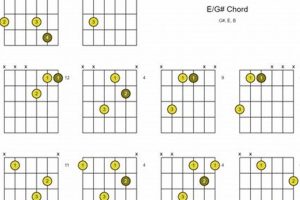
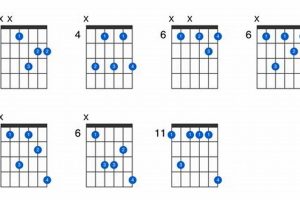
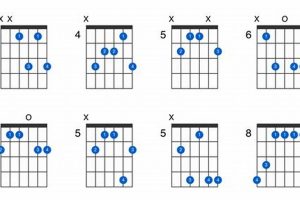
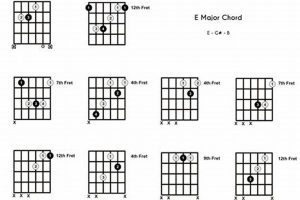
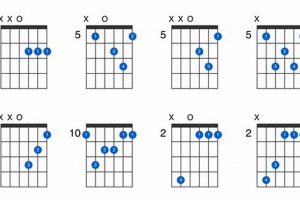
Unlock the Labyrinth of Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Editor’s Note:Advanced jazz guitar chords are the intricate tapestry that weaves the fabric of captivating jazz melodies, adding depth and sophistication to every note. Understanding these advanced chords is a gateway to unlocking a universe of musical expression.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve meticulously crafted this comprehensive guide to advanced jazz guitar chords. It’s your roadmap to mastering these complex voicings, empowering you to elevate your playing to new heights.
Key Differences:
| Basic Jazz Chords | Advanced Jazz Chords |
|---|---|
| Triads and Seventh Chords | Altered Chords, Extended Chords |
| Simpler Fingerings | Complex Fingerings, Extended Fingerboard Range |
| Provide Basic Harmonic Framework | Enrich Harmonic Complexity, Create Dissonance |
Main Article Topics:
- Exploring Altered Chords: A World of Altered Tensions
- Extended Chords: Expanding the Harmonic Palette
- Inversions and Voicings: Unlocking Melodic Potential
- Practice Techniques: Tips and Exercises for Mastery
- Application in Jazz Standards: Bringing Chords to Life
1. Altered Tensions
Altered tensions are a defining characteristic of advanced jazz guitar chords, introducing dissonance and enriching harmonic complexity. They involve altering the natural tensions within a chord, such as the 3rd, 5th, 7th, or 9th, by raising or lowering them by a semitone. This creates a dynamic interplay between consonance and dissonance, adding depth and sophistication to the overall sound.
The most common altered tensions in jazz guitar chords include:
- 5 (flatted fifth): Creates a sense of tension and instability.
- #5 (sharpened fifth): Adds brightness and dissonance to the chord.
- 9 (flatted ninth): Provides a smooth, dissonant extension to the chord.
- #9 (sharpened ninth): Adds a sharp dissonance to the chord, creating a sense of urgency.
Altered tensions can be found in a wide range of advanced jazz guitar chords, such as:
- Minor 75 chords (e.g., Dm75)
- Major 7#5 chords (e.g., Cmaj7#5)
- Dominant 79 chords (e.g., G79)
- Minor 9#9 chords (e.g., Dm9#9)
Understanding and utilizing altered tensions is crucial for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create sophisticated jazz voicings. By incorporating altered tensions into their playing, guitarists can add depth, dissonance, and a unique personal touch to their music.
| Chord | Altered Tension | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Dm7 | 5 | Creates a sense of tension and instability. |
| Cmaj7 | #5 | Adds brightness and dissonance to the chord. |
| G7 | 9 | Provides a smooth, dissonant extension to the chord. |
| Dm9 | #9 | Adds a sharp dissonance to the chord, creating a sense of urgency. |
2. Extended Voicings
Extended voicings are an essential aspect of advanced jazz guitar chords, expanding the harmonic palette and adding depth to the overall sound. They involve extending the basic triad or seventh chord structure by adding additional notes, typically above the root. This creates a richer and more complex harmonic tapestry, allowing guitarists to explore new and innovative voicings.
- 9th, 11th, and 13th extensions
These extensions add upper harmonics to the chord, creating a more dissonant and complex sound. They are commonly used in dominant 7th chords, such as G13 (G7 with added 11th and 13th) and C9 (C7 with added 9th). - Added 6th and added 2nd extensions
These extensions add color and dissonance to the chord. The added 6th creates a more open and spacious sound, while the added 2nd adds a touch of dissonance. They are commonly used in major 7th chords, such as Cmaj9 (Cmaj7 with added 9th) and Dm7add11 (Dm7 with added 11th). - Suspended voicings
Suspended voicings omit the 3rd or 5th of the chord, creating a more ambiguous and unresolved sound. They are commonly used to create tension and anticipation, and can be found in a variety of jazz standards, such as “All the Things You Are” and “Blue Monk”.
Extended voicings are a powerful tool for jazz guitarists, allowing them to create sophisticated and expressive harmonies. By understanding and utilizing extended voicings, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and take their playing to the next level.
3. Melodic Potential
Advanced jazz guitar chords unlock a vast melodic potential, empowering guitarists to create intricate and expressive melodic lines within their chords. Unlike basic jazz chords, which often serve as harmonic foundations, advanced chords provide a rich harmonic canvas upon which melodies can dance and soar.
The extended voicings and altered tensions found in advanced jazz guitar chords create a complex harmonic landscape that invites melodic exploration. Guitarists can craft melodic lines that weave in and out of the chord’s harmonic structure, creating a sense of movement and depth. This melodic potential is particularly evident in genres such as bebop and modal jazz, where improvisers use advanced chords as a springboard for their melodic flights.
Examples of melodic potential in advanced jazz guitar chords include:
- Using the 9th, 11th, and 13th extensions to create melodic lines that resolve to the root or 3rd of the chord.
- Employing altered tensions such as the flatted 5th or sharpened 9th to create dissonant melodic intervals that add tension and release.
- Combining different voicings of the same chord to create a sense of melodic movement and harmonic variation.
Understanding and utilizing the melodic potential of advanced jazz guitar chords is crucial for guitarists who want to create sophisticated and expressive solos. By embracing the harmonic richness of these chords, guitarists can expand their melodic vocabulary and take their playing to new heights.
| Chord | Melodic Potential | Example |
|---|---|---|
| G13 |
Melodic line that resolves to the root (G) or 3rd (B ). | G – B – D – E – G |
| Cmaj9#5 | Dissonant melodic interval created by the sharpened 5th (#5). | C – E – G – B – D |
| Dm7add11 | Melodic movement created by combining different voicings of the chord. | D – F – A – C – E – G |
4. Harmonic Dissonance
Harmonic dissonance is a crucial component of advanced jazz guitar chords, adding a sense of tension and depth to the music. It occurs when two or more notes clash, creating a jarring or unstable sound. This dissonance can be used to create a variety of effects, from a sense of urgency to a feeling of resolution.
In advanced jazz guitar chords, dissonance is often created through the use of altered tensions, such as the flatted 5th or the sharpened 9th. These altered tensions introduce intervals that are dissonant with the root of the chord, creating a sense of tension and instability. This tension can then be resolved by moving to a more consonant chord, or by using other techniques such as voice leading or chromaticism.
Harmonic dissonance is a powerful tool that can be used to create a wide range of emotions and effects in jazz music. By understanding and utilizing dissonance, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and take their playing to the next level.
Examples of Harmonic Dissonance in Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Here are some examples of how harmonic dissonance is used in advanced jazz guitar chords:
| Chord | Dissonant Interval | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| G13 | b5 | Creates a sense of tension and instability. |
| Cmaj7#5 | #5 | Adds brightness and dissonance to the chord. |
| Dm9 | b9 | Provides a smooth, dissonant extension to the chord. |
| Dm7add11 | #11 | Adds a sharp dissonance to the chord, creating a sense of urgency. |
5. Complex Fingerings in Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Advanced jazz guitar chords demand complex fingerings, a crucial aspect that elevates the harmonic possibilities of the guitar. Mastering these fingerings empowers guitarists to execute intricate chord voicings and extended ranges, expanding their technical abilities and creative expression.
- Wide Intervallic Stretches: Advanced jazz chords often involve wide intervals between notes, requiring guitarists to stretch their fingers across multiple frets. This enhances the chord’s harmonic complexity and allows for voicings that would be impossible with traditional fingerings.
- Barre Chords: Barre chords are a staple of jazz guitar, involving fretting multiple strings with one finger. They enable guitarists to create complex chord voicings across the entire fretboard, providing a wider range of harmonic options.
- Hybrid Picking: Hybrid picking combines the use of a pick and fingers to produce intricate melodic lines within chords. This technique allows guitarists to create independent voices within the chord, adding harmonic depth and rhythmic complexity.
- Tapping: Tapping involves using the picking hand to tap notes on the fretboard, extending the guitarist’s reach and enabling rapid-fire melodic passages. In advanced jazz guitar chords, tapping can be used to create dissonant intervals and extended harmonies.
These complex fingerings are essential for guitarists who want to unlock the full potential of advanced jazz guitar chords. By mastering these techniques, guitarists gain the ability to execute challenging voicings, enhance their harmonic vocabulary, and push the boundaries of their playing.
6. Extended Range
In the realm of advanced jazz guitar chords, extended range plays a pivotal role in expanding the harmonic possibilities and unlocking new dimensions of expression. It refers to the utilization of notes beyond the traditional range of the guitar, venturing into higher or lower registers.
- Upper Register Extensions: By venturing into the higher frets, guitarists access a wider array of notes, allowing for extended voicings and intricate melodic lines. These upper register extensions add brilliance and clarity to chords, enriching their harmonic complexity.
- Lower Register Extensions: Extending into the lower registers provides a foundation of depth and resonance to chords. These low notes add weight and harmonic support, creating a fuller and more robust sound.
- Multi-Octave Voicings: Advanced jazz guitar chords often employ multi-octave voicings, spreading the notes of the chord across multiple octaves. This technique creates a sense of spaciousness and harmonic interest, adding a sophisticated touch to the music.
- Extended Techniques: Some guitarists incorporate extended techniques, such as tapping and harmonics, to access notes beyond the conventional range of the instrument. These techniques allow for the execution of complex and dissonant intervals, expanding the harmonic vocabulary of jazz guitar.
Mastering extended range techniques empowers jazz guitarists to create innovative and harmonically rich chords that push the boundaries of traditional guitar playing. It opens up a vast sonic landscape, enabling them to explore new harmonic territories and express themselves with greater depth and nuance.
7. Jazz standards and advanced jazz guitar chords
Jazz standards serve as a fertile ground for the exploration and application of advanced jazz guitar chords, offering a rich harmonic context that challenges guitarists to push the boundaries of their playing. These classic compositions provide a structured framework within which guitarists can experiment with sophisticated chord voicings, extended harmonies, and complex fingerings.
- Harmonic Complexity: Jazz standards often feature complex chord progressions that demand a deep understanding of advanced jazz guitar chords. Guitarists must navigate through intricate harmonic changes, utilizing altered tensions, extended voicings, and chromaticism to create sophisticated and nuanced interpretations.
- Improvisational Vocabulary: The harmonic vocabulary of jazz standards provides a rich source of inspiration for guitarists to develop their improvisational skills. By studying the chord progressions and harmonic structures of standards, guitarists expand their harmonic knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of how to create melodic lines that complement and enhance the underlying harmony.
- Technical Proficiency: The technical demands of jazz standards require guitar
ists to master advanced jazz guitar chords and fingerings. Complex chord voicings, wide intervallic stretches, and intricate rhythmic patterns challenge guitarists to develop their technical proficiency and dexterity. - Historical Context: Jazz standards represent a rich historical tradition that has shaped the development of jazz guitar. By studying and playing standards, guitarists connect with the lineage of jazz guitarists who have come before them, gaining insights into the evolution of the instrument and the genre itself.
In conclusion, jazz standards provide an essential platform for the exploration and application of advanced jazz guitar chords. They challenge guitarists to expand their harmonic knowledge, develop their improvisational skills, and master complex fingerings, while also connecting them to the historical legacy of jazz guitar. Through the study and performance of jazz standards, guitarists gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between harmony, melody, and rhythm, empowering them to become more versatile and expressive musicians.
8. Practice Techniques for Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Unlocking the complexities of advanced jazz guitar chords requires a commitment to dedicated practice. Here are essential practice techniques that will guide you towards mastery:
- Chord Voicing and Fingerboard Visualization:
Develop a strong understanding of different chord voicings and their placement on the fingerboard. Practice visualizing chord shapes and transitions to enhance your dexterity and accuracy.
- Intervallic Ear Training and Harmonic Analysis:
Train your ears to recognize intervals and chord structures. Analyze the harmonic progressions in jazz standards and practice identifying the advanced chords used.
- Technical Exercises and Finger Independence:
Engage in regular technical exercises to improve your finger independence and dexterity. Practice scales, arpeggios, and chord inversions to strengthen your fingers and build muscle memory.
- Slow Practice and Metronome Use:
Break down complex chords into smaller parts and practice them slowly with a metronome. This methodical approach will help you develop precision and consistency.
By incorporating these practice techniques into your routine, you will lay a solid foundation for mastering advanced jazz guitar chords. Remember, practice is a journey, and patience and perseverance are key to achieving your musical goals.
9. Chord Inversions
In the realm of advanced jazz guitar chords, chord inversions play a pivotal role in expanding harmonic possibilities and enhancing musical expression. By inverting chords, guitarists can create new voicings, enrich harmonic textures, and explore melodic variations.
- Harmonic Embellishment:
Chord inversions allow guitarists to embellish harmonies by placing different notes in the bass. This creates a richer and more sophisticated sound, adding depth and interest to chord progressions.
- Melodic Independence:
Inversions provide melodic independence, enabling guitarists to create bass lines that complement and interact with the melody. This interplay between bass and melody adds rhythmic interest and harmonic complexity to solos and improvisations.
- Extended Range:
By inverting chords, guitarists can access notes that may not be easily erreichbar in root position. This extended range opens up new harmonic possibilities and allows for more intricate and varied voicings.
- Smooth Transitions:
Chord inversions facilitate smooth transitions between chords, creating a more fluid and cohesive harmonic flow. This technique is particularly useful in fast-paced chord progressions and complex harmonic modulations.
Mastering chord inversions is essential for advanced jazz guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their musical expression. By understanding and utilizing inversions, guitarists can unlock a wealth of creative possibilities and elevate their playing to new heights.
10. Harmonic Framework and Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Within the intricate world of advanced jazz guitar chords, harmonic framework serves as the foundation upon which complex and sophisticated harmonies are built. Understanding and utilizing this framework is paramount for guitarists seeking to master the art of jazz chord voicings.
- Tonal Centers and Chord Progressions:
Advanced jazz guitar chords often exist within specific tonal centers, establishing a harmonic roadmap for improvisation and composition. Guitarists must possess a deep understanding of chord progressions and their relationships to create cohesive and meaningful solos.
- Functional Harmony:
Functional harmony plays a crucial role in shaping the harmonic framework of jazz chords. By understanding the function of each chord within a progression, guitarists can anticipate chord changes and create logical and coherent harmonic movement.
- Extended and Altered Chords:
Advanced jazz guitar chords often incorporate extended and altered voicings, expanding the harmonic palette beyond basic triad structures. These chords add richness, depth, and complexity to chord progressions, challenging guitarists to navigate their intricate harmonies.
- Voice Leading and Smooth Transitions:
Voice leading principles guide the movement of individual notes within a chord progression, ensuring smooth and logical transitions between chords. Advanced jazz guitarists must master the art of voice leading to create seamless and musically satisfying harmonic progressions.
By mastering the harmonic framework of advanced jazz guitar chords, guitarists gain the ability to construct sophisticated and captivating harmonies that drive improvisation and enhance musical expression. This framework provides a structured approach to understanding and utilizing the complex world of jazz chord voicings, empowering guitarists to create their own unique harmonic landscapes.
11. Advanced Theory and Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Advanced music theory serves as the cornerstone upon which advanced jazz guitar chords are built. It provides the framework for understanding their construction, function, and application within jazz harmony. Delving into advanced theory empowers guitarists to navigate the complex harmonic landscape of jazz and create sophisticated and expressive chord voicings.
- Chord Extensions and Alterations:
Advanced theory explores the concept of chord extensions and alterations, which expand the harmonic possibilities beyond basic triad structures. These extended and altered chords add richness, depth, and complexity to chord progressions, challenging guitarists to master their intricate voicings.
- Voice Leading and Smooth Transitions:
Voice leading principles guide the movement of individual notes within a chord progression, ensuring smooth and logical transitions between chords. Advanced jazz guitarists must master the art of voice leading to create seamless and musically satisfying harmonic progressions.
- Modal Interchange and Polytonality:
Advanced theory ventures into the realms of modal interchange and polytonality, where guitarists explore the interplay between different scales and keys. These techniques create unique and evocative harmonic landscapes, expanding the expressive range of jazz guitarists.
Functional harmony analyzes chords based on their role and function within a tonal center. Understanding functional harmony enables guitarists to predict chord progressions, anticipate chord changes, and create logical and coherent harmonic movement.
By mastering advanced music theory, jazz guitarists gain the ability to construct sophisticated and captivating harmonies that drive improvisation and enhance musical expression. This theoretical foundation empowers them to navigate the complexities of jazz chord progressions, create their own unique harmonic landscapes, and communicate their musical ideas with depth and nuance.
Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding advanced jazz guitar chords, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What are the key differences between basic and advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Advanced jazz guitar chords extend beyond basic triads and seventh chords, incorporating altered tensions, extended voicings, and complex fingerings. They provide a wider harmonic palette, enabling jazz guitarists to create sophisticated and expressive chord voicings.
Question 2: How do altered tensions contribute to advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Altered tensions introduce dissonance and harmonic complexity by altering specific notes within a chord, such as the 5th, 7th, or 9th. These tensions create a dynamic interplay, adding depth and interest to advanced jazz guitar chords.
Question 3: What are the advantages of using extended voicings in advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Extended voicings expand the harmonic range of chords, adding richness and depth to the sound. They provide additional harmonic options, allowing guitarists to create more sophisticated and expressive chord voicings.
Question 4: How does voice leading influence the construction of advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Voice leading principles guide the smooth and logical movement of individual notes within a chord progression. Advanced jazz guitar chords often employ voice leading techniques to create seamless transitions between chords, enhancing the overall harmonic flow.
Question 5: What is the role of advanced music theory in understanding advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Advanced music theory provides a framework for analyzing and understanding the construction and function of advanced jazz guitar chords. It enables guitarists to comprehend the harmonic relationships and principles that underpin these complex chords.
Question 6: How can I practice and develop my skills in playing advanced jazz guitar chords?
Answer: Regular practice and dedication are essential for mastering advanced jazz guitar chords. Focus on developing finger independence, practicing chord voicings and inversions, and studying jazz standards to gain a deeper understanding of harmonic progressions.
In summary, advanced jazz guitar chords offer a gateway to harmonic exploration and expressive possibilities. Understanding their construction, function, and application empowers guitarists to create sophisticated and captivating harmonic landscapes.
Moving forward, the next section will delve into the practical application of advanced jazz guitar chords within the context of jazz improvisation.
Tips for Mastering Advanced Jazz Guitar Chords
Embarking on the journey of mastering advanced jazz guitar chords requires dedication, practice, and a strategic approach. Here are some invaluable tips to guide your progress:
Tip 1: Dedicate Time to Practice: Consistent and focused practice is the cornerstone of mastery. Allocate dedicated time each day to practice advanced chords, fingerings, and harmonic progressions.
Tip 2: Analyze Jazz Standards: Study jazz standards to understand how advanced chords are used in real-world musical contexts. Analyze chord progressions, voice leading, and the interplay between harmony and melody.
Tip 3: Experiment with Chord Inversions and Voicings: Explore different chord inversions and voicings to expand your harmonic vocabulary. Experiment with placing various notes in the bass to create unique and sophisticated sounds.
Tip 4: Focus on Voice Leading and Smooth Transitions: Pay attention to voice leading principles to ensure smooth and logical movement between chords. Avoid abrupt voice crossings and strive for a cohesive harmonic flow.
Tip 5: Study Advanced Music Theory: Delve into advanced music theory to gain a deeper understanding of the construction and function of advanced jazz guitar chords. This knowledge will empower you to analyze and create sophisticated harmonic progressions.
Tip 6: Incorporate Advanced Chords into Improvisation: Gradually incorporate advanced chords into your improvisational solos. Start by using them sparingly and gradually increase their frequency as you gain confidence.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular practice is crucial for developing proficiency in advanced jazz guitar chords.
- Studying jazz standards provides insights into the practical application of advanced chords.
- Experimenting with chord inversions and voicings expands harmonic possibilities.
- Understanding voice leading principles ensures smooth and logical chord transitions.
- Advanced music theory enhances the comprehension and use of advanced jazz guitar chords.
- Incorporating advanced chords into improvisation adds depth and sophistication to musical expression.
By diligently following these tips, jazz guitarists can embark on a fulfilling journey of mastering advanced jazz guitar chords, unlocking new levels of harmonic sophistication and expanding their musical horizons.
Conclusion
Advanced jazz guitar chords stand as a testament to the boundless creativity and harmonic possibilities within the realm of jazz guitar. They empower players to transcend basic chord structures, venturing into a world of altered tensions, extended voicings, and complex fingerings.
By embracing the intricacies of these advanced chords, guitarists unlock a universe of sophisticated and expressive harmonic landscapes. They gain the ability to create dynamic and dissonant harmonies, enrich chord progressions with depth and complexity, and navigate the complexities of jazz improvisation with unpa
ralleled fluency.
The journey towards mastering advanced jazz guitar chords is one of dedication, practice, and a profound understanding of music theory. It requires guitarists to delve into the intricacies of voice leading, explore the relationships between chords and scales, and develop a deep familiarity with jazz standards.
As guitarists embark on this journey, they embark on a path of continuous growth and exploration. Advanced jazz guitar chords become a tool for expressing their unique musical voices, pushing the boundaries of harmonic convention, and captivating audiences with their sophisticated and nuanced playing.