When it comes to playing the guitar, understanding different guitar chords is essential. Among the various chords, the “gdim guitar chord” stands out as a unique and versatile option for guitarists.
Editor’s Note:The “gdim guitar chord” is a diminished chord that adds depth and complexity to musical compositions. Its distinctive sound makes it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to the “gdim guitar chord.” Our aim is to provide guitarists with a thorough understanding of this chord, its construction, and its effective use in various musical contexts.
Key Differences:
| Standard gdim Chord | gdim7 Chord | |
|---|---|---|
| Notes: | G, Bb, Db | G, Bb, Db, F |
| Intervals: | Root, minor third, diminished fifth | Root, minor third, diminished fifth, minor seventh |
| Sound: | Dissonant, tense | More dissonant, unstable |
Main Article Topics:
- Construction and Fingering of the gdim Guitar Chord
- The Harmonic Function of the gdim Chord
- Using the gdim Chord in Chord Progressions
- Tips for Incorporating the gdim Chord into Your Playing
1. Construction
The gdim guitar chord is constructed using the notes G, Bb, and Db. These notes form a diminished triad, which is a type of chord that has a dissonant, tense sound. The diminished quality of the chord comes from the diminished fifth interval between the root (G) and the third (Db). This interval is smaller than a perfect fifth, which gives the chord its characteristically unstable sound.
The gdim guitar chord is often used to create tension or drama in music. It can also be used as a passing chord to connect two other chords. Jazz and classical guitarists frequently use the gdim chord, and it can also be found in some rock and pop songs.
Understanding the construction of the gdim guitar chord is important for guitarists who want to use it effectively in their playing. By understanding the notes that make up the chord and the intervals between them, guitarists can better understand how the chord functions harmonically and how it can be used to create different moods and atmospheres in music.
Table: Construction and Function of the gdim Guitar Chord
| Note | Interval from Root | Function |
|---|---|---|
| G | Root | Provides stability |
| Bb | Minor Third | Adds tension and dissonance |
| Db | Diminished Fifth | Creates instability and leads to resolution |
2. Intervals
The gdim guitar chord is constructed using the notes G, Bb, and Db, which form intervals of root, minor third, and diminished fifth, respectively. These intervals play a crucial role in defining the unique sound and harmonic function of the gdim chord.
The root, or fundamental, of the gdim chord is G. The minor third, Bb, adds tension and dissonance to the chord. Finally, the diminished fifth, Db, creates instability and leads to a sense of resolution. The combination of these intervals results in the characteristically dissonant and unstable sound of the gdim chord.
Understanding the intervals that make up the gdim chord is essential for guitarists who want to use it effectively in their playing. By understanding the role of each interval, guitarists can better understand how the chord functions harmonically and how it can be used to create different moods and atmospheres in music.
Table: Intervals and their Function in the gdim Guitar Chord
| Interval | Function |
|---|---|
| Root (G) | Provides stability and tonal center |
| Minor Third (Bb) | Adds tension and dissonance |
| Diminished Fifth (Db) | Creates instability and leads to resolution |
3. Sound
The gdim guitar chord is characterized by its dissonant, tense sound, which is a result of the intervals used in its construction. The diminished fifth interval between the root and the third creates instability, while the minor third adds further tension. This combination of intervals gives the gdim chord its distinctive dissonant sound.
- Unresolved tension: The gdim chord creates a sense of unresolved tension, as it does not provide a clear resolution to the ear. This tension can be used to create a sense of anticipation or suspense in music.
- Harmonic contrast: The dissonant sound of the gdim chord can be used to create harmonic contrast with other chords in a piece of music. This contrast can be used to highlight certain sections of the music or to create a sense of drama or excitement.
- Dissonant embellishment: The gdim chord can be used as a dissonant embellishment to other chords. This can add interest and complexity to a chord progression and can help to create a more sophisticated sound.
- Melodic dissonance: The gdim chord can also be used to create melodic dissonance. This occurs when the notes of the chord clash with the notes of the melody. Melodic dissonance can be used to create a sense of tension or drama in a piece of music.
The dissonant, tense sound of the gdim guitar chord makes it a versatile tool for guitarists. It can be used to create a wide range of moods and atmospheres in music, from tension and suspense to contrast and embellishment.
4. Function
The gdim guitar chord is characterized by its harmonic instability, meaning that it does not provide a clear sense of resolution. This instability is caused by the diminished fifth interval between the root and the third, which creates a sense of tension and uncertainty. The gdim chord is often used as a leading tone chord, which means that it is used to lead to a more stable chord. This is because the instability of the gdim chord creates a strong desire for resolution, which can be provided by the following chord.
p>
For example, the gdim chord is often used to lead to the I chord in a major key. The I chord is the most stable chord in a major key, and it provides a strong sense of resolution. The gdim chord can also be used to lead to other chords, such as the V chord or the IV chord. These chords are also relatively stable, and they can provide a sense of resolution after the instability of the gdim chord.
Understanding the function of the gdim guitar chord as a harmonic instability and leading tone is essential for guitarists who want to use it effectively in their playing. By understanding how the chord functions harmonically, guitarists can better understand how to use it to create different moods and atmospheres in music.
Table: Function of the gdim Guitar Chord
| Function | Effect |
|---|---|
| Harmonic instability | Creates a sense of tension and uncertainty |
| Leading tone | Leads to a more stable chord |
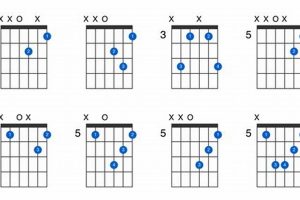
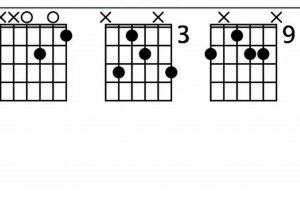
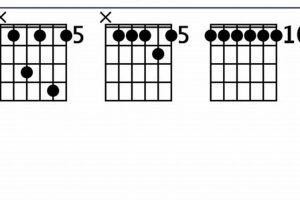
5. Voicings
The gdim guitar chord, like many other chords, can be played in multiple positions on the guitar neck. This versatility allows guitarists to choose the voicing that best suits their playing style and the musical context. Different voicings of the gdim chord can create different harmonic effects and textures.
For example, a gdim chord played in the open position has a bright and jangly sound, while a gdim chord played in a higher position on the neck may have a more muted and mellow sound. The choice of voicing can also affect the chord’s overall tonality. A gdim chord played with the root note on the lowest string may sound more dissonant and unstable, while a gdim chord played with the root note on a higher string may sound more consonant and resolved.
Understanding the multiple voicings of the gdim guitar chord is essential for guitarists who want to use the chord effectively in their playing. By understanding the different harmonic effects and textures that can be created by different voicings, guitarists can choose the voicing that best suits the musical context and their own personal style.
Table: Different Voicings of the gdim Guitar Chord
| Voicing | Sound | Tonal Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Open position | Bright and jangly | Dissonant and unstable |
| Higher position on the neck | Muted and mellow | More consonant and resolved |
| Root note on the lowest string | Dissonant and unstable | Strong bass presence |
| Root note on a higher string | More consonant and resolved | Less bass presence |
6. Progression
The gdim guitar chord is frequently employed in jazz and classical music due to its dissonant and unstable nature, which lends itself well to creating harmonic tension and progression.
- Jazz Harmony:
In jazz, the gdim chord is often used as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord, particularly in ii-V-I progressions. Its dissonant quality adds complexity and tension to the harmony, creating a sense of anticipation and resolution when it leads to the tonic chord.
- Classical Cadences:
In classical music, the gdim chord is commonly found in deceptive cadences, where it is used to create a sense of harmonic surprise or instability. For example, a V-vi-gdim-I cadence resolves unexpectedly to the minor tonic chord, creating a sense of harmonic ambiguity and emotional depth.
- Voice Leading:
The gdim chord’s dissonant intervals allow for interesting voice leading possibilities. The chromatic movement of the diminished fifth interval can create a sense of melodic tension and resolution, adding depth and sophistication to the musical texture.
- Harmonic Tension and Release:
The gdim chord’s inherent instability makes it an effective tool for creating and releasing harmonic tension. Its dissonant sound can create a sense of anticipation and unease, which is resolved when the chord progresses to a more stable harmony. This technique is commonly used in both jazz and classical music to add drama and emotional impact to the composition.
Overall, the gdim guitar chord’s versatility and dissonant nature make it a valuable harmonic tool in jazz and classical music, allowing composers and musicians to create complex and expressive musical passages.
7. Expression
The gdim guitar chord’s distinctive dissonant sound makes it an expressive tool for conveying emotions such as tension, anticipation, or drama in music. Its inherent instability creates a sense of unease and uncertainty, which can be effectively employed in various musical contexts.
In jazz improvisation, the gdim chord is often used as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord, particularly in ii-V-I progressions. Its dissonant quality adds complexity and tension to the harmony, creating a sense of anticipation and resolution when it leads to the tonic chord. This technique is commonly found in bebop and hard bop styles of jazz, where it contributes to the genre’s characteristic harmonic sophistication.
Classical composers have also harnessed the expressive power of the gdim chord. In classical harmony, the gdim chord is frequently employed in deceptive cadences, where it creates a sense of harmonic surprise or instability. For example, a V-vi-gdim-I cadence resolves unexpectedly to the minor tonic chord, creating a sense of harmonic ambiguity and emotional depth. This technique is evident in the works of composers such as J.S. Bach and Ludwig van Beethoven, who used it to evoke a range of emotions, from sadness and regret to dramatic intensity.
The gdim guitar chord’s versatility extends beyond jazz and classical music. In contemporary popular music, it is often used to add a sense of tension or drama to songs. For instance, the gdim chord is prominently featured in the chorus of Radiohead’s “Creep,” where it contributes to the song’s overall mood of anxiety and self-doubt.
Understanding the expressive capabilities of the gdim guitar chord is essential for musicians who wish to convey a wide range of emotions and create impactful musical experiences. Its dissonant nature and harmonic instability make it a valuable tool for generating tension, anticipation, and drama, adding depth and complexity to musical compositions.
Table: Examples of gdim Guitar Chord’s Expressive Use
| Musical Genre | Example | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Jazz | “All the Things You Are” by Charlie Parker | Creates tension and anticipation in the ii-V-I progression |
| Classical | “Moonlight Sonata” by Ludwig van Beethoven | Evokes a sense of sadness and regret in the deceptive cadence |
| Contemporary Popular Music | “Creep” by Radiohead | Adds tension and drama to the chorus |
8. Example
The renowned jazz standard “Autumn Leaves” by Miles Davis features the gdim guitar chord as an integral part of its harmonic structure, contributing to the song’s melancholic and reflective mood.
- Harmonic Tension and Release:
The gdim chord, with its dissonant diminished fifth interval, creates a sense of harmonic tension within the chord progression. This tension is resolved when the chord progresses to the more stable major or minor chords, creating a sense of movement and emotional release.
- Modal Interchange:
The gdim chord is used as a modal interchange, borrowed from the parallel minor scale, adding depth and complexity to the harmony. This technique creates a sense of harmonic movement and interest, enhancing the song’s overall sophistication.
- Emotional Expression:
The dissonant nature of the gdim chord contributes to the song’s melancholic and reflective mood. Its use in the bridge section, particularly, evokes a sense of longing and nostalgia, perfectly capturing the essence of the autumn season.
- Jazz Improvisation:
Jazz musicians often use the gdim chord as a starting point for improvisation, exploring its dissonant qualities and harmonic possibilities. This technique allows for creative exploration and adds an element of spontaneity to the performance.
In summary, the gdim guitar chord plays a crucial role in “Autumn Leaves” by Miles Davis, contributing to the song’s harmonic complexity, emotional depth, and improvisational potential, making it a prime example of the chord’s versatility and expressive power in jazz music.
Frequently Asked Questions about the gdim Guitar Chord
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the gdim guitar chord, providing informative answers to enhance understanding and practical application.
Question 1: What is the construction of the gdim guitar chord?
Answer: The gdim guitar chord is constructed with the notes G, Bb, and Db, forming a diminished triad with a root, minor third, and diminished fifth.
Question 2: How does the gdim chord function harmonically?
Answer: The gdim chord functions as a harmonic instability, creating tension and anticipation due to its dissonant diminished fifth interval. It often leads to more stable chords, resolving the tension.
Question 3: What are the common voicings of the gdim chord on the guitar?
Answer: The gdim chord has multiple voicings on the guitar, allowing guitarists to choose the voicing that best suits their playing style and the musical context.
Question 4: How is the gdim chord commonly used in jazz music?
Answer: In jazz, the gdim chord is frequently employed as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord, particularly in ii-V-I progressions, adding complexity and tension to the harmony.
Question 5: What is the role of the gdim chord in classical music?
Answer: Classical composers utilize the gdim chord in deceptive cadences, creating a sense of harmonic surprise and instability. It adds emotional depth and harmonic sophistication to classical pieces.
Question 6: How does the gdim chord contribute to the emotional expression in music?
Answer: The dissonant nature of the gdim chord evokes emotions such as tension, anticipation, or drama. It is effectively employed to create and release tension, adding depth and expressiveness to musical compositions.
Summary: Understanding the construction, function, and expressive qualities of the gdim guitar chord empowers guitarists to use it effectively in various musical contexts. Its versatility and dissonant sound make it a valuable tool for creating harmonic tension, adding depth, and conveying emotions in music.
Transition: Explore further resources to delve deeper into the world of guitar chords and their applications in different musical styles.
Tips for Using the gdim Guitar Chord
Incorporating the gdim guitar chord into your playing can add depth and sophistication to your music. Here are some tips to help you use this versatile chord effectively:
Tip 1: Understand its Construction and FunctionUnderstanding the construction (G, Bb, Db) and harmonic function (harmonic instability, leading tone) of the gdim chord is essential. This knowledge will guide you in using it effectively in different musical contexts.Tip 2: Experiment with Different VoicingsThe gdim chord has multiple voicings on the guitar neck. Experiment with different voicings to find the one that best suits your playing style and the desired harmonic effect.Tip 3: Use it as a Substitute or ExtensionIn jazz, the gdim chord can be used as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord in ii-V-I progressions. It can also be used as an extension to add complexity to major or minor chords.Tip 4: Create Harmonic Tension and ReleaseThe dissonant nature of the gdim chord makes it perfect for creating harmonic tension. Use it to build anticipation and then resolve it with a more stable chord, creating a sense of movement and emotional release.Tip 5: Explore its Expressive QualitiesThe gdim chord can convey a range of emotions, from tension and anticipation to drama and sadness. Experiment with using it in different musical contexts to explore its expressive potential.Summary: By understanding the construction, function, and expressive qualities of the gdim guitar chord, you can effectively incorporate it into your playing. Experiment with different voicings and techniques to add depth, complexity, and emotion to your music.
Conclusion
The gdim guitar chord stands as a versatile and expressive tool for musicians seeking to enhance their harmonic vocabulary. Its unique dissonant sound adds tension, anticipation, or drama to musical compositions, making it a valuable asset in various genres.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the construction, function, voicings, and effective use of the gdim chord. By understanding its harmonic properties and exploring its expressive potential, guitarists can incorporate this chord into their playing to create sophisticated and emotionally resonant music.
The gdim guitar chord invites further exploration and experimentation. As musicians continue to discover its nuances and applications, its role in shaping the future of music remains an exciting prospect. Embrace the gdim chord and unlock the doors to harmonic possibilities in your musical journey.