord progressions, exploring their role as transitional chords, tension-building devices, or harmonic embellishments.
- Improvisational Fluency
Mastering b dim chords through regular practice enhances a guitarist’s improvisational fluency. The ability to play these chords comfortably and accurately allows guitarists to incorporate them spontaneously into solos and improvisations, adding harmonic depth and interest to their playing.
In summary, the connection between “Practice: Regular practice is essential for mastering b dim chords” and “b dim chords guitar” underscores the importance of consistent practice in developing the technical proficiency, voicing exploration, harmonic understanding, and improvisational fluency necessary to utilize these chords effectively on the guitar.
FAQs about b dim chords guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding b dim chords guitar to provide clarity and enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the construction of a b dim chord on the guitar?
Answer: A b dim chord, often notated as “b dim,” consists of three notes: the root, flattened third, and flattened fifth. For example, in the key of C, the C b dim chord would be composed of the notes C, Eb, and Gb.
Question 2: How do b dim chords differ from regular minor chords?
Answer: Unlike minor chords, which have a flattened third but a perfect fifth, b dim chords have both a flattened third and a flattened fifth. This unique combination creates a more dissonant and unresolved sound.
Question 3: What are the common uses of b dim chords in guitar playing?
Answer: B dim chords are commonly employed in jazz, blues, and classical music. They are often used to add tension, color, and harmonic interest to chord progressions. In jazz, they are frequently used as passing chords or as part of complex chord voicings.
Question 4: Are there different voicings or inversions for b dim chords?
Answer: Yes, like other chords, b dim chords have multiple voicings and inversions. Different voicings involve arranging the notes of the chord in various positions on the guitar neck, while inversions involve changing the order of the notes, resulting in different harmonic effects.
Question 5: How can I incorporate b dim chords into my guitar playing?
Answer: To incorporate b dim chords into your playing, start by practicing their basic construction and fingerings. Experiment with different voicings to find those that suit your musical style. Gradually introduce them into your chord progressions and solos, paying attention to their harmonic function and how they interact with other chords.
Question 6: What are some tips for mastering b dim chords on the guitar?
Answer: Regular practice is essential for mastering b dim chords. Focus on developing finger dexterity and accuracy. Study music theory to understand their harmonic function and how they fit into different musical contexts. Listen to recordings of guitarists who effectively utilize b dim chords to gain inspiration and learn from their techniques.
In summary, b dim chords guitar offer a unique and versatile harmonic tool for guitarists. By understanding their construction, exploring different voicings and inversi
ons, and practicing regularly, guitarists can effectively incorporate these chords into their playing, enhancing their harmonic vocabulary and musical expression.
Transition to the next article section:
To further expand your knowledge of guitar chords, explore our comprehensive guide to extended chords, covering their construction, types, and practical applications.
Tips for Mastering b dim chords guitar
Incorporating b dim chords into your guitar playing can greatly enhance your harmonic vocabulary and musical expression. Here are some tips to help you master these chords effectively:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is essential for developing the finger dexterity and muscle memory required to play b dim chords cleanly and accurately. Dedicate time each day to practice their fingerings and voicings, gradually increasing the speed and complexity of your
Tip 2: Explore Different Voicings
B dim chords offer a diverse range of voicings, each providing a unique harmonic color. Experiment with different fingerings and positions on the fretboard to discover the voicings that best suit your musical style and the specific musical context.
Tip 3: Understand Harmonic Function
Grasping the harmonic function of b dim chords is crucial for using them effectively in your playing. Study music theory to understand how these chords function within chord progressions and how they interact with other chords. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions about when and how to incorporate b dim chords into your music.
Tip 4: Listen to Others
Listen to recordings of guitarists who effectively utilize b dim chords. Pay attention to their technique, phrasing, and how they incorporate these chords into their solos and compositions. This can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own playing.
Tip 5: Experiment and Innovate
Once you have a solid foundation in the basics, don’t be afraid to experiment with different approaches to b dim chords. Try combining them with other extended chords, using them in unexpected harmonic contexts, or creating your own unique voicings. Innovation can lead to exciting and original musical ideas.
Summary:
Mastering b dim chords guitar requires dedication, practice, and a deep understanding of their harmonic function. By following these tips, you can effectively incorporate these chords into your playing, enhancing your harmonic vocabulary and opening up new possibilities for musical expression.
Transition to the conclusion:
With consistent effort and a commitment to learning, you can unlock the full potential of b dim chords guitar and elevate your musical journey to new heights.
Conclusion
Our exploration of “b dim chords guitar” has illuminated their unique construction, harmonic function, and expressive potential. These chords, with their dissonant and unresolved nature, add color, tension, and interest to guitar playing across various genres.
Mastering b dim chords requires regular practice, a deep understanding of their harmonic role, and the ability to experiment with different voicings and applications. By incorporating these chords into your playing, you can expand your harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and expressive music.
The journey of learning b dim chords guitar is an ongoing one, filled with opportunities for discovery and musical growth. Embrace the challenge, practice diligently, and unlock the full potential of these versatile and evocative chords.