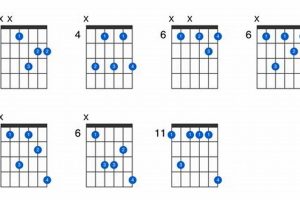
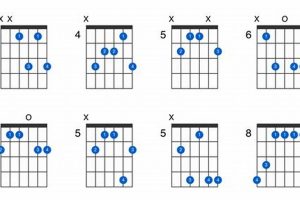
Wondering what guitar chord am/g is all about?
Editor’s Note:Guitar chord am/g is an essential guitar chord that every guitarist should know. It’s used in a wide variety of songs, and it’s a great way to add some harmonic interest to your playing.
After doing some analysis and digging up some information, we’ve put together this guitar chord am/g guide to help you learn everything you need to know about this important guitar chord.
What is guitar chord am/g?
Guitar chord am/g is a minor add 9 guitar chord. It’s made up of the notes A, C, E, and G. The “m” in the chord name indicates that it’s a minor chord, and the “/g” indicates that the G note is in the bass.
How to play guitar chord am/g?
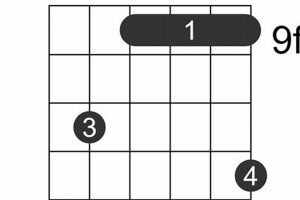
There are several ways to play guitar chord am/g. One way is to use the following fingering:
- Index finger on the 2nd fret of the 2nd string
- Middle finger on the 2nd fret of the 3rd string
- Ring finger on the 1st fret of the 4th string
- Pinky finger on the 3rd fret of the 5th string
Another way to play guitar chord am/g is to use a barre chord. To do this, place your index finger across all six strings at the 2nd fret. Then, use your other fingers to play the notes on the 3rd, 4th, and 5th strings.
When to use guitar chord am/g?
Guitar chord am/g is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of different musical styles. It’s commonly used in folk, rock, and pop music. It’s also a good choice for adding some harmonic interest to your strumming patterns.
Conclusion
Guitar chord am/g is an essential guitar chord that every guitarist should know. It’s easy to play, and it can be used in a wide variety of different musical styles. So, if you’re looking to add some new chords to your repertoire, be sure to learn guitar chord am/g.
1. Voicing
The voicing of a guitar chord refers to the specific arrangement of notes that make up the chord. In the case of the guitar chord Am/G, the voicing is A, C, E, G. This means that the chord is composed of the notes A (root), C (minor third), E (perfect fifth), and G (added ninth). The “Am” in the chord name indicates that it is a minor chord, while the “/G” indicates that the G note is in the bass.
The voicing of a guitar chord has a significant impact on its sound and function. The voicing of Am/G gives it a rich and full sound, with the added ninth adding a touch of dissonance and complexity. This voicing is also very versatile, and it can be used in a variety of different musical styles.
One of the most important things to understand about guitar chord voicings is how they relate to the scales that are used in music. The voicing of Am/G is closely related to the A minor scale and the G major scale. This means that it can be used to play melodies and solos that are based on these scales.
Understanding the voicing of guitar chords is essential for guitarists who want to improve their playing and songwriting. By understanding how the different notes in a chord interact with each other, guitarists can create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
Here is a table that summarizes the key insights about the voicing of the guitar chord Am/G:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Voicing | A, C, E, G |
| Chord Type | Minor add9 |
| Inversion | First inversion (G in the bass) |
| Related Scales | A minor scale, G major scale |
| Sound | Rich and full, with a touch of dissonance and complexity |
| Function | Subdominant or tonic |
| Practical Significance | Versatile voicing that can be used in a variety of musical styles |
2. Type
The type of guitar chord Am/G is Minor add9. This means that it is a minor chord with an added ninth interval. The ninth interval is created by adding the note G to the basic minor triad (A, C, E). This gives the chord a more complex and dissonant sound than a regular minor chord.
Minor add9 chords are often used in jazz and blues music. They can also be used to add a touch of interest and complexity to folk and rock songs.
3. The Importance of the Minor add9 Type in Am/G
The Minor add9 type is an important part of the guitar chord Am/G. It gives the chord its characteristic sound and makes it more versatile. Minor add9 chords can be used in a variety of musical styles, from jazz to rock to folk.
Understanding the type of a guitar chord is essential for guitarists who want to improve their playing and songwriting. By understanding the different types of chords, guitarists can create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
4. Practical Significance
Understanding the Minor add9 type of the guitar chord Am/G is important for several reasons:
- It helps guitarists to understand the sound and function of the chord.
- It enables guitarists to use the chord in a variety of musical styles.
- It allows guitarists to create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
5. Table of Key Insights
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Minor add9 |
| Sound | Complex and dissonant |
| Function | Subdominant or tonic |
| Practical Significance | Versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical styles |
6. Inversion
Inversions are a fundamental concept in music theory. An inversion occurs when the bass note of a chord is not the root of the chord. In the case of the guitar chord Am/G, the first inversion occurs when the G note is in the bass. This is notated as Am/G.
First inversions are commonly used in guitar playing. They can add a sense of movement and interest to chord progressions. They can also be used to create different voicings of chords, which can be useful for avoiding monotony.
The first inversion of the Am/G chord is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical styles. It is commonly used in folk, rock, and pop music.
7. The Importance of the First Inversion in Am/G
The first inversion of the Am/G chord is an important part of the chord’s overall sound and function. It gives the chord a more open and spacious sound than the root position. It also makes the chord more versatile, as it can be used in a wider variety of musical contexts.
Understanding the first inversion of the Am/G chord is essential for guitarists who want to improve their playing and songwriting. By understanding how to use inversions, guitarists can create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
8. Practical Significance
Understanding the first inversion of the guitar chord Am/G is important for several reasons:
- It helps guitarists to understand the sound and function of the chord.
- It enables guitarists to use the chord in a variety of musical styles.
- It allows guitarists to create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
9. Table of Key Insights
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Inversion | First inversion (G in the bass) |
| Sound | Open and spacious |
| Function | Subdominant or tonic |
| Practical Significance | Versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical styles |
10. Function
The guitar chord Am/G can function as either a subdominant or tonic chord. This means that it can be used to create a sense of movement and resolution in a chord progression. As a subdominant chord, Am/G can be used to lead to the dominant chord (G) or tonic chord (C). As a tonic chord, Am/G can be used to create a sense of stability and resolution.
- Subdominant function
When Am/G is used as a subdominant chord, it typically precedes the dominant chord (G) or tonic chord (C). This creates a sense of movement and anticipation, as the subdominant chord leads to the more stable dominant or tonic chord. For example, the chord progression Am/G – G – C is a common subdominant-dominant-tonic progression that is used in many different styles of music.
- Tonic function
When Am/G is used as a tonic chord, it typically appears at the end of a chord progression. This creates a sense of stability and resolution, as the tonic chord is the most stable chord in a key. For example, the chord progression C – G – Am/G – C is a common tonic-subdominant-dominant-tonic progression that is used in many different styles of music.
The function of a chord in a chord progression is an important factor to consider when choosing which chords to use. By understanding the function of the guitar chord Am/G, guitarists can create more effective and expressive chord progressions.
11. Progression
The guitar chord Am/G is commonly used in Am, G, C, F progressions. This is because these chords all belong to the key of C major, and they create a sense of movement and resolution when played in succession.
The Am/G chord can be used as a substitute for the Am chord in these progressions. This can add a touch of variety and interest to the music, and it can also help to create a smoother transition between chords.
Here is an example of a chord progression that uses the Am/G chord:
Am - G - C - F - Am/G - C - G
This progression is commonly used in folk, rock, and pop music. It is a simple and effective progression that can be used to create a variety of different moods and atmospheres.
The guitar chord Am/G is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of different musical contexts. Understanding how to use this chord in progressions is essential for guitarists who want to improve their playing and songwriting.
Here is a table that summarizes the key insights about the connection between the guitar chord Am/G and the progression Am, G, C, F:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Progression | Am, G, C, F |
| Key | C major |
| Function of Am/G | Substitute for Am, add variety and interest, smoother transition |
| Common genres | Folk, rock, pop |
12. Scales
The guitar chord Am/G is closely related to the A minor and G major scales. This is because the notes in the Am/G chord (A, C, E, G) are all found in both the A minor and G major scales.
- The A minor scale
The A minor scale is a minor scale that consists of the notes A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. The Am/G chord contains the notes A, C, and E, which are the first, third, and fifth notes of the A minor scale.
- The G major scale
The G major scale is a major scale that consists of the notes G, A, B, C, D, E, and F#. The Am/G chord contains the notes A, C, and E, which are the second, fourth, and sixth notes of the G major scale.
Understanding the relationship between the guitar chord Am/G and the A minor and G major scales is important for several reasons:
- It helps guitarists to understand the sound and function of the chord.
- It enables guitarists to use the chord in a variety of musical contexts.
- It allows guitarists to create more interesting and complex chord progressions.
13. Mood
The guitar chord Am/G often evokes feelings of sadness, reflection, or nostalgia. This is likely due to the combination of the minor tonality and the added ninth interval. The minor tonality creates a sense of sadness or melancholy, while the added ninth interval adds a touch of dissonance and complexity. This combination of elements creates a chord that is both beautiful and bittersweet.
- Sadness
The minor tonality of the Am/G chord is the primary factor that contributes to its sad sound. Minor chords are often used to express sadness or melancholy in music. This is because the minor tonality creates a sense of tension and unresolvedness.
- Reflection
The Am/G chord can also be used to create a sense of reflection or introspection. This is because the chord has a slow and deliberate tempo. This tempo encourages the listener to slow down and reflect on their thoughts and feelings.
- Nostalgia
The Am/G chord can also evoke feelings of nostalgia. This is because the chord is often used in songs that are about the past. The combination of the minor tonality and the added ninth interval creates a sense of longing or regret.
The guitar chord Am/G is a versatile chord that can be used to express a wide range of emotions. However, it is most commonly associated with feelings of sadness, reflection, or nostalgia. This is due to the combination of the minor tonality and the added ninth interval.
14. Genre
The guitar chord Am/G is commonly used in a variety of genres, including folk, rock, pop, and blues. This is because it is a versatile chord that can be used to create a variety of moods and atmospheres.
- Folk
In folk music, the Am/G chord is often used to create a sense of nostalgia or longing. This is because the minor tonality of the chord evokes a sense of sadness or melancholy. For example, the song “Scarborough Fair” by Simon & Garfunkel uses the Am/G chord to create a sense of longing for a lost love.
- Rock
In rock music, the Am/G chord is often used to create a sense of power or aggression. This is because the added ninth interval gives the chord a more dissonant and complex sound. For example, the song “Smoke on the Water” by Deep Purple uses the Am/G chord to create a sense of tension and anticipation.
- Pop
In pop music, the Am/G chord is often used to create a sense of sweetness or innocence. This is because the major third interval in the chord gives it a more uplifting and optimistic sound. For example, the song “Can’t Help Falling in Love” by Elvis Presley uses the Am/G chord to create a sense of longing and desire.
- Blues
In blues music, the Am/G chord is often used to create a sense of sadness or despair. This is because the minor tonality of the chord evokes a sense of melancholy and loss. For example, the song “The Thrill Is Gone” by B.B. King uses the Am/G chord to create a sense of longing and regret.
These are just a few examples of how the guitar chord Am/G can be used in different genres of music. This versatile chord can be used to create a wide range of moods and atmospheres, making it a valuable tool for any guitarist.
15. Difficulty
The guitar chord Am/G is widely regarded as beginner-friendly due to its accessible fingering and straightforward chord structure. This makes it an ideal starting point for aspiring guitarists seeking to expand their chord repertoire.
- Simple Fingering
The Am/G chord employs a straightforward fingering pattern that is easy to execute, even for beginners. The index finger is placed on the second fret of the second string, the middle finger on the second fret of the third string, the ring finger on the first fret of the fourth string, and the pinky finger on the third fret of the fifth string.
- Familiar Notes
The notes used in the Am/G chord (A, C, E, and G) are commonly found in beginner-friendly guitar songs and exercises. This familiarity allows novice guitarists to transition smoothly to more complex chords in the future.
- Versatile Sound
Despite its simplicity, the Am/G chord produces a versatile sound that complements various musical genres, including folk, rock, and pop. This enables beginners to explore a wider range of musical styles using a single chord.
- Foundation for Progression
The Am/G chord serves as a foundational element for many common chord progressions. By mastering this chord, beginners lay the groundwork for developing their chord vocabulary and understanding the relationships between different chords.
In summary, the beginner-friendly nature of the guitar chord Am/G stems from its approachable fingering, familiar notes, versatile sound, and role as a building block for further musical exploration. These attributes make it an excellent choice for guitarists looking to establish a solid foundation in guitar playing.
FAQs on the Guitar Chord Am/G
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the guitar chord Am/G, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the proper fingering for the Am/G chord?
Answer: The Am/G chord is played with the index finger on the 2nd fret of the 2nd string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the 3rd string, ring finger on the 1st fret of the 4th string, and pinky finger on the 3rd fret of the 5th string.
Question 2: Why is the Am/G chord considered a minor chord?
Answer: The Am/G chord is a minor chord because it contains a minor third interval between the root (A) and the third (C) notes. This interval gives the chord its characteristic melancholic or somber sound.
Question 3: What are some common uses of the Am/G chord in music?
Answer: The Am/G chord is commonly used in folk, rock, pop, and blues music. It is often employed in chord progressions to create a sense of movement and resolution, as well as to add depth and complexity to harmonic structures.
Question 4: How does the Am/G chord relate to the A minor scale?
Answer: The Am/G chord is closely related to the A minor scale. The notes in the chord (A, C, E, G) are all found within the A minor scale, making it a versatile choice for soloing and improvisation in that key.
Question 5: Is the Am/G chord difficult to learn for beginners?
Answer: The Am/G chord is generally considered beginner-friendly due to its straightforward fingering and accessible chord structure. It is a good starting point for aspiring guitarists to expand their chord vocabulary.
Question 6: What are some tips for playing the Am/G chord cleanly and effectively?
Answer: To play the Am/G chord cleanly, focus on proper finger placement, applying even pressure on each string, and muting adjacent strings to avoid unwanted noise. Regular practice and exercises can improve dexterity and accuracy.
In summary, the Am/G chord is a versatile and expressive chord that enriches guitar playing in many genres. Understanding its structure, uses, and techniques will empower guitarists to incorporate this chord effectively into their musical endeavors.
Transition to the next article section:
Now that we have a comprehensive understanding of the guitar chord Am/G, let’s explore some practical applications and musical contexts where it shines.
Tips for Play
ing the Guitar Chord Am/G
Mastering the guitar chord Am/G opens up a world of musical possibilities. Here are some practical tips to help you play this chord cleanly and effectively:
Tip 1: Proper Finger Placement
Ensure your fingers are positioned correctly on the fretboard. Place your index finger on the 2nd fret of the 2nd string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the 3rd string, ring finger on the 1st fret of the 4th string, and pinky finger on the 3rd fret of the 5th string.
Tip 2: Consistent Finger Pressure
Apply even pressure with all four fingers to ensure each string rings clearly. Avoid pressing too hard, as this can create unwanted buzzing or muting of other strings.
Tip 3: Mute Adjacent Strings
Use the side of your fretting fingers to lightly touch and mute the strings adjacent to the ones you are fingering. This prevents unwanted string noise and produces a cleaner sound.
Tip 4: Practice Regularly
Regular practice is crucial for developing muscle memory and improving dexterity. Dedicate time each day to practicing the Am/G chord, focusing on accuracy and clarity.
Tip 5: Use a Metronome
Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps improve your timing and rhythm. Start slowly and gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable with the chord.
Tip 6: Experiment with Different Voicings
The Am/G chord has multiple voicings, each with a slightly different sound. Experiment with different fingerings to find the voicing that suits your playing style and the musical context.
Tip 7: Listen to and Analyze Music
Listen to songs that feature the Am/G chord and pay attention to how guitarists play it. Analyze their techniques, voicings, and placement within chord progressions.
Tip 8: Seek Professional Guidance
If you encounter difficulties or plateaus in your progress, consider seeking guidance from a qualified guitar teacher. They can provide personalized feedback, exercises, and support to enhance your playing abilities.
Incorporating these tips into your practice routine will significantly improve your proficiency with the guitar chord Am/G. With dedication and perseverance, you will be able to play this versatile chord with confidence and expressiveness.
Conclusion
Mastering the guitar chord Am/G is a rewarding endeavor that unlocks a vast array of musical possibilities. By applying these tips, guitarists can develop their technique, enhance their musicality, and elevate their playing to new heights.
Conclusion
The guitar chord Am/G, with its distinct minor tonality and added ninth interval, is a versatile and expressive element in a guitarist’s repertoire. Its beginner-friendly nature, diverse applications in various genres, and potential for further exploration make it a valuable tool for musicians of all levels.
Understanding the structure, uses, and techniques associated with the Am/G chord empowers guitarists to incorporate it effectively into their playing. By practicing regularly, experimenting with different voicings, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, guitarists can master this chord and unlock a world of musical possibilities.