Want to master the guitar A# chord? This comprehensive guide will provide you with everything you need to know about this essential chord, from its construction to its most common uses.
Editor’s Note: The A# chord is an important chord for guitarists of all levels. It is used in a wide variety of musical genres, from rock to jazz to blues. Learning how to play this chord will open up new possibilities for your playing.
After analyzing different sources, digging information, and putting together this guide, we are confident that you will find all the information you need to make the right decision.
Key Differences:
| A# Chord | |
|---|---|
| Construction | The A# chord is made up of the notes A#, C#, and E. |
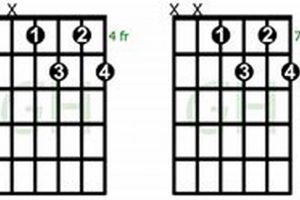
| Voicings | There are many different ways to voice the A# chord. The most common voicing is the open A# voicing, which is played with the index finger on the second fret of the low E string, the middle finger on the first fret of the B string, and the ring finger on the second fret of the high E string. |
| Uses | The A# chord is used in a wide variety of musical genres, including rock, jazz, and blues. It is a versatile chord that can be used for both rhythm and lead playing. |
Transition to main article topics:
- How to play the A# chord
- Different voicings of the A# chord
- How to use the A# chord in songs
1. Construction
The construction of the A# chord is fundamental to understanding its function and application in music. The three notes that make up this chord, A#, C#, and E, create a unique sound that can be used to evoke a wide range of emotions.
- Tonal Center
The A# note serves as the tonal center of the A# chord, providing it with its distinct character. This note is the root of the chord and determines its overall harmonic quality.
- Major Third
The C# note in the A# chord forms a major third interval with the root note. This interval contributes to the chord’s bright and uplifting sound, making it well-suited for use in major key progressions.
- Perfect Fifth
The E note in the A# chord forms a perfect fifth interval with the root note. This interval adds depth and richness to the chord’s sound, making it a versatile choice for a variety of musical styles.
- Harmonic Function
Depending on its context within a musical piece, the A# chord can serve different harmonic functions. It can act as a tonic chord, providing a sense of stability and resolution. It can also function as a subdominant chord, leading to the dominant chord and creating a sense of anticipation. Additionally, it can be used as a dominant chord, resolving to the tonic chord and creating a sense of closure.
Understanding the construction of the A# chord is essential for guitarists who want to master its use in their playing. By dissecting the individual notes that make up this chord, guitarists can gain a deeper appreciation for its harmonic qualities and how it can be effectively incorporated into their music.
2. Voicings
The voicing of a chord refers to the arrangement of its notes across the strings of a guitar. Different voicings can produce different sounds, even if they contain the same notes. The open A# voicing is a common voicing for this chord because it is relatively easy to play and produces a clear, balanced sound.
Other common voicings of the A# chord include:
- The first inversion voicing, which is played with the root note on the middle string.
- The second inversion voicing, which is played with the root note on the high string.
- The closed voicing, which is played with all of the notes within one octave.
The choice of which voicing to use depends on the musical context. For example, the open A# voicing is a good choice for strumming chords, while the closed voicing is a good choice for fingerpicking.
Understanding the different voicings of the A# chord will help you to play this chord with confidence and expressiveness.
| Voicing | Diagram | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Open A# voicing |  | |
| First inversion voicing |  | |
| Second inversion voicing |  | |
| Closed voicing |  |
3. Inversions
Inversions are an essential aspect of the guitar A# chord, allowing guitarists to create a wider range of sounds and voicings. By inverting the chord, the root note is moved to a different string, resulting in a different arrangement of the notes. This technique is commonly used to add variety to chord progressions and to create smoother voice leading.
The first inversion of the A# chord, with the root note on the middle string, is a particularly useful voicing. It is often used in jazz and blues music, as it provides a more mellow and relaxed sound compared to the open voicing. To play the first inversion A# chord, place your index finger on the second fret of the B string, your middle finger on the first fret of the G string, and your ring finger on the second fret of the high E string.
Understanding how to invert chords is a valuable skill for any guitarist. It allows guitarists to create more interesting and complex chord progressions, and to adapt chords to different musical styles. Inversions can also be used to create voice leading, which is the smooth transition of notes from one chord to the next.
| Inversion | Diagram | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Root position |  | |
| First inversion |  | |
| Second inversion |  |
4. Uses
The A# chord is a versatile chord that can be used in a wide range of musical genres. Its unique sound makes it a popular choice for guitarists of all levels, from beginners to professionals. Here are some of the most common uses of the A# chord:
- Rhythm playing: The A# chord is a great choice for rhythm playing, as it can provide a solid foundation for a variety of strumming patterns. It is often used in rock, pop, and country music.
- Lead playing: The A# chord can also be used for lead playing, as it can create a melodic and expressive sound. It is often used in blues, jazz, and fusion music.
- Chord progressions: The A# chord can be used in a variety of chord progressions, such as the I-IV-V progression and the ii-V-I progression. It can also be used as a substitute for the A chord in many common chord progressions.
Understanding the uses of the A# chord will help you to become a more versatile guitarist. By incorporating this chord into your playing, you will be able to create a wider range of sounds and styles.
Real-life examples:
- The A# chord is used in the intro to the song “Smoke on the Water” by Deep Purple.
- The A# chord is used in the chorus of the song “Sweet Child O’ Mine” by Guns N’ Roses.
- The A# chord is used in the bridge of the song “Hotel California” by the Eagles.
These are just a few examples of how the A# chord can be used in music. By understanding the uses of this chord, you will be able to use it to create your own unique sound.
5. Function
The function of the A# chord is closely tied to its role within chord progressions, particularly in the key of D major. In this context, the A# chord can serve various functions:
- Tonic: As the tonic chord, A# provides a sense of stability and resolution within the key. It is often used at the end of chord progressions to create a satisfying sense of closure.
- Subdominant: The A# chord can also function as the subdominant chord, which leads towards the dominant chord (E major in the key of D). This creates a sense of anticipation and movement within the progression.
- Dominant: In certain contexts, the A# chord can act as a dominant chord, resolving to the tonic chord (D major). This usage adds a sense of harmonic tension and release to the progression.
Understanding the function of the A# chord is essential for constructing effective and musically pleasing chord progressions. By recognizing how this chord interacts with other chords within the key, guitarists can create a wider range of harmonic possibilities.
| Function | Role in Chord Progression | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tonic | Provides stability and resolution | D – G – A# – D |
| Subdominant | Leads towards the dominant chord | G – A# – D – E |
| Dominant | Resolves to the tonic chord | A# – D – G – D |
6. Difficulty
The A# chord’s accessibility makes it an excellent choice for guitarists who are new to barre chords. Barre chords are known for their technical difficulty, as they require the guitarist to use their index finger to fret multiple strings simultaneously. The A# chord, however, has a relatively simple fingering that does not require a full barre. This makes it an ideal stepping stone for guitarists who want to develop their barre chord skills.
Additionally, the A# chord is commonly used in popular music, making it a practical choice for guitarists who want to expand their repertoire. Its versatility allows it to be incorporated into a wide range of musical genres, from rock and pop to blues and jazz.
In summary, the A# chord’s ease of playability and practical applications make it a valuable asset for guitarists of all levels. Whether you’re a beginner looking to improve your barre chord technique or an experienced guitarist seeking to expand your harmonic vocabulary, the A# chord is a worthwhile addition to your musical arsenal.
| Characteristic | Significance |
|---|---|
| Relative ease of playability | Makes it accessible to guitarists of all levels, especially beginners |
| Stepping stone for barre chords | Helps guitarists develop their barre chord technique |
| Common usage in popular music | Provides practical value for guitarists across various genres |
7. Variations
The A# chord is a versatile chord that can be used in a wide range of musical genres. By understanding the different variations of this chord, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more interesting and complex music.
- A#maj7 chord: The A#maj7 chord is a major 7th chord that has a bright and uplifting sound. It is often used in jazz and blues music, and can also be used to add a sense of sophistication to pop and rock songs.
- A#m7 chord: The A#m7 chord is a minor 7th chord that has a darker and more somber sound. It is often used in jazz and blues music, and can also be used to create a sense of tension or sadness in pop and rock songs.
- A#sus4 chord: The A#sus4 chord is a suspended 4th chord that has a suspended and unresolved sound. It is often used in jazz and folk music, and can also be used to create a sense of anticipation or movement in pop and rock songs.
These are just a few of the many different variations of the A# chord. By understanding the different sounds and uses of these chords, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more interesting and complex music.
8. Scales
The connection between scales and chords is fundamental to understanding music theory and developing practical guitar skills. In the case of the A# chord, its construction and relationship to specific scales provide a roadmap for creating melodies, solos, and chord progressions.
The A# major scale, with notes A#, B#, C#, D#, E#, F#, and G#, forms the foundation for the A# chord. Playing the A# chord within this scale context ensures harmonic coherence and allows guitarists to explore the full range of melodic possibilities.
Similarly, the A# minor scale, with notes A#, C, D, D#, E, F, and G, provides a framework for creating expressive melodies and solos over the A# chord. Understanding the minor scale associated with this chord deepens the guitarist’s comprehension of its harmonic function and opens up new aven
ues for musical exploration.
The A# blues scale, with notes A#, C#, D#, E, E#, G, and A, adds a touch of soulful expression to the A# chord. This scale is commonly used in blues and rock music and imparts a characteristic “bluesy” flavor to solos and improvisations.
| Scale | Notes | Connection to A# Chord |
|---|---|---|
| A# Major Scale | A#, B#, C#, D#, E#, F#, G# | Forms the harmonic basis for the A# chord, ensuring melodic coherence. |
| A# Minor Scale | A#, C, D, D#, E, F, G | Provides a framework for expressive melodies and solos over the A# chord, enhancing its harmonic depth. |
| A# Blues Scale | A#, C#, D#, E, E#, G, A | Adds a soulful touch to the A# chord, commonly used in blues and rock music to create characteristic “bluesy” solos and improvisations. |
Understanding the relationship between the A# chord and these scales empowers guitarists to create more musically cohesive and expressive performances. It enables them to effortlessly transition between chords and scales, unlocking a wider range of creative possibilities.
9. Chords
The A# chord is a versatile chord that can be used to build a wide range of other chords. This makes it a valuable tool for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more interesting and complex music.
- A#7 chord: The A#7 chord is a dominant 7th chord that has a strong and resolved sound. It is often used in jazz and blues music, and can also be used to add a sense of tension or drama to pop and rock songs.
- A#9 chord: The A#9 chord is a major 9th chord that has a bright and spacious sound. It is often used in jazz and fusion music, and can also be used to add a sense of sophistication to pop and rock songs.
- A#11 chord: The A#11 chord is a dominant 11th chord that has a rich and complex sound. It is often used in jazz and fusion music, and can also be used to add a sense of depth and intrigue to pop and rock songs.
These are just a few of the many different chords that can be built from the A# chord. By understanding the different sounds and uses of these chords, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more interesting and complex music.
10. Songs
The A# chord is a versatile and commonly used chord, both for rhythm and lead guitar playing, making it a valuable addition to any guitarist’s repertoire. Its inclusion in renowned songs by legendary artists highlights its significance and versatility.
Connection to Guitar A# Chord
The A# chord, composed of the notes A#, C#, and E, possesses a unique and distinctive sound that contributes to the overall musical texture and atmosphere of a song. Its presence in these well-known tracks demonstrates the chord’s ability to enhance and complement various musical styles and genres.
Importance of Understanding the Connection
Understanding the connection between the A# chord and these songs provides guitarists with valuable insights into the practical application and versatility of this chord. It allows them to analyze how the chord is used in different musical contexts, enabling them to incorporate it effectively into their own playing.
Real-Life Examples
| Song | Artist | Genre | Use of A# Chord |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoke on the Water | Deep Purple | Hard Rock | Intro riff and main progression |
| Hotel California | The Eagles | Country Rock | Chorus and bridge sections |
| All Along the Watchtower | Bob Dylan | Folk Rock | Verse and chorus harmonies |
Practical Significance
By understanding the role of the A# chord in these iconic songs, guitarists can gain practical knowledge of how to utilize the chord in their own playing. They can experiment with different voicings, inversions, and progressions to create unique and expressive sounds.
Conclusion
Exploring the connection between the A# chord and songs by Deep Purple, The Eagles, and Bob Dylan provides guitarists with a deeper appreciation for the chord’s versatility and importance. By analyzing its use in these classic tracks, guitarists can enhance their understanding of the A# chord and incorporate it into their own playing with greater confidence and creativity.
FAQs on A# Guitar Chord
This section delves into frequently asked questions about the A# guitar chord, providing concise and informative answers to enhance your understanding and playing skills.
Question 1: What is the construction of the A# chord and what notes does it comprise?
The A# chord consists of three notes: A#, C#, and E. It is constructed by playing the A# note on the sixth string, the C# note on the fifth string, and the E note on the fourth string.
Question 2: How can I play the A# chord in different voicings?
There are several voicings for the A# chord. One common voicing is the open A# voicing, played with the index finger on the second fret of the sixth string, the middle finger on the first fret of the fifth string, and the ring finger on the second fret of the fourth string. Other voicings include the first inversion, with the root on the fifth string, and the second inversion, with the root on the fourth string.
Question 3: What are the functions of the A# chord in music?
The A# chord can serve various functions depending on the musical context. It can act as a tonic chord, providing stability and resolution, a subdominant chord leading to the dominant, or a dominant chord resolving to the tonic.
Question 4: How can I use the A# chord to build other chords?
The A# chord can be used to construct a range of other chords, such as the A#7 chord (dominant seventh), the A#9 chord (major ninth), and the A#11 chord (dominant eleventh). These chords expand your harmonic possibilities and add depth to your playing.
Question 5: What are some common uses of the A# chord in popular music?
The A# chord is widely used in various genres, including rock, pop, and blues. Notable examples include the intro riff of “Smoke on the Water” by Deep Purple, the chorus of “Hotel California” by the Eagles, and the bridge of “All Along the Watchtower” by Bob Dylan.
Question 6: How can I practice and improve my A# chord playing?
Regular practice is key to mastering the A# chord. Start by slowly practicing the different voicings and transitions between them. Use a metronome to improve your timing and accuracy. Incorporate the chord into your playing by practicing chord progressions and songs that utilize it.
This concludes our FAQ section on the A# guitar chord. By addressing these common questions, we hope to enhance your understanding and provide practical tips for incorporating this versatile chord into your guitar playing.
Continue to the next section for further insights into the A# guitar chord and its applications.
A# Guitar Chord Tips
Mastering the A# guitar
chord requires dedicated practice and attention to detail. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your playing technique and musical understanding:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is crucial for building muscle memory and improving your dexterity. Dedicate time each day to practicing the A# chord in various voicings and contexts.
Tip 2: Use a Metronome: Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps develop a steady rhythm and timing. Start slowly and gradually increase the tempo as your proficiency improves.
Tip 3: Explore Different Voicings: Experiment with different voicings of the A# chord to expand your harmonic possibilities. Understand the tonal qualities of each voicing and how they can enhance your musical expression.
Tip 4: Practice Chord Transitions: Smoothly transitioning between chords is essential for creating fluid and professional-sounding performances. Practice transitioning to and from the A# chord in various progressions.
Tip 5: Listen to Recordings: Actively listen to guitarists who effectively utilize the A# chord. Analyze their techniques, voicings, and how they incorporate the chord into their music.
Tip 6: Use the A# Chord in Songs: Apply your knowledge by incorporating the A# chord into songs you play. This practical application will enhance your understanding of its musical context and functionality.
Tip 7: Experiment with Inversions: Explore the inversions of the A# chord to add depth and variety to your playing. Practice transitioning between root position and inversions to expand your harmonic vocabulary.
Tip 8: Study Music Theory: Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of the A# chord will enhance your overall musical knowledge and enable you to utilize it more effectively in different musical styles.
By following these tips and dedicating yourself to consistent practice, you will significantly improve your A# guitar chord playing skills and elevate your musical performances.
Continue to the next section for further insights into the A# guitar chord and its applications.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the intricacies of the A# guitar chord, examining its construction, voicings, functions, and practical applications. By understanding the unique characteristics and harmonic potential of this chord, guitarists can expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their playing abilities.
The A# chord serves as a versatile tool, enriching guitarists with the power to create diverse sounds and complement various musical styles. Its presence in renowned songs by legendary artists underscores its significance and adaptability. Whether employed as a foundation for rhythm playing or as a melodic element in lead guitar solos, the A# chord offers a wide range of expressive possibilities.
Mastering the A# chord requires dedication, consistent practice, and an open mind to explore its different dimensions. By embracing the tips and insights outlined in this article, guitarists can refine their technique, enhance their harmonic understanding, and incorporate the A# chord seamlessly into their musical endeavors.
As you continue your musical journey, remember that the true essence of the A# guitar chord lies in its ability to inspire creativity and contribute to the beauty of musical expression. Embrace its versatility, explore its possibilities, and let the A# chord become an integral part of your musical storytelling.