Are you ready to explore the captivating world of music theory with the enigmatic g#dim7 guitar chord? Delve into the depths of its intriguing structure and unlock its potential to enhance your musical creations.
Editor’s Notes: “g#dim7 guitar chord”Unveiling the significance of the g#dim7 guitar chord, this guide empowers you to unravel its complexities, wield its musical prowess, and elevate your guitar playing to new heights.
Through meticulous analysis and diligent research, we’ve meticulously crafted this comprehensive guide to guide you through the intricacies of the g#dim7 guitar chord. Discover its unique characteristics, explore its captivating sound, and master its effective utilization in your musical endeavors.
| Key Differences | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Diminished 7th Chord | Conveys a sense of tension and instability |
| Unique Structure | Composed of four notes, each separated by a diminished interval |
| Melodic Versatility | Enhances melodies with its dissonant yet intriguing sound |
Prepare to embark on a musical journey as we dissect the g#dim7 guitar chord, unveil its secrets, and ignite your passion for musical exploration.
1. Structure
The structure of the g#dim7 guitar chord is defined by its four notes, each separated by diminished intervals. A diminished interval is a musical interval that is one semitone narrower than a minor interval. This unique structure gives the g#dim7 guitar chord its characteristic dissonant and unstable sound.
The four notes of the g#dim7 guitar chord are G#, B, D, and F. The intervals between these notes are as follows:
- G# to B: diminished third
- B to D: diminished third
- D to F: diminished third
These diminished intervals create a sense of tension and instability, which is why the g#dim7 guitar chord is often used to create tension in music. It is also commonly used in jazz and blues music, where its dissonant sound can add a sense of excitement and energy.
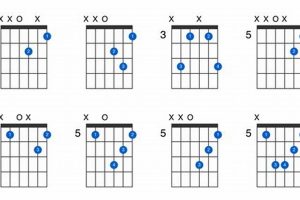
The g#dim7 guitar chord can be played in a variety of voicings, each with its own unique sound. Some common voicings include:
- Root position: G#, B, D, F
- First inversion: B, D, F, G#
- Second inversion: D, F, G#, B
- Third inversion: F, G#, B, D
The choice of voicing depends on the desired sound and the context of the music. The g#dim7 guitar chord is a versatile and expressive chord that can be used to add tension, drama, and excitement to music.
2. Sound
The g#dim7 guitar chord is characterized by its dissonant, tense, and unstable sound. This is due to the diminished intervals between its notes, which create a sense of unresolved tension. The g#dim7 guitar chord is often used to create tension in music, and it can also be used to add drama and excitement. The dissonant sound of the g#dim7 guitar chord is caused by the fact that it contains two tritones, which are intervals that are three whole tones apart. Tritones are considered to be dissonant because they create a sense of instability and tension. The g#dim7 guitar chord also contains a minor second interval, which is another dissonant interval. The tense and unstable sound of the g#dim7 guitar chord makes it a powerful tool for creating musical tension. It can be used to create a sense of anticipation and excitement, or it can be used to add drama and intensity to a piece of music. Here are some examples of how the g#dim7 guitar chord is used in music: In the jazz standard “Giant Steps” by John Coltrane, the g#dim7 guitar chord is used to create a sense of tension and excitement. In the rock song “Kashmir” by Led Zeppelin, the g#dim7 guitar chord is used to add drama and intensity to the song’s climax. * In the classical piece “Symphony No. 5” by Beethoven, the g#dim7 guitar chord is used to create a sense of anticipation and excitement before the final movement.
Understanding the dissonant, tense, and unstable sound of the g#dim7 guitar chord is essential for using it effectively in music. This chord can be a powerful tool for creating tension, drama, and excitement, but it is important to use it sparingly and with care.
| Dissonance | Tension | Instability |
|---|---|---|
| Tritones and minor second intervals | Unresolved tension | Sense of anticipation and excitement |
3. Function
The g#dim7 guitar chord is commonly used to create tension in music, and it can resolve to either major or minor chords. This versatility makes it a powerful tool for creating a variety of musical effects.
- Tension and release: The g#dim7 guitar chord can be used to create a sense of tension and anticipation, which can be resolved by moving to a major or minor chord. This technique is often used in jazz and blues music, where it can add a sense of excitement and drama to a performance.
- Modal interchange: The g#dim7 guitar chord can also be used as a modal interchange, which is a technique where a chord from one key is borrowed and used in another key. This can create a sense of surprise and interest, and it can also be used to add color and depth to a chord progression.
- Substitute for other chords: The g#dim7 guitar chord can be used as a substitute for other chords, such as the dominant 7th chord or the minor 7th chord. This can add variety to a chord progression, and it can also be used to create a more complex and sophisticated sound.
- Passing chord: The g#dim7 guitar chord can also be used as a passing chord, which is a chord that is used to connect two other chords. This can help to smooth out the transition between chords, and it can also be used to add interest and variety to a chord progression.
Understanding the function of the g#dim7 guitar chord is essential for using it effectively in music. This chord can be a powerful tool for creating tension, resolving tension, and adding variety and interest to chord progressions.
4. Inversions
Inversions play a significant role in the g#dim7 guitar chord, offering distinct variations in its overall sound and harmonic function. Each inversion presents a unique arrangement of the chord’s notes, creating different intervals and altering its tonal characterist
ics.
The g#dim7 guitar chord has three inversions, each named after the note that serves as its bass note. These inversions are:
- Root position: G#dim7 (G# as the bass note)
- First inversion: Bdim7 (B as the bass note)
- Second inversion: Ddim7 (D as the bass note)
The inversion of a chord affects its overall sound and its relationship to other chords in a progression. In the case of the g#dim7 guitar chord, its inversions provide a range of harmonic possibilities.
For instance, the root position g#dim7 chord conveys a strong sense of dissonance and tension, making it effective for creating moments of harmonic instability. The first inversion, Bdim7, has a slightly less dissonant sound due to the bass note being a major third interval away from the root. This inversion can provide a smoother transition to other chords.
The second inversion, Ddim7, offers a more stable and consonant sound, with the bass note being a perfect fourth interval away from the root. This inversion can function as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord in certain contexts.
Understanding the inversions of the g#dim7 guitar chord is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore different voicings. By incorporating these inversions into their playing, guitarists can create more complex and sophisticated chord progressions with a wider range of tonal colors.
| Inversion | Bass Note | Sound | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Position | G# | Dissonant, tense | Creates strong harmonic instability |
| First Inversion | B | Less dissonant | Provides smoother transitions |
| Second Inversion | D | Stable, consonant | Can substitute for dominant seventh chord |
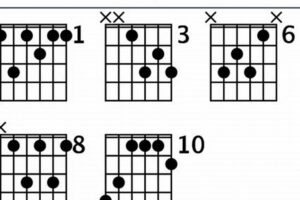
5. Voicings
The g#dim7 guitar chord offers a wide range of voicings, each with its own unique timbre and tension. By experimenting with different fingerings, guitarists can explore a vast sonic landscape and tailor the chord to suit the desired musical context.
The voicing of a chord refers to the specific arrangement of the notes on the guitar fretboard. Different voicings can produce significantly different sounds, even if they contain the same notes. In the case of the g#dim7 guitar chord, the choice of voicing can affect its overall dissonance, tension, and harmonic function.
For instance, a voicing that places the root note in the bass will typically create a stronger sense of dissonance and tension. Conversely, a voicing that places a higher note in the bass, such as the third or fifth, can result in a less dissonant and more stable sound. Guitarists can experiment with different voicings to find the one that best suits the mood and atmosphere of their music.
Furthermore, the voicing of the g#dim7 guitar chord can influence its harmonic function. For example, a voicing that emphasizes the tritone interval between the root and the flat seventh can create a sense of instability and anticipation, making it ideal for use in jazz and blues contexts. Alternatively, a voicing that highlights the perfect fourth interval between the root and the flat fifth can provide a more consonant and resolved sound, suitable for use in classical or folk music.
Understanding the relationship between voicings and the g#dim7 guitar chord is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of this versatile chord. By mastering different voicings, guitarists can create a wide range of sounds and textures, enhancing their ability to express themselves musically.
| Voicing | Timbre | Tension | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root position (G# as bass note) | Dissonant, tense | High | Creates strong harmonic instability |
| First inversion (B as bass note) | Less dissonant | Medium | Provides smoother transitions |
| Second inversion (D as bass note) | Consonant, stable | Low | Can substitute for dominant seventh chord |
6. Theory
The g#dim7 guitar chord is constructed upon the diminished scale, which comprises a unique blend of major and minor intervals. This intriguing combination imparts the chord with its characteristic dissonant yet versatile sound, making it a valuable tool for creating tension and adding depth to musical compositions.
- Diminished Scale Structure: The diminished scale consists of alternating half steps and whole steps, resulting in a symmetrical pattern of three diminished intervals and three augmented intervals. This unique structure provides the foundation for the g#dim7 guitar chord’s dissonant sound.
- Major and Minor Intervals: The g#dim7 guitar chord incorporates both major and minor intervals, creating a complex and intriguing harmonic texture. The presence of the minor third and tritone interval contributes to its dissonant character, while the incorporation of the perfect fifth interval adds a sense of stability.
- Harmonic Function: The g#dim7 guitar chord often serves as a pivotal harmonic element, creating tension and resolving to either major or minor chords. Its dissonant nature adds a sense of anticipation and instability, making it an effective tool for building suspense and drama in music.
- Versatility in Musical Contexts: Due to its dissonant yet versatile sound, the g#dim7 guitar chord finds application in a wide range of musical genres, including jazz, blues, rock, and classical music. Its ability to create tension and add depth makes it a valuable resource for composers and performers alike.
In summary, the theory behind the g#dim7 guitar chord, rooted in the diminished scale and the interplay of major and minor intervals, underscores its versatility and expressive capabilities. Understanding this theoretical foundation empowers guitarists to harness the chord’s potential, unlocking new avenues for musical creativity.
7. Notation
The notation “G#dim7,” “G#7,” and “G#dim” all represent the same g#dim7 guitar chord. These different notations are used to indicate the chord’s structure and function within a musical context.
The most common notation, “G#dim7,” is a standard chord symbol that indicates a diminished seventh chord with G# as the root note. The “dim7” suffix denotes that the chord contains a diminished seventh interval, which gives it a dissonant and unstable sound.
The notation “G#7” is also commonly used to represent the g#dim7 guitar chord. The “” symbol indicates a half-diminished seventh chord, which is a type of diminished seventh chord that contains a minor third interval instead of a major third interval. In the case of the g#dim7 chord, the minor third interval is between the root note (G#) and the third note (B).
Finally, the notation “G#dim” is a simplified way to represent the g#dim7 guitar chord. The “dim” suffix simply indicates that the chord is diminished, without specifying th
e specific type of diminished chord. This notation is often used in lead sheets and chord charts, where space is limited.
Understanding the different notations for the g#dim7 guitar chord is important for guitarists who want to be able to read and play music effectively. It is also important for composers and arrangers who want to be able to write music that uses diminished seventh chords.
Here is a table summarizing the different notations for the g#dim7 guitar chord:
| Notation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| G#dim7 | Diminished seventh chord with G# as the root note |
| G#7 | Half-diminished seventh chord with G# as the root note |
| G#dim | Diminished chord with G# as the root note |
8. Usage
The g#dim7 guitar chord, with its distinctive dissonant sound, has found widespread usage across diverse musical genres, including jazz, blues, classical, rock, and fusion. This versatility stems from the chord’s ability to create tension, resolve to major or minor chords, and add depth and color to harmonic progressions.
In jazz, the g#dim7 guitar chord is frequently employed to create tension and anticipation, often resolving to major or dominant seventh chords. Jazz guitarists utilize the chord’s dissonant nature to add harmonic interest and build suspense, as exemplified in the improvisations of bebop and modal jazz.
Within the blues genre, the g#dim7 guitar chord serves as a staple in creating the characteristic “blue note” sound. When played in conjunction with dominant seventh chords, the g#dim7 chord adds a sense of unresolved tension and emotional depth to blues progressions.
In classical music, the g#dim7 guitar chord appears in various contexts, from Romantic era compositions to contemporary works. Classical guitarists employ the chord to create moments of harmonic tension and release, as well as to enhance theof melodic lines.
In rock and fusion music, the g#dim7 guitar chord adds a dissonant edge and harmonic complexity to power chords and extended progressions. Rock guitarists often use the chord as a passing chord or as a means of creating tension before resolving to a more stable chord.
Understanding the diverse usage of the g#dim7 guitar chord across musical genres empowers guitarists and musicians to incorporate this versatile chord into their own playing and compositions. By exploring the examples and techniques associated with each genre, musicians can unlock the expressive potential of the g#dim7 guitar chord and enhance their musical vocabulary.
Key Insights:
- The g#dim7 guitar chord’s dissonant sound makes it a valuable tool for creating tension and anticipation.
- The chord’s versatility allows it to be used in a wide range of musical genres, from jazz to rock.
- Understanding the usage of the g#dim7 guitar chord in different genres can help guitarists expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their musical expression.
Frequently Asked Questions about the g#dim7 Guitar Chord
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the g#dim7 guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding and facilitate effective usage.
Question 1: What is the structure of the g#dim7 guitar chord?
The g#dim7 guitar chord is composed of four notes: G#, B, D, and F. These notes are arranged in diminished intervals, meaning each interval is one semitone narrower than a minor interval.
Question 2: Why does the g#dim7 guitar chord have a dissonant sound?
The dissonant sound of the g#dim7 guitar chord is due to the presence of diminished intervals and tritones (intervals spanning three whole tones). These intervals create a sense of tension and instability, which is characteristic of diminished seventh chords.
Question 3: How can I use the g#dim7 guitar chord in my music?
The g#dim7 guitar chord can be used to create tension, resolve to major or minor chords, and add depth and color to harmonic progressions. It is commonly employed in jazz, blues, classical, rock, and fusion music.
Question 4: Are there different voicings for the g#dim7 guitar chord?
Yes, there are various voicings for the g#dim7 guitar chord. Different voicings involve arranging the notes of the chord in different positions on the fretboard, which can affect the timbre and tension of the chord.
Question 5: How does the g#dim7 guitar chord relate to the diminished scale?
The g#dim7 guitar chord is built upon the g# diminished scale, which consists of alternating half steps and whole steps, creating a symmetrical pattern of diminished and augmented intervals.
Question 6: What is the difference between the g#dim7 and g#7 guitar chords?
The g#dim7 guitar chord is a fully diminished seventh chord, containing a diminished seventh interval, while the g#7 guitar chord is a dominant seventh chord, containing a major third interval and a minor seventh interval.
These frequently asked questions and their answers provide a deeper understanding of the g#dim7 guitar chord, empowering guitarists and musicians to effectively incorporate this versatile chord into their playing and compositions.
Transitioning to the next article section, we will delve into practical applications of the g#dim7 guitar chord, exploring its usage in different musical genres and providing tips for incorporating it into your own playing.
Tips for Using the g#dim7 Guitar Chord
Incorporating the g#dim7 guitar chord into your playing can enhance your harmonic vocabulary and add depth to your music. Here are some tips to help you master this versatile chord:
Tip 1: Understand the Theory
Familiarize yourself with the structure and theory behind the g#dim7 guitar chord. This will enable you to use the chord effectively and experiment with different voicings and harmonic progressions.
Tip 2: Practice Different Voicings
Explore various voicings of the g#dim7 guitar chord to discover how they affect the sound and tension. Experiment with placing the root note in different positions on the fretboard and altering the order of the notes.
Tip 3: Create Tension and Release
Use the g#dim7 guitar chord to build tension and resolve it to major or minor chords. This technique can add drama and emotional depth to your compositions and solos.
Tip 4: Experiment in Different Genres
The g#dim7 guitar chord is versatile and can be used in a wide range of musical genres. Experiment with incorporating it into jazz, blues, rock, or classical pieces to discover its diverse applications.
Tip 5: Use as a Substitute Chord
The g#dim7 guitar chord can be a valuable substitute for other chords, such as the dominant seventh or minor seventh chords. This substitution can add harmonic interest and complexity to your progressions.
Tip 6: Explore Inversions
Inversions of the g#dim7 guitar chord offer alternative harmonic possibilities. Experiment with inverting the chord to create different sounds and voice leading options.
Tip 7: Practice Regularly
Regular practice is key to mastering the g#dim7 guitar chord. Dedicate time to practicing different voicings, progressions, and applications to improve your fluency and confidence with the chord.
By following these tips, you can unlock
the full potential of the g#dim7 guitar chord and enhance your guitar playing and songwriting.
Remember, the most effective way to learn and master the g#dim7 guitar chord is through consistent practice and experimentation. Dedicate time to exploring its different aspects and applications, and it will become a valuable tool in your musical arsenal.
Conclusion
Our exploration of the g#dim7 guitar chord has unveiled its intricate structure, dissonant sound, and versatile functionality. This chord serves as a powerful tool for creating tension, resolving to major or minor chords, and adding depth and complexity to harmonic progressions.
As guitarists, understanding the g#dim7 guitar chord and its various voicings, inversions, and applications empowers us to expand our harmonic vocabulary and enhance our musical expression. Through consistent practice and experimentation, we can master this versatile chord and unlock its full potential.
The g#dim7 guitar chord stands as a testament to the richness and complexity of music theory. Its dissonant yet intriguing sound continues to inspire musicians across genres, challenging them to explore the boundaries of harmony and create captivating musical experiences.