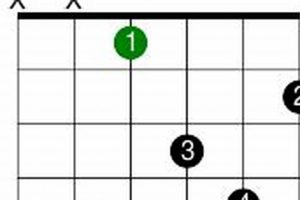
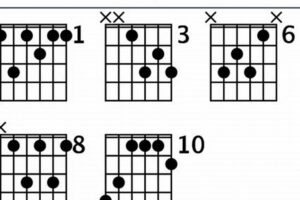
Explore the Enchanting World of Jewish Chords for Guitar
Editor’s Note:Jewish chords on the guitar captivate with their unique melodies and profound cultural significance. Dive into this comprehensive guide to unravel their beauty and explore why they hold a special place in the hearts of musicians and music enthusiasts alike.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve compiled this guide to empower you with the knowledge and techniques to master Jewish guitar chords. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting your musical journey, this article will provide valuable insights and inspire you to create enchanting melodies.
Key Differences: Jewish Chords vs. Traditional Chords
| Characteristic | Jewish Chords | Traditional Chords |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Rooted in Jewish musical traditions | Found in various musical genres worldwide |
| Scales | Often utilize the Phrygian dominant scale | Typically adhere to major or minor scales |
| Emotional Impact | Evoke a distinct sense of longing, joy, and spirituality | Convey a wide range of emotions, depending on the chord progression |
Main Article Topics:
- Historical Origins of Jewish Chords
- Essential Jewish Guitar Chord Shapes
- Techniques for Playing Jewish Chords
- Musical Applications of Jewish Chords
- Prominent Jewish Guitarists and Their Contributions
1. Phrygian Dominance
The Phrygian dominant scale is a distinctive musical scale that plays a pivotal role in the captivating sound of Jewish chords for guitar. Its unique intervallic structure, featuring a minor third, augmented second, and diminished fifth, creates a characteristically haunting and evocative atmosphere.
- Emotional Depth: The Phrygian dominant scale imparts a profound emotional depth to Jewish chords. Its minor third conveys a sense of longing and melancholy, while the augmented second and diminished fifth add an air of mystery and intrigue.
- Cultural Connection: The Phrygian dominant scale has deep roots in Jewish musical traditions, particularly in Eastern European and Middle Eastern melodies. Its use in Jewish chords for guitar connects these contemporary expressions to centuries-old musical lineages.
- Improvisational Freedom: The Phrygian dominant scale provides a fertile ground for improvisation. Guitarists can explore its unique intervals and melodic patterns to create expressive and soulful solos and embellishments.
- Genre-Bending Potential: While strongly associated with Jewish music, the Phrygian dominant scale has also found its way into other musical genres, including jazz, rock, and heavy metal. Its distinctive sound adds a touch of exoticism and intrigue to contemporary musical landscapes.
In conclusion, the Phrygian dominant scale is an essential component of Jewish chords for guitar, contributing to their haunting melodies, deep emotional resonance, and cultural significance. Its unique intervals and improvisational possibilities make it a versatile and expressive tool for guitarists, enabling them to create captivating and emotionally evocative music.
2. Modal Harmony
Modal harmony, a cornerstone of Jewish chords for guitar, plays a pivotal role in shaping their distinctive sound and emotional impact. Unlike traditional major and minor chords, modal harmony utilizes scales that emphasize certain intervals, creating a sense of spaciousness and spirituality.
The Phrygian dominant scale, prevalent in Jewish music, is a prime example of a modal scale. Its unique intervallic structure, featuring a minor third, augmented second, and diminished fifth, imparts a haunting and evocative quality to Jewish chords. This scale encourages guitarists to explore unconventional chord voicings and progressions, resulting in rich and resonant harmonies.
Modal harmony in Jewish chords for guitar extends beyond the Phrygian dominant scale. The use of the Dorian, Mixolydian, and other modal scales adds further depth and variety to the musical landscape. These scales evoke a range of emotions, from the contemplative and serene to the joyous and celebratory.
The practical significance of understanding modal harmony in Jewish chords for guitar is immense. It empowers guitarists to:
- Create unique and expressive chord progressions
- Improvise over Jewish melodies with greater fluency
- Compose original music that draws upon the rich traditions of Jewish music
In conclusion, modal harmony is an indispensable aspect of Jewish chords for guitar, contributing to their distinctive sound, emotional depth, and cultural significance. By embracing modal harmony, guitarists can unlock new possibilities for musical expression and connect with the ancient traditions of Jewish music.
| Characteristic | Effect on Jewish Chords for Guitar |
|---|---|
| Emphasized Intervals | Creates a sense of spaciousness and spirituality |
| Phrygian Dominant Scale | Imparts a haunting and evocative quality |
| Unconventional Voicings and Progressions | Encourages exploration and innovation |
| Emotional Depth | Evokes a range of emotions, from contemplation to joy |
3. Ornamentation
Ornamentation is an intrinsic part of Jewish chords for guitar, adding an expressive layer that enhances their emotional impact and cultural significance. Embellishments such as grace notes and trills are delicately interwoven into the melodic fabric, creating a unique and captivating sound.
Grace notes, played just before the main note, add a subtle grace and fluidity to the melody. They create a sense of anticipation and movement, enhancing the emotional depth of the chords. Trills, on the other hand, involve rapidly alternating between two adjacent notes, adding a vibrant and energetic quality to the music.
The use of ornamentation in Jewish chords for guitar draws upon centuries-old musical traditions. These embellishments were often employed by Jewish musicians to convey a range of emotions, from joy and celebration to sorrow and longing. The Phrygian dominant scale, commonly used in Jewish music, lends itself particularly well to ornamentation, as its unique intervals and melod
ic patterns provide ample space for expressive embellishments.
Practically, understanding ornamentation in Jewish chords for guitar allows musicians to:
- Add depth and nuance to their playing
- Connect with the cultural heritage of Jewish music
- Create unique and personal interpretations of Jewish melodies
In conclusion, ornamentation is an indispensable aspect of Jewish chords for guitar, contributing to their expressive power and emotional resonance. By embracing ornamentation, guitarists can unlock the full potential of these chords and create music that is both technically impressive and deeply moving.
| Characteristic | Effect on Jewish Chords for Guitar |
|---|---|
| Grace Notes | Add grace and fluidity, enhance emotional depth |
| Trills | Add vibrancy and energy, create a sense of movement |
| Cultural Heritage | Connects to centuries-old musical traditions |
| Expressive Power | Allows musicians to convey a range of emotions |
4. Rhythmic Patterns
The rhythmic patterns employed in Jewish chords for guitar play a significant role in shaping their unique and captivating sound. Syncopated rhythms, characterized by the placement of accents on unexpected beats, are a defining feature of Jewish music, contributing to its infectious energy and sense of movement.
- Offbeat Accents: Jewish chords often feature accents on offbeats, creating a sense of syncopation and rhythmic drive. These offbeat accents add rhythmic interest and propel the music forward, giving it a lively and engaging quality.
- Cross-String Picking: Cross-string picking patterns are commonly used in Jewish guitar playing. This technique involves picking strings in a non-sequential order, creating a syncopated effect that enhances the rhythmic complexity of the chords.
- Percussive Elements: Jewish guitarists often incorporate percussive elements into their playing, such as tapping on the body of the guitar or using their fingernails to create a rhythmic accompaniment. These percussive elements add an additional layer of syncopation and create a unique and captivating soundscape.
- Improvisational Freedom: Syncopated rhythms provide a fertile ground for improvisation. Jewish guitarists often use syncopation as a starting point for exploring new rhythmic ideas and creating spontaneous and expressive solos.
In conclusion, the rhythmic patterns employed in Jewish chords for guitar are an integral part of their distinctive sound and cultural significance. Syncopated rhythms create a sense of movement and vitality, adding rhythmic interest and complexity to the music. Understanding and incorporating these rhythmic patterns into one’s playing is essential for capturing the authentic and captivating essence of Jewish chords for guitar.
5. Cultural Heritage
The profound connection between Jewish chords and Jewish culture and history is a testament to the enduring power of music as a cultural and spiritual force. This connection manifests itself in various facets that illuminate the unique significance of Jewish chords for guitar.
- Roots in Jewish Liturgy and Folklore: Jewish chords have their roots in the musical traditions of Jewish liturgy and folklore. From the haunting melodies of synagogue prayers to the lively rhythms of klezmer dance tunes, Jewish chords carry the echoes of centuries-old musical practices.
- Expression of Jewish Identity: Jewish chords have played a vital role in expressing Jewish identity and cultural continuity. Through music, Jewish communities have preserved their heritage, celebrated their traditions, and connected with their shared experiences.
- Cultural Exchange and Influence: Jewish chords have been influenced by and have influenced other musical cultures, reflecting the rich tapestry of cultural exchange throughout history. The Phrygian dominant scale, prevalent in Jewish music, has found its way into various musical genres, from flamenco to jazz.
- Contemporary Relevance: Jewish chords continue to be a vibrant and evolving part of contemporary Jewish music. Jewish guitarists are pushing the boundaries of traditional styles, incorporating elements from other genres, and creating new and innovative expressions of Jewish musical heritage.
In conclusion, the cultural heritage embedded in Jewish chords for guitar serves as a testament to the enduring power of music to connect people, preserve traditions, and inspire creativity. By understanding and appreciating this deep connection, guitarists can not only enhance their technical skills but also gain a profound appreciation for the cultural and historical significance of Jewish music.
6. Emotional Expression
The emotive power of Jewish chords for guitar lies in their ability to evoke a profound range of emotions, from the depths of longing and sorrow to the heights of joy and celebration. This emotional expressiveness is deeply rooted in the cultural and historical context of Jewish music, where music has served as a vessel for expressing the joys, sorrows, and spiritual aspirations of the Jewish people.
One key element that contributes to the emotional impact of Jewish chords is the use of the Phrygian dominant scale. This scale, with its characteristic minor third and augmented second intervals, creates a sense of longing and melancholy that is often associated with Jewish music. Additionally, the use of modal harmony, with its emphasis on certain scale degrees, further enhances the emotional depth of Jewish chords.
The emotional expressiveness of Jewish chords for guitar has practical significance for musicians and listeners alike. For musicians, understanding the emotional potential of these chords allows them to convey a wide range of emotions in their playing, creating music that is both technically proficient and deeply moving. For listeners, the emotional resonance of Jewish chords can provide a powerful and cathartic experience, allowing them to connect with the music on a profound level.
In conclusion, the emotional expressiveness of Jewish chords for guitar is a testament to the enduring power of music to convey the human experience. By understanding and harnessing the emotional potential of these chords, guitarists can create music that touches the hearts and souls of their listeners.
| Characteristic | Emotional Impact |
|---|---|
| Phrygian Dominant Scale | Longing, melancholy |
| Modal Harmony | Emotional depth, resonance |
| Cultural Context | Expression of joys, sorrows, spiritual aspirations |
7. Improvisation
Improvisation plays a vital role in the captivating world of “jewish chords guitar,” allowing guitarists to express their creativity and showcase their technical prowess. Jewish guitarists have a rich tradition of improvising over chord progressions, drawing upon the expressive potential of Jewish chords and their deep understanding of musical structure.
The ability to improvise effectively requires a thorough grasp of the underlying chord progressions and the scales and melodic patterns that complement them. Jewish guitarists often utilize the Phrygian dominant scale, a distinctive scale that lends a haunting and evocative quality to their improvisations. Additionally, they employ various rhythmic patterns and techniques, such as syncopated rhythms and cross-string picking, to create a dynamic and engaging musical experience.
Improvisation serves several important functions in “jewish chords guitar”:
- Personal Expression: Improvisation allows guitarists to express their unique musical ideas and emotions, creating spontaneous and unrepeatable performances.
- Deepening Musical Understanding: Through improvisation, guitarists develop a deeper understanding of the relationships between chords, scales, and rhythmic patterns, enhancing their overall musicianship.
- Audience Engagement: Improvised solos and embellishments captivate audiences, creating a sense of excitement and unpredictability.
In conclusion, improvisation is an integral aspect of “jewish chords guitar,” showcasing the creativity, technical skill, and deep musical understanding of Jewish guitarists. By embracing improvisation, guitarists not only enhance their performances but also contribute to the vibrant and evolving tapestry of Jewish music.
| Characteristic | Significance |
|---|---|
| Expressive Potential | Allows guitarists to convey their creativity and emotions |
| Musical Understanding | Deepens guitarists’ understanding of musical structure and relationships |
| Audience Engagement | Captivates audiences and creates a sense of excitement |
8. Communal Music
In the realm of “jewish chords guitar,” the communal aspect of music holds immense significance, fostering a sense of togetherness and shared experience that transcends individual performances.
- Shared Cultural Heritage: Jewish chords are deeply rooted in Jewish history and traditions, serving as a common musical language that connects people across generations and backgrounds. When played in communal settings, these chords evoke a shared sense of cultural identity and belonging.
- Collective Expression: Communal music provides a platform for collective expression, allowing individuals to contribute their voices and instruments to create a rich and vibrant musical tapestry. This shared experience fosters a sense of unity and strengthens the bonds within the community.
- Emotional Connection: Music has a powerful ability to evoke emotions and create a sense of connection. When Jewish chords are played in communal settings, they can elicit feelings of joy, nostalgia, and spiritual uplift, uniting individuals through shared emotional experiences.
- Educational Value: Communal music serves as an educational tool, allowing participants to learn from each other and pass on musical traditions to younger generations. Through shared playing and listening, individuals can deepen their understanding of Jewish music and its cultural significance.
The communal aspect of “jewish chords guitar” extends beyond formal performances, permeating various social and religious gatherings. From joyous wedding celebrations to contemplative Shabbat services, Jewish chords provide a soundtrack that weaves together the fabric of community life.
9. Contemporary Adaptations
In the realm of “jewish chords guitar,” contemporary adaptations play a vital role, showcasing the versatility and enduring appeal of Jewish chords beyond their traditional confines.
- Fusion with Other Genres: Jewish chords have seamlessly blended with contemporary musical genres such as jazz, rock, and pop, creating captivating and innovative sounds. Guitarists are experimenting with fusion, incorporating Jewish chord progressions and melodic elements into their compositions, resulting in a fresh and dynamic musical landscape.
- Cross-Cultural Exchange: The adaptation of Jewish chords into contemporary genres has fostered cross-cultural exchange, introducing Jewish musical traditions to a wider audience. Through collaborations and shared musical experiences, Jewish guitarists are contributing to a global tapestry of musical expression, breaking down barriers and promoting understanding.
- Preservation and Evolution: Contemporary adaptations serve as a means of preserving and evolving Jewish musical heritage. By incorporating Jewish chords into modern contexts, guitarists ensure that these traditions remain relevant and accessible to new generations. Adaptation allows Jewish music to evolve and flourish, while retaining its essence and emotional depth.
- Global Recognition: The incorporation of Jewish chords into contemporary genres has garnered global recognition for Jewish guitarists and their unique musical contributions. Through their innovative and expressive playing, they are showcasing the beauty and versatility of Jewish music on a worldwide stage, earning critical acclaim and inspiring other musicians.
In conclusion, contemporary adaptations of Jewish chords for guitar are a testament to the enduring power and adaptability of Jewish music. By embracing fusion, cross-cultural exchange, preservation, and evolution, Jewish guitarists are pushing the boundaries of traditional genres and captivating audiences worldwide.
10. Cultural Exchange
Jewish chords for guitar are deeply rooted in Jewish musical traditions, yet they have also been influenced by and have influenced other musical genres and cultures. This cultural exchange has resulted in a vibrant and diverse soundscape that reflects the rich tapestry of Jewish history and its interactions with other cultures.
- Influence on Western Classical Music: Jewish musicians have made significant contributions to Western classical music, particularly in the Romantic and early 20th-century periods. Composers such as Gustav Mahler, Leonard Bernstein, and Arnold Schoenberg incorporated Jewish musical elements, including chords and melodies, into their compositions, enriching the Western classical repertoire.
- Connection to Flamenco: Jewish and flamenco music share common historical and geographical roots in Spain. This shared heritage is reflected in the use of similar melodic and rhythmic patterns, as well as the use of the Phrygian dominant scale, which is prevalent in both traditions.
- Inspiration for Jazz
and Popular Music: Jewish musicians have played a pivotal role in the development of jazz and popular music. Jazz guitarists such as Django Reinhardt and Wes Montgomery incorporated Jewish musical elements into their playing, influencing the sound and style of jazz guitar. Additionally, Jewish songwriters and composers have contributed numerous popular songs to the American songbook, many of which feature Jewish musical influences. - Global Influences: In recent decades, Jewish guitarists have drawn inspiration from a wide range of global musical traditions, including Indian, Arabic, and African music. This cross-cultural pollination has resulted in a new generation of Jewish guitarists who are creating innovative and eclectic music that defies traditional boundaries.
The cultural exchange that has shaped Jewish chords for guitar is a testament to the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of music. Jewish musicians have not only preserved and celebrated their own musical heritage but have also embraced and incorporated influences from other cultures, creating a rich and diverse musical tapestry that continues to inspire and captivate audiences worldwide.
FAQs on Jewish Chords for Guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Jewish chords for guitar, providing informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the defining characteristics of Jewish chords for guitar?
Jewish chords for guitar are characterized by their unique sound and emotional depth, often utilizing the Phrygian dominant scale and employing modal harmony. They frequently incorporate embellishments such as grace notes and trills, and their rhythmic patterns often feature syncopation, creating a sense of movement and vitality.
Question 2: What is the significance of the Phrygian dominant scale in Jewish music?
The Phrygian dominant scale plays a pivotal role in Jewish music, particularly in guitar playing. Its characteristic intervals, including a minor third, augmented second, and diminished fifth, impart a haunting and evocative quality to Jewish chords. This scale encourages exploration of unconventional chord voicings and progressions, resulting in rich and resonant harmonies.
Question 3: How does ornamentation contribute to Jewish chords for guitar?
Ornamentation is an essential aspect of Jewish chords for guitar, adding an expressive layer that enhances their emotional impact. Grace notes and trills are commonly used to embellish melodies, creating a sense of grace, fluidity, and rhythmic interest. These embellishments draw upon centuries-old musical traditions and allow guitarists to convey a range of emotions, from joy and celebration to sorrow and longing.
Question 4: What is the role of rhythmic patterns in Jewish chords for guitar?
Rhythmic patterns play a significant role in shaping the unique sound of Jewish chords for guitar. Syncopated rhythms, characterized by the placement of accents on unexpected beats, create a sense of movement and vitality. Cross-string picking patterns and percussive elements are also commonly employed, adding rhythmic complexity and interest to the music. Understanding and incorporating these rhythmic patterns is crucial for capturing the authentic feel and energy of Jewish chords for guitar.
Question 5: How have Jewish chords for guitar been influenced by other musical traditions?
Jewish chords for guitar have been influenced by and have influenced other musical traditions throughout history. The Phrygian dominant scale, prevalent in Jewish music, has found its way into various musical genres, including flamenco and jazz. Jewish musicians have also drawn inspiration from global musical traditions, such as Indian, Arabic, and African music, resulting in a diverse and eclectic soundscape that reflects the rich tapestry of cultural exchange.
Question 6: What are the benefits of learning Jewish chords for guitar?
Learning Jewish chords for guitar offers numerous benefits for musicians. It expands their musical knowledge and vocabulary, allowing them to explore new and expressive sounds. Understanding the cultural and historical context of these chords deepens their appreciation for the richness of Jewish musical traditions. Additionally, incorporating Jewish chords into their playing enhances their technical skills, rhythmic dexterity, and ability to convey a wide range of emotions through music.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of the essential aspects and significance of Jewish chords for guitar. Embracing these unique and captivating chords empowers guitarists to create music that is both technically proficient and deeply expressive, connecting with the rich cultural heritage and emotional depth of Jewish musical traditions.
Transition to the next article section:
To further enhance your understanding and playing of Jewish chords for guitar, explore additional resources and delve into the fascinating world of Jewish music. Whether you are a seasoned guitarist or just beginning your musical journey, the beauty and expressiveness of Jewish chords await your discovery.
Tips for Mastering Jewish Chords for Guitar
Embarking on the journey of mastering Jewish chords for guitar requires dedication, practice, and a deep appreciation for the cultural and musical nuances they embody. Here are five essential tips to guide your exploration:
Tip 1: Immerse Yourself in Jewish Music
Immerse yourself in the rich tapestry of Jewish music to develop a profound understanding of its melodies, rhythms, and harmonic progressions. Attend concerts, listen to recordings, and engage with Jewish musical communities to absorb the essence and feel of this unique musical tradition.
Tip 2: Study the Phrygian Dominant Scale
The Phrygian dominant scale is a cornerstone of Jewish music, particularly in guitar playing. Dedicate time to studying its intervals, melodic patterns, and ways to incorporate it into chord voicings. Experiment with different fingerings and explore how this scale can evoke haunting and evocative melodies.
Tip 3: Practice Ornamented Playing
Ornamentation is an integral part of Jewish chords for guitar, adding layers of expression and nuance. Practice grace notes, trills, and other embellishments to enhance the emotional depth of your playing. Focus on incorporating these ornaments tastefully and with precision.
Tip 4: Develop Rhythmic Proficiency
Jewish music is characterized by its infectious rhythms, often featuring syncopation and cross-string picking patterns. Dedicate time to developing your rhythmic dexterity by practicing these patterns and exploring different ways to create rhythmic drive and momentum.
Tip 5: Explore Jewish Musical Heritage
Jewish chords for guitar are deeply rooted in Jewish culture and history. Take the time to explore the diverse musical traditions of Jewish communities around the world. Learn about the origins of different chords, their cultural significance, and how they have evolved over time.
By embracing these tips and dedicating yourself to the practice and study of Jewish chords for guitar, you will embark on a rewarding musical journey that will enrich your understanding and playing abilities. Immerse yourself in the beauty and expressiveness of this unique musical tradition, and let the chords resonate with your soul.
Conclusion
Our exploration of “jewish chords guitar” has unveiled the captivating beauty and profound significance of these musical elements. Jewish chords, deeply rooted in Jewish musical traditions, possess a distinc
t sound and emotional depth that sets them apart from conventional chords.
Through the Phrygian dominant scale, modal harmony, ornamentation, and rhythmic patterns, Jewish chords for guitar evoke a wide range of emotions, from longing and sorrow to joy and celebration. They serve as a powerful means of cultural expression, fostering a sense of togetherness and shared experience within Jewish communities.
As we continue to embrace and explore Jewish chords for guitar, we not only enrich our musical knowledge but also connect with the rich tapestry of Jewish culture and history. These chords invite us on a journey of musical discovery, reminding us of the enduring power of music to express the human experience and transcend boundaries.