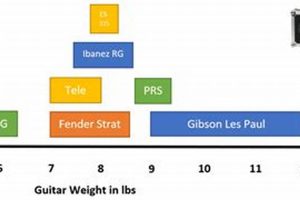
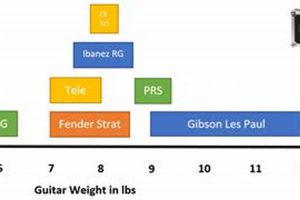
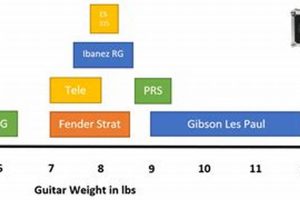
Electric guitars are a popular choice for musicians of all levels, from beginners to professionals. They offer a wide range of sounds and styles, making them versatile instruments for a variety of genres. But what are the different parts of an electric guitar, and what do they do?
Editor’s Note: Understanding the parts of an electric guitar is essential for any guitarist. It will help you to choose the right guitar for your needs, make repairs and adjustments, and get the most out of your instrument.
To help you out, we’ve put together this comprehensive guide to the parts of an electric guitar. We’ll cover everything from the body and neck to the pickups and electronics. So whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, read on to learn more about the parts of an electric guitar.
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Body | The body of the guitar is the main part of the instrument. It’s usually made of wood, and it houses the pickups, electronics, and bridge. |
| Neck | The neck of the guitar is the long, thin part of the instrument that connects the body to the headstock. It’s usually made of wood, and it has a fretboard on top. |
| Headstock | The headstock is the part of the guitar that contains the tuning pegs. It’s usually made of wood, and it’s sometimes decorated with a logo or design. |
| Pickups | Pickups are the devices that convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. They’re usually mounted on the body of the guitar, and they come in a variety of types. |
| Electronics | The electronics of the guitar control the sound of the instrument. They include the volume and tone controls, as well as the pickup selector switch. |
| Bridge | The bridge of the guitar is the part of the instrument that holds the strings in place. It’s usually made of metal, and it can be either fixed or floating. |
Now that you know the different parts of an electric guitar, you can start to learn how to play it. With a little practice, you’ll be able to master the basics of guitar playing and start making music of your own.
The body of an electric guitar is the main part of the instrument. It’s usually made of wood, and it houses the pickups, electronics, and bridge. The body is responsible for the overall sound of the guitar, as it affects the resonance and sustain of the strings.
There are many different types of guitar bodies, each with its own unique sound. Some of the most popular body types include:
- Solid body: Solid body guitars have a solid body, which gives them a bright, punchy sound. They are popular for playing rock, pop, and country music.
- Semi-hollow body: Semi-hollow body guitars have a hollow body with a solid center block. This gives them a warmer, more resonant sound than solid body guitars. They are popular for playing jazz, blues, and rock music.
- Hollow body: Hollow body guitars have a fully hollow body. This gives them a warm, mellow sound with a lot of sustain. They are popular for playing jazz and blues music.
The type of wood used for the body of the guitar also affects the sound. Some of the most popular woods used for guitar bodies include:
- Mahogany: Mahogany is a dense wood that produces a warm, resonant sound. It is popular for use in solid body and semi-hollow body guitars.
- Alder: Alder is a lightweight wood that produces a bright, clear sound. It is popular for use in solid body guitars.
- Ash: Ash is a hard wood that produces a bright, punchy sound. It is popular for use in solid body guitars.
The body of the guitar is an important part of the instrument’s overall sound and feel. By understanding the different types of bodies and woods available, you can choose the right guitar for your needs.
1. Neck
The neck of the guitar is an essential part of the instrument. It provides the platform for the strings and allows the player to fret the notes. The neck is also responsible for the overall feel and playability of the guitar.
- The neck’s shape and size can vary depending on the type of guitar. Electric guitars typically have a narrower neck than acoustic guitars, which makes them easier to play for some players. The length of the neck also affects the scale of the guitar, which is the distance between the nut and the bridge. A longer scale length produces a higher pitch, while a shorter scale length produces a lower pitch.
- The neck is made of wood, and the type of wood used can affect the sound and feel of the guitar. Some of the most common woods used for guitar necks include maple, mahogany, and rosewood. Each type of wood has its own unique tonal qualities and feel.
- The fretboard is the part of the neck where the strings are pressed down to create notes. The fretboard is usually made of wood or a composite material, and it can be either flat or radiused. A flat fretboard has a straight surface, while a radiused fretboard has a curved surface. The radius of the fretboard affects the feel of the guitar and the ease of playing certain chords.
- The neck is attached to the body of the guitar at the heel. The heel can be either square or rounded, and it can affect the balance and feel of the guitar. The neck is also attached to the headstock at the nut. The nut is a small piece of bone or plastic that holds the strings in place and determines the spacing between them.
The neck of the guitar is a complex and important part of the instrument. By understanding the different parts of the neck and how they work together, you can choose the right guitar for your needs and playing style.
2. Headstock
The headstock is an important part of the electric guitar. It houses the tuning pegs, which are used to tune the strings. The headstock also provides a place to attach the guitar strap. The headstock can be made of a variety of materials, including wood, metal, and plastic. However, wood is the most common material used for headstocks.
- Function: The headstock’s primary function is to house the tuning pegs. The tuning pegs are used to adjust the tension of the strings, which in turn changes the pitch of the notes played on the guitar.
- Materials: Headstocks are typically made of wood, although other materials such as metal and plastic can also be used. Wood is the most popular choice for headstocks because it is strong, durable, and relatively lightweight.
- Shape: The shape of the headstock can vary depending on the make and model of the guitar. However, most headstocks are eith
er symmetrical or asymmetrical. Symmetrical headstocks have a mirror image on both sides of the center line, while asymmetrical headstocks have a different shape on each side. - Decoration: The headstock is often decorated with a logo or design. This can be anything from a simple decal to a complex inlay. The decoration on the headstock can help to identify the make and model of the guitar.
The headstock is an important part of the electric guitar. It provides a place to attach the tuning pegs and the guitar strap. The headstock also contributes to the overall aesthetic of the guitar.
3. Pickups
Pickups are an essential part of an electric guitar. They convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals, which are then amplified and sent to the speakers. Without pickups, an electric guitar would not be able to produce any sound.
There are many different types of pickups, each with its own unique sound. The most common types of pickups are single-coil pickups and humbucking pickups. Single-coil pickups are known for their bright, twangy sound, while humbucking pickups are known for their thicker, more powerful sound.
The position of the pickups on the guitar’s body also affects the sound. Pickups that are closer to the bridge produce a brighter sound, while pickups that are closer to the neck produce a warmer sound.
The type of pickups used in a guitar is a major factor in determining the overall sound of the instrument. By understanding the different types of pickups available, you can choose the right guitar for your needs.
| Type of Pickup | Sound | Position |
|---|---|---|
| Single-coil | Bright, twangy | Closer to the bridge |
| Humbucking | Thicker, more powerful | Closer to the neck |
4. Electronics
The electronics of an electric guitar are an essential part of the instrument. They allow the player to control the sound of the guitar, including the volume, tone, and pickup selection.
The volume control allows the player to adjust the overall of the guitar. The tone control allows the player to adjust the EQ of the guitar, making the sound brighter or darker. The pickup selector switch allows the player to select which pickup or combination of pickups is used to amplify the sound of the strings.
The electronics of an electric guitar are relatively simple, but they play a vital role in the sound of the instrument. By understanding how the electronics work, you can get the most out of your guitar and create the sound you want.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Volume control | Adjusts the overall of the guitar |
| Tone control | Adjusts the EQ of the guitar, making the sound brighter or darker |
| Pickup selector switch | Selects which pickup or combination of pickups is used to amplify the sound of the strings |
5. Bridge
The bridge is an essential part of an electric guitar. It provides a stable platform for the strings, and it also helps to transfer the vibrations of the strings to the guitar’s body. The design of the bridge can have a significant impact on the sound of the guitar.
- Type of bridge: There are two main types of bridges: fixed bridges and floating bridges. Fixed bridges are attached to the body of the guitar, while floating bridges are not. Floating bridges allow the player to adjust the intonation of the guitar, which is the process of adjusting the length of the strings to ensure that they are in tune.
- Material: Bridges are typically made of metal, but they can also be made of other materials, such as wood or plastic. The material of the bridge can affect the sound of the guitar. For example, metal bridges produce a brighter sound than wood bridges.
- Design: The design of the bridge can also affect the sound of the guitar. For example, bridges with a larger mass will produce a warmer sound than bridges with a smaller mass.
- Function: The bridge plays an important role in the overall sound and playability of the guitar. By understanding the different types of bridges available, you can choose the right bridge for your needs.
The bridge is an essential part of an electric guitar. By understanding the different components, materials, and designs of bridges, you can choose the right bridge for your needs and playing style.
6. Strings
Strings are an essential part of an electric guitar. They vibrate when plucked or strummed, creating the sound that is amplified by the guitar’s electronics. The type of strings used can affect the sound of the guitar, so it is important to choose the right strings for your playing style.
- Material: Electric guitar strings are typically made of metal, but they can also be made of other materials, such as nylon or silk. Metal strings produce a brighter sound than nylon or silk strings.
- Gauge: The gauge of a string refers to its thickness. Thinner strings are easier to play, but they produce a less powerful sound. Thicker strings are more difficult to play, but they produce a more powerful sound.
- Winding: Strings can be either wound or unwound. Wound strings are made by wrapping a thin wire around a thicker core wire. Unwound strings are made from a single strand of wire. Wound strings produce a warmer sound than unwound strings.
- Coating: Some strings are coated with a thin layer of material, such as nickel or polymer. Coated strings last longer than uncoated strings and they are less likely to corrode.
- Function: The strings are an essential part of an electric guitar. They vibrate when plucked or strummed, creating the sound that is amplified by the guitar’s electronics. The type of strings used can affect the sound of the guitar, so it is important to choose the right strings for your playing style.
The different combinations of material, gauge, winding, and coating can create a wide variety of sounds. Experimenting with different strings is a great way to find the sound that you want.
7. Frets
Frets are an essential part of an electric guitar. They divide the neck of the guitar into semitones, which are the smallest intervals used in Western music. This allows guitarists to play notes in tune and to create melodies and chords.
- Function: Frets serve the primary function of dividing the strings into specific note intervals, enabling guitarists t
o play accurate notes and chords. Without frets, it would be extremely difficult to play notes in tune on an electric guitar. - Material: Frets are typically made of metal, most commonly nickel-plated steel. This material is durable and resistant to wear and tear, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the frets.
- Size and Shape: The size and shape of frets can vary depending on the type of guitar and the playing style of the guitarist. Larger frets are often used on electric guitars designed for rock and metal music, while smaller frets are common on guitars intended for jazz and classical music.
- Installation: Frets are typically installed on the fretboard using a process called fretting. This involves cutting slots into the fretboard and then inserting the frets into the slots. Fretting is a specialized skill that requires precision and expertise.
Overall, frets are an integral part of an electric guitar, enabling guitarists to play notes in tune and to create a wide range of musical sounds.
8. Tuning pegs
Tuning pegs are an essential part of any electric guitar. They allow the player to adjust the tension of the strings, which in turn changes the pitch of the notes played on the guitar. Without tuning pegs, it would be impossible to keep an electric guitar in tune.
- Function: The primary function of tuning pegs is to adjust the tension of the strings. This is done by turning the tuning pegs clockwise to tighten the strings and raise the pitch, or counterclockwise to loosen the strings and lower the pitch.
- Materials: Tuning pegs are typically made of metal, such as steel or brass. Metal is a durable material that can withstand the tension of the strings without bending or breaking.
- Shape and size: Tuning pegs come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The most common type of tuning peg is the slotted head tuning peg, which has a slotted head that the player turns with a tuning key. Other types of tuning pegs include the friction tuning peg, which is tightened by hand, and the locking tuning peg, which has a locking mechanism to prevent the strings from slipping.
- Location: Tuning pegs are located on the headstock of the guitar. The headstock is the part of the guitar that extends from the neck and contains the tuning pegs, nut, and string trees.
Tuning pegs are an essential part of an electric guitar. They allow the player to adjust the tension of the strings, which in turn changes the pitch of the notes played on the guitar. By understanding the function, materials, shape and size, and location of tuning pegs, you can better understand how an electric guitar works and how to keep it in tune.
The strap button is a small but essential part of an electric guitar. It allows the player to attach a guitar strap, which helps to distribute the weight of the guitar and makes it more comfortable to play. Without a strap button, it would be difficult to play an electric guitar for long periods of time.
Most electric guitars have a single strap button located on the back of the body, near the neck. However, some guitars may have two strap buttons, one on the back of the body and one on the side of the body. This allows the player to choose the most comfortable position for the guitar strap.
Strap buttons are typically made of metal, such as steel or brass. This ensures that they are strong enough to withstand the tension of the guitar strap. Strap buttons are also usually recessed into the body of the guitar, so that they do not interfere with the player’s hand when they are playing.
The strap button is a small but important part of an electric guitar. It allows the player to attach a guitar strap, which helps to distribute the weight of the guitar and makes it more comfortable to play. By understanding the function and importance of the strap button, you can better understand how an electric guitar works and how to use it.
| Part | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Strap button | To attach a guitar strap | Helps to distribute the weight of the guitar and makes it more comfortable to play |
FAQs about Parts of an Electric Guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the parts of an electric guitar, providing clear and concise answers to enhance your understanding.
Question 1: What is the difference between a solid body and a hollow body electric guitar?
Answer: Solid body guitars have a solid body, which gives them a brighter, more focused sound. They are popular for rock, pop, and country music. Hollow body guitars have a hollow body, which gives them a warmer, more resonant sound. They are popular for jazz, blues, and rockabilly music.
Question 2: What is the function of the pickups on an electric guitar?
Answer: Pickups convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals, which are then amplified and sent to the speakers. Different types of pickups produce different sounds, such as single-coil pickups for a brighter sound and humbucking pickups for a warmer, thicker sound.
Question 3: What is the purpose of the bridge on an electric guitar?
Answer: The bridge holds the strings in place and transfers their vibrations to the body of the guitar. It also allows the player to adjust the intonation of the guitar, ensuring that the notes are played in tune.
Question 4: What is the difference between a fixed bridge and a floating bridge?
Answer: A fixed bridge is attached to the body of the guitar, while a floating bridge is not. Floating bridges allow the player to adjust the tension of the strings, which can affect the pitch and tone of the guitar.
Question 5: What is the function of the frets on an electric guitar?
Answer: Frets divide the neck of the guitar into semitones, which allows the player to play notes in tune. They are usually made of metal and are inserted into the fretboard.
Question 6: What is the purpose of the strap button on an electric guitar?
Answer: The strap button is a small button on the body of the guitar that allows the player to attach a guitar strap. This helps to distribute the weight of the guitar and makes it more comfortable to play.
Summary: Understanding the different parts of an electric guitar is essential for playing, maintaining, and customizing the instrument. Each part plays a vital role in producing the sound, feel, and overall performance of the guitar.
Transition: To further explore the world of electric guitars, let’s delve into the different types of pickups and their impact on the sound.
Tips for Understanding the Parts of an Electric Guitar
Understanding the different parts of an electric guitar is essential for playing, maintaining, and customizing the instrument. Here are a few helpful tips to enhance your knowledge:
Tip 1: Familiarize yourself with the basic parts
Start by learning the names and functions of the major
components, such as the body, neck, headstock, pickups, and bridge. This will give you a solid foundation for further exploration.
Tip 2: Study the different types of bodies
Electric guitar bodies come in various shapes and sizes, each producing a unique sound. Explore the differences between solid body, semi-hollow body, and hollow body guitars to find the one that best suits your musical style.
Tip 3: Understand pickup construction and placement
The type and placement of pickups significantly impact the sound of an electric guitar. Learn about single-coil, humbucking, and P-90 pickups, as well as their optimal positions on the body.
Tip 4: Explore bridge options and their impact
The bridge not only holds the strings in place but also affects the guitar’s tone and playability. Discover the distinctions between fixed bridges, floating bridges, and tremolo systems.
Tip 5: Learn about fretboard materials and construction
The fretboard is a crucial part of the guitar’s neck. Explore different fretboard materials like rosewood, maple, and ebony, and understand how they influence the sound and feel of the instrument.
Summary: By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding of the parts of an electric guitar and make informed decisions when choosing, playing, and maintaining your instrument.
Transition: With a thorough understanding of the guitar’s components, you can now delve deeper into the fascinating world of electric guitar tones and techniques.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the fundamental parts of an electric guitar, delving into their functions, materials, and impact on the instrument’s sound and playability. From the body and neck to the pickups, bridge, and frets, each component contributes to the unique character and versatility of the electric guitar.
Understanding the different parts of an electric guitar empowers you to make informed decisions when choosing, playing, and maintaining your instrument. Whether you’re a seasoned guitarist or just starting your musical journey, this knowledge will enhance your ability to express yourself through this iconic instrument.