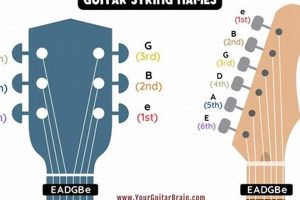
Wondering what those numbers on your guitar strings mean? You’re not alone. Many guitarists, especially beginners, are confused by the numbers on their strings. But don’t worry, we’re here to help.
Editor’s Note:Numbers on guitar strings are an important part of understanding how to play the guitar. By understanding what the numbers mean, you can learn how to tune your guitar, play chords, and even write your own songs.
We’ve put together this “numbers on guitar strings” guide to help you make sense of the numbers on your strings. We’ll explain what the numbers mean, how to use them to tune your guitar, and how to use them to play chords.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
| String | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 1 | E |
| 2nd | 2 | B |
| 3rd | 3 | G |
| 4th | 4 | D |
| 5th | 5 | A |
| 6th | 6 | E |
Transition to main article topics
Now that you know what the numbers on your guitar strings mean, you can start learning how to play guitar. Here are a few resources to help you get started:
- How to Play Guitar for Beginners
- JustinGuitar Beginner Guitar Lessons
- 5 Easy Guitar Songs for Beginners
1. Identification
This numerical identification system for guitar strings is a crucial aspect of the instrument’s functionality and learning process. The numbers serve as a reference point for various guitar-related tasks, making it easier to understand and play the instrument.
- Tuning: The numbers correspond to specific notes (E, A, D, G, B, E), which aids in accurate tuning using a tuner or reference pitches.
- Chords: Chord diagrams often utilize numbers to indicate which strings to play and where to place fingers, simplifying the process of learning and playing chords.
- Scales: Numbers help visualize and navigate scales on the fretboard, connecting notes and patterns, making it easier to understand and practice scales.
- String Gauges: Numbers represent the thickness or gauge of strings, affecting tone, tension, and playability, allowing guitarists to choose the appropriate strings for their playing style and desired sound.
In summary, the numerical identification of guitar strings provides a standardized system for understanding, playing, and maintaining the instrument. It facilitates tuning, chord playing, scale navigation, and string selection, making it an essential aspect of the guitar-playing experience.
2. Tuning
The connection between tuning and the numbers on guitar strings is fundamental to playing the guitar accurately and producing the desired sound. The numbers assigned to each string correspond to specific notes (E, A, D, G, B, E), providing a clear reference point for tuning the guitar.
Accurate tuning is essential for several reasons:
- Intonation: Correct tuning ensures that the notes played on the guitar are in tune with each other, producing harmonious and pleasing sounds.
- Chord Voicing: Proper tuning allows for accurate chord voicings, as the notes within a chord must be in the correct relationship to each other to sound consonant.
- Scale Patterns: Tuning affects the accuracy of scale patterns, as the intervals between notes on the fretboard must be consistent to produce the correct scale.
Using a tuner or reference pitches, guitarists can adjust the tension of each string until the corresponding note is reached. The numbers on the strings serve as a guide, indicating which string should be tuned to which note. This process ensures that the guitar is in tune and ready to play.
In summary, the numbers on guitar strings provide a crucial reference point for tuning, enabling guitarists to achieve accurate intonation, proper chord voicings, and correct scale patterns. Understanding this connection is essential for playing the guitar effectively and producing the desired musical sounds.
3. Chords
The connection between chord diagrams and the numbers on guitar strings is crucial for understanding and playing chords on the guitar. Chord diagrams are visual representations of chords, showing which strings to play and where to place your fingers on the fretboard. The numbers on the guitar strings serve as a reference point for these diagrams, making it easier to learn and play chords.
Chord diagrams typically use numbers to indicate the following:
- Which strings to play: The numbers indicate which strings should be played to form the chord. For example, in a C chord diagram, the numbers 1, 2, and 3 may be used to indicate that the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd strings should be played.
- Where to place your fingers: The numbers also indicate where to place your fingers on the fretboard. For example, in a C chord diagram, the number 1 may be used to indicate that you should place your index finger on the first fret of the 2nd string.
By understanding the connection between chord diagrams and the numbers on guitar strings, you can quickly and easily learn how to play a wide variety of chords. This is especially helpful for beginner guitarists who are still learning the fretboard and finger placement.
Here are some real-life examples of how the numbers on guitar strings are used in chord diagrams:
- C chord diagram: The numbers 1, 2, and 3 indicate that you should play the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd strings. The number 1 also indicates that you should place your index finger on the first fret of the 2nd string.
- G chord diagram: The numbers 1, 2, and 3 indicate that you should play the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd strings. The numbers 2 and 3 also indicate that you should place your middle finger on the second fret of the 3rd string and your ring finger on the third fret of the 4th string.
- D chord diagram: The numbers 1, 2, and 3 indicate that you should play the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd strings. The numbers 2 and 3 also indicate that you should place your middle finger on the second fret of the 2nd string and your ring finger on the third fret of the 3rd string.
By understanding the connection between chord diagrams and the numbers on guitar strings, you can quickly and easily learn how to play a wide variety of chords. This is especially h
elpful for beginner guitarists who are still learning the fretboard and finger placement.
Key Insights:
- The numbers on guitar strings provide a reference point for chord diagrams, making it easier to learn and play chords.
- Chord diagrams use numbers to indicate which strings to play and where to place your fingers on the fretboard.
- Understanding the connection between chord diagrams and the numbers on guitar strings is essential for learning how to play the guitar.
4. Scales
The connection between scales and the numbers on guitar strings is crucial for understanding and playing scales on the guitar. Scales are a series of musical notes played in ascending or descending order, and they form the foundation of many guitar solos, riffs, and chord progressions.
- Visualizing Scales: The numbers on guitar strings provide a visual reference for scales, making it easier to see the patterns and relationships between notes. For example, the C major scale can be visualized on the fretboard using the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
- Navigating Scales: The numbers on guitar strings also help guitarists navigate scales more easily. By understanding the numerical sequence of a scale, guitarists can quickly and accurately move from one note to the next, even if they are not familiar with the fretboard.
- Connecting Notes and Patterns: The numbers on guitar strings help guitarists connect the notes in a scale and identify patterns. For example, the C major scale has a repeating pattern of whole steps and half steps, which can be easily seen when the scale is visualized using the numbers on the strings.
- Learning Scales: The numbers on guitar strings can also be helpful for learning scales. By associating the numbers with the notes in a scale, guitarists can more easily memorize the scale and its patterns.
Overall, the connection between scales and the numbers on guitar strings is essential for understanding, playing, and learning scales on the guitar. The numbers provide a visual reference, help guitarists navigate scales more easily, and make it easier to connect the notes and patterns in a scale.
5. String Gauges
The connection between string gauges and the numbers on guitar strings is crucial for understanding the impact of string thickness on the sound, feel, and playability of the guitar. The numbers on guitar strings represent the gauge, or thickness, of each string, with higher numbers indicating thicker strings and lower numbers indicating thinner strings.
- Tone: The gauge of a string affects its tone, with thicker strings producing a warmer, fuller sound and thinner strings producing a brighter, more articulate sound. For example, a guitar with heavy gauge strings will have a warmer, more resonant tone than a guitar with light gauge strings.
- Tension: The gauge of a string also affects its tension, with thicker strings having higher tension and thinner strings having lower tension. Higher tension strings are more difficult to bend and stretch, while lower tension strings are easier to bend and stretch. This difference in tension can impact the playability of the guitar, especially for techniques such as bending and vibrato.
- Playability: The gauge of a string can also affect the playability of the guitar, with thicker strings being more difficult to fret and thinner strings being easier to fret. This difference in playability can be especially noticeable for beginner guitarists who may find it easier to play on guitars with lighter gauge strings.
- String Choice: The choice of string gauge is ultimately a matter of personal preference, as different guitarists have different playing styles and preferences. However, the numbers on guitar strings provide a useful reference point for guitarists when selecting strings that will best suit their playing style and the desired sound.
In summary, the connection between string gauges and the numbers on guitar strings is important for understanding the impact of string thickness on the tone, tension, and playability of the guitar. The numbers on guitar strings provide a useful reference point for guitarists when selecting strings that will best suit their playing style and the desired sound.
6. String Material
The connection between string material and the numbers on guitar strings is important for understanding the different types of strings available and how they affect the sound and playability of the guitar.
The two most common types of guitar strings are nylon and steel. Nylon strings are typically used on classical guitars, while steel strings are used on acoustic and electric guitars. The numbers on guitar strings indicate the gauge, or thickness, of the string. Thicker strings produce a warmer, fuller sound, while thinner strings produce a brighter, more articulate sound.
The numbering system for nylon strings is different from the numbering system for steel strings. Nylon strings are typically numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the thinnest string and 6 being the thickest string. Steel strings, on the other hand, are typically numbered from .009 to .056, with .009 being the thinnest string and .056 being the thickest string.
The different numbering systems for nylon and steel strings can be confusing, but it is important to understand the difference between the two systems in order to choose the right strings for your guitar.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between nylon and steel strings:
| Characteristic | Nylon Strings | Steel Strings |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Nylon | Steel |
| Numbering System | 1 to 6 | .009 to .056 |
| Sound | Warm, full | Bright, articulate |
| Playability | Easier to fret | More difficult to fret |
Ultimately, the choice of string material and gauge is a matter of personal preference. However, understanding the connection between string material and the numbers on guitar strings is essential for making an informed decision about which strings to use on your guitar.
7. Alternate Tunings
The connection between alternate tunings and the numbers on guitar strings is essential for guitarists who want to explore different sounds and expand their musical horizons. Alternate tunings involve changing the standard tuning of the guitar to create new and unique sonic possibilities.
- Establishing Alternate Tunings: Numbers serve as a guide for setting up alternate tunings. By adjusting the strings to specific notes or intervals, guitarists can create a wide range of alternate tunings, such as drop D, open G, or DADGAD.
- Visualizing
Fingerings: The numbers on the strings provide a visual reference for fingerings in alternate tunings. This helps guitarists visualize the new note patterns and scale shapes, making it easier to learn and play in these tunings. - Understanding Chord Voicings: Numbers assist in understanding how chords are voiced in alternate tunings. By observing the numerical relationship between the strings, guitarists can identify the root notes and construct chords in different voicings, expanding their harmonic possibilities.
- Exploring New Sounds: Alternate tunings, made possible by the numbers on the strings, allow guitarists to access novel and inspiring sounds. These tunings can create drone effects, enhance open string resonances, and facilitate unique melodic and rhythmic patterns.
In summary, the numbers on guitar strings are crucial for understanding and utilizing alternate tunings. They provide a framework for setting up different tunings, visualizing fingerings, comprehending chord voicings, and unlocking a vast array of sonic possibilities. Embracing alternate tunings empowers guitarists to transcend the confines of standard tuning and explore the boundless creativity that the guitar has to offer.
8. String Order
The numerical order of guitar strings (E-A-D-G-B-E) plays a crucial role in memorization and fretboard orientation. This standardized sequence provides a logical framework for understanding the guitar’s layout and facilitates efficient learning and navigation.
- Memorization: The numerical order serves as a mnemonic device, helping guitarists memorize the names and positions of the strings. The sequential arrangement makes it easier to recall the string order, especially for beginners.
- Fretboard Orientation: The numerical order establishes a consistent reference point for locating notes on the fretboard. By understanding the numerical sequence, guitarists can quickly identify the position of any note relative to the other strings, aiding in scale visualization, chord construction, and improvisation.
- Chord Shapes: The numerical order facilitates the understanding and execution of chord shapes. Chord diagrams often use the string numbers to indicate which strings to play and where to place fingers, making it easier to learn and play chords accurately.
- Scales and Patterns: The numerical order provides a framework for visualizing and practicing scales and patterns on the fretboard. By following the sequence, guitarists can systematically move through different scale positions and arpeggios, enhancing their technical proficiency and musical vocabulary.
In summary, the numerical order of guitar strings (E-A-D-G-B-E) is an essential aspect of “numbers on guitar strings.” It aids in memorization, fretboard orientation, chord shapes, and scale patterns, providing a solid foundation for guitarists to learn, navigate, and express themselves on the instrument.
FAQs on “Numbers on Guitar Strings”
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the topic of numbers on guitar strings, providing clear and informative answers.
Question 1: What is the significance of the numbers on guitar strings?
The numbers on guitar strings indicate the string’s position, thickness, and corresponding note. They serve as a reference point for tuning, learning chords, and understanding musical concepts.
Question 2: How do the numbers assist in tuning a guitar?
Each string is assigned a number and a corresponding note (E, A, D, G, B, E). Using a tuner or reference pitches, guitarists adjust the string tension until the desired note is achieved.
Question 3: What role do the numbers play in learning chords?
Chord diagrams often utilize numbers to indicate which strings to play and where to place fingers. This numerical system simplifies learning and playing chords.
Question 4: How do the numbers help in understanding scales on the fretboard?
The numbers provide a visual reference for scales. By observing the numerical sequence, guitarists can visualize scale patterns and navigate the fretboard more efficiently.
Question 5: Do different string materials have varying numbering systems?
Yes, nylon and steel strings, commonly used on classical and acoustic/electric guitars respectively, may have different numbering systems. Understanding these variations is crucial for selecting the appropriate strings for your guitar.
Question 6: How are the numbers involved in alternate tunings?
Alternate tunings involve adjusting the standard string tuning to create unique sounds. The numbers serve as a guide for setting up these tunings and understanding the resulting note relationships.
Tips on “Numbers on Guitar Strings”
Numbers on guitar strings are more than just identifiers. Understanding their significance can greatly enhance your guitar playing journey. Here are some valuable tips to help you utilize the numbers effectively:
Tip 1: Memorize the String Order:
The numerical order (E-A-D-G-B-E) is crucial for memorizing string names and positions. Practice reciting the order to develop muscle memory and enhance your fretboard orientation.
Tip 2: Use Numbers for Accurate Tuning:
Numbers correspond to specific notes (E, A, D, G, B, E). Utilize a tuner or reference pitches to adjust the string tension until the desired note is achieved, ensuring accurate tuning.
Tip 3: Simplify Chord Learning:
Chord diagrams often use numbers to indicate which strings to play and where to place fingers. By understanding the numerical system, you can easily learn and execute various chords.
Tip 4: Visualize Scales with Numbers:
Numbers provide a visual reference for scales. Observe the numerical sequence to understand scale patterns and navigate the fretboard more efficiently, improving your scale playing.
Tip 5: Understand String Gauges:
Numbers also represent string thickness (gauge). Different gauges affect tone, tension, and playability. Choose strings that suit your playing style and desired sound by understanding the gauge system.
Tip 6: Explore Alternate Tunings:
Numbers guide you in setting up alternate tunings. Experiment with different tunings to create unique sounds and expand your sonic possibilities.
Tip 7: Learn String Material Differences:
Nylon and steel strings have varying numbering systems. Be aware of these differences to select the appropriate strings for your guitar type and playing needs.
Tip 8: Practice Regularly:
Regular practice is key to developing proficiency in utilizing numbers on guitar strings. Dedicate time to practicing tuning, chords, scales, and other techniques to enhance your overall guitar playing.
Remember, mastering the numbers on your guitar strings is not just about memorization, but about understanding their significance in various aspects of guitar playing. By incorporating these tips into your practice, you’ll gain a deeper comprehension of your instrument and unlock new levels of musical expression.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of “numbers on guitar strings,” we have uncovered their multifaceted significance in understanding, playing, and maintaining the guitar. From ide
ntifying strings and facilitating tuning to simplifying chord learning and visualizing scales, the numbers serve as a comprehensive system for navigating the instrument.
Embracing the role of numbers empowers guitarists to unlock their musical potential. By understanding string gauges, exploring alternate tunings, and recognizing string material differences, players can tailor their guitars to their unique playing styles and sonic preferences. The numbers on guitar strings are not mere labels but a gateway to a deeper comprehension of the instrument’s mechanics and musical possibilities.
As you continue your guitar journey, remember the importance of these numbers. They are not just identifiers but tools for unlocking your creativity and expanding your musical horizons. Embrace the numbers, delve into their significance, and let them guide you toward becoming a proficient and expressive guitarist.