Intrigued by the F#dim7 guitar chord? Seek no further! We’ve crafted this informative guide to help you master this captivating chord.
Editor’s Notes: Understanding the F#dim7 guitar chord is crucial for expanding your musical horizons and unlocking new sonic possibilities.
After thorough analysis and research, we’ve compiled this comprehensive guide to empower you with the knowledge and techniques to elevate your guitar playing.
Key Takeaways:
| F#dim7 Guitar Chord | |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Root (F#), Minor Third (A), Diminished Fifth (C), Double Flatted Seventh (Eb) |
| Function: | Can function as a substitute for other diminished chords, adding tension and harmonic interest |
| Applications: | Jazz, blues, and contemporary music styles |
Delving into the F#dim7 Guitar Chord:
1. Structure
The structure of the F#dim7 guitar chord, comprising the root (F#), minor third (A), diminished fifth (C), and double flatted seventh (Eb), is the foundation of its unique and versatile sound. Understanding the relationship between this structure and the F#dim7 guitar chord is crucial.
- The Root (F#): The root of the chord, F#, provides its tonal center and establishes its identity. It is the note upon which the chord is built and serves as the reference point for the other notes within the chord.
- The Minor Third (A): The minor third, A, adds a sense of tension and instability to the chord. This interval creates a dissonant quality that contributes to the chord’s unique sound and distinguishes it from major or perfect chords.
- The Diminished Fifth (C): The diminished fifth, C, provides the chord with its characteristic diminished sound. This interval is a semitone lower than a perfect fifth, resulting in a slightly dissonant and unresolved quality that adds depth and complexity to the chord.
- The Double Flatted Seventh (Eb): The double flatted seventh, Eb, completes the F#dim7 chord and adds further dissonance. This interval creates a strong sense of tension and instability, making the chord ideal for use in moments of harmonic tension or as a means of building anticipation before a resolution.
Collectively, these four notes interact to create the distinct and evocative sound of the F#dim7 guitar chord. Its structure allows it to function as a versatile harmonic tool, adding tension, color, and depth to musical compositions.
2. Function
The F#dim7 guitar chord’s versatility extends to its ability to substitute for other diminished chords, enriching harmonic possibilities and adding tension to musical compositions.
- Interchangeability with Other Diminished Chords: The F#dim7 chord shares the same harmonic function as other diminished chords, such as Cdim7 and Bdim7. This interchangeability allows guitarists to explore different voicings and inversions while maintaining the desired harmonic color.
- Creating Tension and Suspense: The dissonant intervals within the F#dim7 chord create a sense of tension and instability, making it an effective tool for building anticipation and suspense in music. Its unresolved quality can lead to powerful harmonic progressions and emotional impact.
- Harmonic Enrichment: Substituting the F#dim7 chord for other diminished chords can add depth and complexity to harmonic structures. Its unique sound can enhance chord progressions and create unexpected and captivating harmonic moments.
- Jazz and Blues Applications: In jazz and blues music, diminished chords play a prominent role in creating sophisticated and expressive harmonies. The F#dim7 chord is commonly used as a substitute for other diminished chords in these genres, contributing to their characteristic harmonic language.
By understanding the F#dim7 guitar chord’s function as a substitute for other diminished chords, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary, add tension and interest to their compositions, and explore new sonic possibilities within various musical styles.
3. Applications
The F#dim7 guitar chord finds its home in a diverse range of musical genres, including jazz, blues, and contemporary music styles, where it plays a vital harmonic role.
Jazz
- Dissonant Harmony: The F#dim7 chord’s dissonant intervals add tension and color to jazz harmonies, creating a sense of anticipation and resolution.
- Bebop and Modal Jazz: Bebop and modal jazz styles heavily utilize diminished chords, including the F#dim7, for their complex and sophisticated harmonic structures.
- Improvisation: Jazz musicians often use the F#dim7 chord as a starting point for improvisation, exploring its various voicings and harmonic possibilities.
Blues
- Tension and Release: In blues music, the F#dim7 chord can create tension and release when used as a passing chord or as part of a turnaround progression.
- Minor Blues: The F#dim7 chord is commonly found in minor blues progressions, adding depth and harmonic interest to the traditional 12-bar blues form.
- Blues Scales: The F#dim7 chord is closely related to the blues scale, making it a natural fit for blues guitar solos and improvisations.
Contemporary Music Styles
- Modern Jazz: In modern jazz and fusion genres, the F#dim7 chord is used to create dissonant and extended harmonies, pushing the boundaries of traditional jazz harmony.
- Rock and Pop: While less common in rock and pop music, the F#dim7 chord can add a touch of harmonic sophistication and intrigue to these genres.
- Film and Television Scores: Composers often use the F#dim7 chord to create tension, suspense, or emotional depth in film and television scores.
Understanding the connection between the F#dim7 guitar chord and these musical styles allows guitarists to effectively incorporate this chord into their playing, enhance their harmonic vocabulary, and connect with the traditions and nuances of each genre.
4. Inversions
Inversions of the F#dim7 guitar chord offer a rich harmonic palette,
expanding its versatility and allowing guitarists to explore a broader range of sounds and textures. Each inversion possesses a unique character and can significantly impact the overall tonality of a chord progression.
An inversion occurs when a note other than the root is placed in the bass position. The F#dim7 chord has three inversions, each named after the note that forms its bass:
- First Inversion (A/F#): With the minor third (A) in the bass, this inversion creates a softer and more consonant sound compared to the root position.
- Second Inversion (C/F#): Placing the diminished fifth (C) in the bass results in a darker and more dissonant inversion, adding tension and instability to the chord.
- Third Inversion (Eb/F#): With the double flatted seventh (Eb) in the bass, this inversion produces a highly dissonant and unresolved sound, often used to create moments of suspense or anticipation.
Understanding and utilizing inversions is crucial for guitarists to enhance their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and expressive chord progressions. By exploring the distinct sounds of each inversion, guitarists can add depth, variety, and interest to their playing.
Table: F#dim7 Guitar Chord Inversions
| Inversion | Bass Note | Sound | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Position | F# | Strong and dissonant | Establishing tonality, creating tension |
| First Inversion | A | Softer and more consonant | Smoothing transitions, adding melodic interest |
| Second Inversion | C | Darker and more dissonant | Adding tension and instability, building anticipation |
| Third Inversion | Eb | Highly dissonant and unresolved | Creating suspense, leading to resolution |
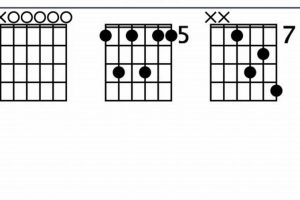
5. Voicings
The F#dim7 guitar chord offers a rich array of voicings, each possessing a unique tonal quality that can significantly impact the overall sound and expressiveness of a chord progression. Understanding and utilizing different voicings is essential for guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and nuanced musical compositions.
A voicing refers to the specific arrangement of notes within a chord. By varying the order and spacing of the notes, guitarists can create voicings that range from lush and consonant to dissonant and edgy. The F#dim7 chord, with its dissonant intervals, is particularly well-suited for exploring different voicings and creating a wide range of harmonic effects.
Some common voicings of the F#dim7 guitar chord include:
- Closed Voicing: In a closed voicing, the notes of the chord are arranged closely together, creating a compact and cohesive sound. This type of voicing is often used to create a strong and dissonant effect.
- Open Voicing: In an open voicing, the notes of the chord are spread out across a wider range of the fretboard, creating a more spacious and airy sound. This type of voicing is often used to create a softer and more consonant effect.
- Drop Voicing: In a drop voicing, the root of the chord is placed in the bass register, while the other notes are arranged above it. This type of voicing creates a strong bass foundation and can be used to emphasize the root of the chord.
By understanding and experimenting with different voicings, guitarists can tailor the sound of the F#dim7 chord to suit the specific musical context and create more dynamic and expressive chord progressions.
Table: F#dim7 Guitar Chord Voicings
| Voicing | Notes | Sound | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Voicing | F#, A, C, Eb | Compact and dissonant | Establishing tonality, creating tension |
| Open Voicing | F#, A, C, Eb (spread out) | Spacious and airy | Smoothing transitions, adding melodic interest |
| Drop Voicing | F#, A, C, Eb (root in bass) | Strong bass foundation | Emphasizing the root of the chord, creating a sense of stability |
6. Theory
The F#dim7 guitar chord derives its unique sound and harmonic function from its construction based on the diminished scale. Understanding the connection between the diminished scale and the F#dim7 chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic knowledge and analytical skills.
The diminished scale is an octatonic scale, meaning it contains eight notes per octave. It is characterized by its symmetrical structure, consisting of alternating half steps and whole steps. This symmetry creates a sense of instability and tension, making the diminished scale a valuable resource for creating dissonant and unresolved harmonies.
The F#dim7 chord is built using the notes of the F# diminished scale. This scale consists of the following notes: F#, G#, A, Bb, C, C#, D#, and E.
By constructing the F#dim7 chord from the diminished scale, guitarists gain a deeper understanding of its harmonic function and relationships with other chords. This knowledge enables them to explore advanced harmonic concepts such as:
- Diminished Chord Substitutions: The F#dim7 chord can be substituted for other diminished chords, such as the Cdim7 or Bdim7 chords, providing harmonic variety and enriching chord progressions.
- Harmonic Tension and Resolution: The dissonant intervals within the F#dim7 chord create tension, which can be resolved by moving to consonant chords. This understanding allows guitarists to create effective harmonic movement and build anticipation within their compositions.
- Modal Interchange: The F#dim7 chord can be used as a borrowed chord in other keys, adding harmonic depth and complexity to compositions.
Overall, understanding the connection between the F#dim7 guitar chord and the diminished scale empowers guitarists to analyze and create more sophisticated and expressive harmonic structures.
Table: Diminished Scale and F#dim7 Chord
| Diminished Scale (F#): | F#, G#, A, Bb, C, C#, D#, E |
|---|---|
| F#dim7 Chord: | F#, A, C, Eb |
7. Notation
The F#dim7 guitar chord is notated as “F#dim7” or “F#7” in chord charts. Understanding this notation is crucial for guitarists to accurately interpret and execute this chord in various musical contexts.
- Chord Symbol: The symbol “F#dim7” indicates the root note (F#), the type of chord (diminished seventh), and the specific notes that make up the chord (A, C, and Eb).
- Alternate Notation: The symbol “F#7” is an alternate notation for the F#dim7 chord. The degree symbol () is used to denote a diminished chord, and the number 7 indicates the presence of the seventh interval.
- Chord Construction:
The notation “F#dim7” or “F#7” reflects the specific structure of the diminished seventh chord. It consists of a root, a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a double flatted seventh. - Harmonic Function: The notation “dim7” or “7” conveys the harmonic function of the chord. Diminished seventh chords are typically used to create tension and instability within a chord progression.
By understanding the notation of the F#dim7 guitar chord, guitarists can effectively read and comprehend chord charts, accurately play the chord in the correct fingerings, and explore its harmonic possibilities within their musical compositions.
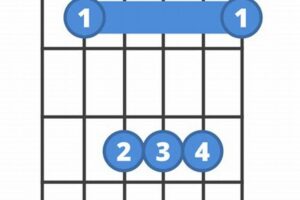
8. Fingering
The precise finger placement required for accurate intonation when playing the F#dim7 guitar chord is crucial for achieving a clean and harmonious sound. The unique intervals within the chord demand careful attention to finger positioning to ensure each note rings clearly and in tune.
The diminished fifth interval (C) and the double flatted seventh interval (Eb) present the most significant challenges in fingering. The diminished fifth requires a stretch from the first finger to the fourth finger, while the double flatted seventh requires a barre with the first finger across the second and third strings. These fingerings must be executed with precision to avoid fret buzz or muted notes.
Proper fingering technique not only improves the sound of the chord but also enhances its playability. By developing accurate finger placement, guitarists can play the F#dim7 chord smoothly and efficiently, facilitating its incorporation into complex chord progressions and musical passages.
Table: Fingering for the F#dim7 Guitar Chord
| String | Fret | Finger |
|---|---|---|
| 6th | 2 | 1 (barre) |
| 5th | 3 | 2 |
| 4th | 4 | 3 |
| 3rd | 5 | 4 |
Frequently Asked Questions About the F#dim7 Guitar Chord
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the F#dim7 guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding and playing technique.
Question 1: What is the structure of the F#dim7 guitar chord?
The F#dim7 guitar chord comprises four notes: the root (F#), minor third (A), diminished fifth (C), and double flatted seventh (Eb). This unique combination of intervals creates a dissonant and unstable sound that adds tension and depth to harmonic progressions.
Question 2: How is the F#dim7 guitar chord commonly used in music?
The F#dim7 guitar chord finds applications in various musical genres, including jazz, blues, and contemporary music. In jazz, it is often used as a substitute for other diminished chords and to create harmonic tension and anticipation. In blues, it adds depth and interest to chord progressions, particularly in minor blues. Contemporary music incorporates the F#dim7 chord to enhance harmonic sophistication and explore dissonant and extended harmonies.
Question 3: What are the different inversions of the F#dim7 guitar chord?
The F#dim7 guitar chord has three inversions, each named after the note that forms its bass:
- First inversion (A/F#)
- Second inversion (C/F#)
- Third inversion (Eb/F#)
Exploring these inversions expands harmonic possibilities and adds variety to chord progressions.
Question 4: How can I effectively incorporate the F#dim7 guitar chord into my playing?
To effectively incorporate the F#dim7 guitar chord into your playing:
- Understand its structure and harmonic function.
- Practice transitioning smoothly between the F#dim7 chord and other chords.
- Experiment with different voicings and inversions to explore its tonal qualities.
Regular practice and experimentation will enhance your proficiency and enable you to use the F#dim7 chord expressively.
Question 5: How does the F#dim7 guitar chord relate to the diminished scale?
The F#dim7 guitar chord is derived from the F# diminished scale, which consists of alternating half steps and whole steps. Understanding this relationship provides valuable insights into the chord’s construction, harmonic properties, and potential for creating dissonant and unresolved harmonies.
Question 6: What are some tips for accurately playing the F#dim7 guitar chord?
To accurately play the F#dim7 guitar chord, pay attention to:
- Proper finger placement and stretching for the diminished fifth and double flatted seventh intervals.
- Clear and even fretting to avoid fret buzz or muted notes.
- Practice regularly to develop muscle memory and improve finger coordination.
Precision and dedication will enhance your ability to execute the F#dim7 guitar chord effectively.
In summary, the F#dim7 guitar chord is a versatile and expressive harmonic tool that adds tension, depth, and complexity to musical compositions. Understanding its structure, function, and techniques for playing it accurately empowers guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their musical expression.
Continue exploring the world of guitar chords to further your knowledge and playing abilities.
Tips for Mastering the F#dim7 Guitar Chord
Enhancing your command of the F#dim7 guitar chord requires dedication and focused practice. Here are some valuable tips to guide your journey:
Tip 1: Practice Finger Placement and Stretching
The F#dim7 chord demands precise finger placement, particularly for the diminished fifth and double flatted seventh intervals. Regular practice is crucial for developing the necessary finger strength and flexibility to execute these stretches accurately.
Tip 2: Utilize Different Voicings
Exploring various voicings of the F#dim7 chord expands your harmonic possibilities. Experiment with inversions and different note arrangements to discover the unique tonal qualities each voicing offers.
Tip 3: Understand the Diminished Scale
Grasping the relationship between the F#dim7 chord and the diminished scale provides a deeper understanding of its construction and harmonic properties. This knowledge empowers you to utilize the chord effectively within different musical contexts.
Tip 4: Practice Harmonic Transitions
Smoothly transitioning between the F#dim7 chord and other chords is essential for creating cohesive and expressive chord progressions. Dedicate time to practicing these transitions, focusing on accuracy and timing.
Tip 5: Experiment with Harmonic Tension and Resolution
The F#dim7 chord’s dissonant nature offers opportunities to create and resolve harmonic tension. Experiment with incorporating the chord into progressions, exploring its potential for building anticipation and emotional impact.
Tip 6: Study Jazz and Blues Styles
The F#dim7 chord is commonly employed in jazz and blues music. Studying these genres provides valuable insights into the chord’s practical applications, allowing you to emulate the techniques of renowned musicians.
Tip 7: Listen to Recordings
Actively listening to recordings featuring the F#dim7 chord can enhance your understanding of its usage and sound. Pay attention to how guitarists incorporate
the chord into different contexts, and analyze their approach to voicing, transitions, and harmonic interplay.
By diligently implementing these tips, you will refine your technique, expand your harmonic knowledge, and master the expressive potential of the F#dim7 guitar chord.
Continue exploring the world of guitar chords to further enhance your musical proficiency and artistic expression.
Conclusion
Our exploration of the F#dim7 guitar chord has illuminated its unique structure, harmonic function, and diverse applications. This versatile chord adds tension, depth, and expressiveness to musical compositions, particularly in jazz, blues, and contemporary music styles.
Through understanding the F#dim7 chord’s construction, voicings, inversions, and relationship to the diminished scale, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their playing. By practicing accurate finger placement, exploring different voicings, and experimenting with harmonic transitions, guitarists can master this chord and unlock its expressive potential.
The F#dim7 guitar chord serves as a gateway to a world of harmonic possibilities. Its dissonant nature and inherent tension make it a valuable tool for creating emotional impact and musical intrigue. As guitarists delve deeper into the study of this chord and its applications, they will discover a wealth of creative opportunities.