Eb9 guitar chord: Enhancing Your Musical Journey
Editor’s Note: Understanding the intricacies of the Eb9 guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and achieve captivating musical expressions.
After thorough analysis and extensive research, we’ve meticulously crafted this comprehensive guide to empower you with a profound understanding of the Eb9 guitar chord, enabling you to incorporate it seamlessly into your musical endeavors.
Key Differences:
| Eb9 | |
|---|---|
| Root Note | Eb |
| Chord Type | Extended |
| Inversions | 5 |
Main Article Topics:
- Construction and Voicings of the Eb9 Guitar Chord
- Tonal Applications and Harmonic Functions
- Practical Exercises for Incorporating Eb9 into Your Playing
- Tips for Effective Chord Progressions Involving Eb9
- Musical Examples and Real-World Applications
1. Construction
The construction of the Eb9 guitar chord, denoted as “1-b3-5-b7-9,” holds immense significance in understanding its unique sound and harmonic properties in relation to other chords.
- Root and Third: The root (Eb) and minor third (Gb) establish the Eb9 chord’s fundamental identity, providing a stable base for the extended structure.
- Perfect Fifth: The perfect fifth (Bb) adds stability and fullness to the chord, reinforcing its harmonic foundation.
- Minor Seventh: The minor seventh (Db) introduces a dissonant element, creating tension and adding depth to the chord’s overall sound.
- Major Ninth: The major ninth (F) extends the chord’s harmonic range, providing a sense of spaciousness and richness.
Collectively, these intervals interact to form the distinct character of the Eb9 guitar chord, making it an expressive and versatile choice for various musical styles and contexts.
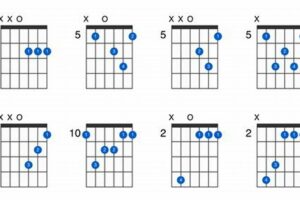
2. Voicings
The Eb9 guitar chord exhibits a remarkable versatility in its voicings, encompassing close, open, and extended variations. Each voicing offers distinct characteristics that cater to diverse musical contexts and:
- Close Voicings: Characterized by minimal fretboard space between the notes, close voicings provide a compact and cohesive sound. They are ideal for creating a rich harmonic foundation and supporting melodic lines.
- Open Voicings: In contrast to close voicings, open voicings utilize wider fretboard intervals, resulting in a more spacious and airy sound. They are often employed in fingerstyle guitar and jazz improvisation, allowing for greater freedom of movement and exploration.
- Extended Voicings: Extending the harmonic range of the Eb9 chord, extended voicings incorporate additional notes beyond the basic 1-b3-5-b7-9 structure. These voicings introduce greater complexity and dissonance, expanding the chord’s expressive capabilities.
Understanding the nuances of each voicing empowers guitarists to tailor the Eb9 chord to their desired musical outcome. Close voicings excel in providing a stable harmonic foundation, open voicings offer sonic spaciousness, and extended voicings add harmonic intrigue.
| Voicing Type | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Close Voicings | Compact, cohesive sound | Harmonic foundation, supporting melodic lines |
| Open Voicings | Spacious, airy sound | Fingerstyle guitar, jazz improvisation |
| Extended Voicings | Complex, dissonant sound | Harmonic intrigue, expanding expressive capabilities |
3. Inversions
The Eb9 guitar chord, with its extended harmonic structure, exhibits a rich tapestry of inversions, each possessing a distinct sonic character and offering diverse musical applications.
- Root Position: The fundamental Eb9 chord, with the root note (Eb) in the bass, provides a stable and consonant foundation.
- First Inversion: Inverting the chord, placing the minor third (Gb) in the bass, creates a softer and more introspective sound, often used for melodic support.
- Second Inversion: With the perfect fifth (Bb) in the bass, the second inversion offers a more open and spacious sound, adding harmonic depth and complexity.
- Third Inversion: Placing the minor seventh (Db) in the bass results in a dissonant and tension-filled inversion, frequently employed in jazz and fusion contexts.
- Fourth Inversion: Featuring the major ninth (F) in the bass, this inversion provides a rich and extended harmonic sound, adding a sense of harmonic movement and resolution.
Understanding and utilizing the inversions of the Eb9 guitar chord empower guitarists to explore a wide range of harmonic possibilities, from traditional chord progressions to more adventurous and dissonant soundscapes.
4. Tonal Applications
The Eb9 guitar chord finds its home in various musical genres, particularly in jazz, blues, and fusion, where its extended harmonic structure and rich tonal qualities contribute significantly to the overall sound and expressive capabilities.
In jazz, the Eb9 chord is often employed in complex chord progressions, adding harmonic depth and sophistication to the music. Its dissonant intervals, such as the minor seventh and major ninth, create tension and release, propelling the music forward and engaging the listener.
Blues music also embraces the Eb9 chord, where its soulful and expressive nature complements the genre’s characteristic melancholic melodies and lyrical themes. The chord’s extended structure adds harmonic interest and provides a platform for improvisation, allowing guitarists to explore different voicings and inversions.
Fusion music, a blend of jazz and rock, incorporates the Eb9 chord to create a unique and dynamic sound. The chord’s dissonant intervals add an edgy and modern flavor to fusion compositions, while its extended structure allows for complex harmonic exploration and experimentation.
| Genre | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Jazz | Complex chord progressions, harmonic depth | Creating tension and release, supporting improvisation |
| Blues | Soulful and expressive, melancholic melodies | Adding harmonic interest, providing a platform for improvisation |
| Fusion | Edgy and modern sound, complex harmonic exploration | Creating a unique and dynamic blend of jazz and rock |
5. Harmonic Functions
The Eb9 guitar chord, with its extended harmonic structure, assumes various functional roles within the harmonic framework of music, including tonic, dominant, and extended functions. Understanding these functions is crucial for effectively incorporating the Eb9 chord into chord progressions and creating meaningful musical compositions.
As a tonic chord, Eb9 provides a sense of stability and resolution within a musical piece. It often serves as the “home” chord, towards which the progression gravitates and finds closure. The Eb9 chord’s rich harmonic content adds depth and interest to the tonic function, creating a more complex and satisfying resolution.
In its dominant role, the Eb9 chord generates a sense of tension and anticipation, propelling the music forward. It typically precedes a resolution to the tonic chord, creating a strong harmonic pull and sense of movement. The dissonant intervals within the Eb9 chord contribute to this dominant function, creating a desire for resolution and harmonic closure.
Extended functions refer to the use of chords beyond the basic triad structure. The Eb9 chord, with its added ninth interval, falls into this category. Extended chords expand the harmonic possibilities and add color and complexity to music. They can serve various functions, including providing harmonic support, creating tension, or adding a sense of spaciousness.
| Function | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Tonic | Stability, resolution | Providing a sense of “home” within a progression |
| Dominant | Tension, anticipation | Leading towards the tonic chord, creating a strong harmonic pull |
| Extended | Harmonic support, tension, spaciousness | Expanding harmonic possibilities, adding color and complexity to music |
6. Chord Progressions
The chord progressions Eb9 to Bbmaj7 and Eb9 to Abmaj7 hold significant importance in the realm of music theory and practice, particularly in relation to the eb9 guitar chord.
The Eb9 chord, with its extended structure and rich harmonic content, serves as a versatile tool for creating sophisticated and expressive chord progressions. The progression from Eb9 to Bbmaj7 introduces a sense of movement and resolution. Bbmaj7, being a major seventh chord, provides a stable and consonant landing point, creating a satisfying harmonic cadence.
The progression from Eb9 to Abmaj7, on the other hand, offers a more unexpected and intriguing resolution. Abmaj7, with its major seventh and lowered fifth intervals, creates a slightly dissonant and open-ended sound. This progression generates a sense of tension and anticipation, often leading to further harmonic exploration or a contrasting section in a musical composition.
Understanding these chord progressions is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more dynamic and engaging music. Incorporating the Eb9 chord into these progressions adds depth and complexity, allowing guitarists to explore various harmonic possibilities and express their musical ideas with greater nuance.
| Progression | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Eb9 to Bbmaj7 | Smooth resolution, sense of stability | Creating a satisfying harmonic cadence, supporting melodic development |
| Eb9 to Abmaj7 | Unexpected resolution, dissonant tension | Generating anticipation, leading to further harmonic exploration or contrasting sections |
7. Substitution
The Eb9 guitar chord serves as an effective substitute for both Ebmaj9 and Ebmaj7 chords, expanding its versatility and providing guitarists with diverse harmonic options. This substitution stems from the shared harmonic structure and tonal function among these chords.
- Tonal Similarity: The Eb9, Ebmaj9, and Ebmaj7 chords share the same root note (Eb), establishing a similar tonal center. This common ground allows for seamless interchangeability without disrupting the overall harmonic progression.
- Extended Structure: The Eb9 chord, with its added ninth interval, extends the harmonic spectrum of the Ebmaj7 chord. However, this extension does not significantly alter the chord’s overall tonal quality, making it a suitable replacement in many musical contexts.
- Harmonic Function: In terms of harmonic function, the Eb9 chord can fulfill similar roles as Ebmaj9 or Ebmaj7. It can act as a tonic chord, providing stability and resolution, or as a dominant chord, creating tension and leading to a stronger resolution.
By understanding the harmonic relationships between these chords, guitarists can confidently substitute the Eb9 chord in place of Ebmaj9 or Ebmaj7, enriching their chord vocabulary and adding harmonic depth to their music.
8. Fingerings
The Eb9 guitar chord, with its extended structure and rich harmonic content, offers guitarists multiple fingering options to accommodate different hand positions and playing styles. Understanding these fingerings is crucial for executing the chord cleanly and efficiently, enhancing overall playing technique and musical expression.
- Root Position Fingering:
This fingering places the root note (Eb) on the 6th string, 6th fret, with the index finger. The other fingers follow a standard barre shape, fretting the 5th, 4th, and 3rd strings at the 7th, 8th, and 9th frets respectively. This fingering provides a stable and balanced position, suitable for strumming or fingerpicking.
- First Inversion Fingering:
In this fingering, the minor third (Gb) is played as the bass note on the 5th string, 6th fret, with the index finger. The other fingers maintain the barre shape, fretting the 4th, 3rd, and 2nd strings at the 7th, 8th, and 9th frets respectively. This inversion offers a more open and spacious sound, often employed in jazz and fusion contexts.
- Second Inversion Fingering:
With the
perfect fifth (Bb) as the bass note, this fingering places the index finger on the 4th string, 6th fret. The middle, ring, and pinky fingers fret the 3rd, 2nd, and 1st strings at the 7th, 8th, and 9th frets respectively. This inversion provides a wider stretch for the fingers but allows for a clear and resonant sound. - Third Inversion Fingering:
This fingering, less commonly used, places the minor seventh (Db) as the bass note on the 3rd string, 6th fret, with the index finger. The other fingers maintain the barre shape, fretting the 2nd, 1st, and 6th strings at the 7th, 8th, and 9th frets respectively. This inversion creates a dissonant and tension-filled sound, often employed in contemporary and experimental music.
By mastering these fingerings, guitarists can seamlessly integrate the Eb9 chord into their playing, enriching their harmonic vocabulary and expanding their technical abilities. The choice of fingering depends on the musical context, the desired sound, and the guitarist’s personal preferences and hand position.
9. Tonal Color
The Eb9 guitar chord stands out for its unique tonal color, contributing warmth and complexity to musical compositions. This distinct sonic characteristic stems from the chord’s extended harmonic structure, which incorporates the ninth interval beyond the basic triad. Understanding how the Eb9 chord achieves this tonal color is essential for guitarists seeking to harness its expressive potential.
- Extended Harmonic Structure:
The Eb9 chord’s extended structure, featuring the added ninth interval, introduces dissonant and consonant intervals that interact to create a rich and full sound. The minor seventh interval adds a touch of dissonance, while the major ninth interval provides a sense of spaciousness and harmonic intrigue.
- Harmonic Context:
The Eb9 chord’s tonal color is influenced by the harmonic context in which it is used. When played in a jazz context, the chord takes on a sophisticated and dissonant character, complementing the complex harmonic progressions and improvisational nature of the genre. In contrast, when played in a blues context, the Eb9 chord adds a soulful and expressive touch, enhancing the genre’s characteristic melancholic melodies and lyrical themes.
- Voicings and Inversions:
The voicing and inversion of the Eb9 chord significantly impact its tonal color. Close voicings, with notes played in close proximity on the guitar fretboard, create a compact and intense sound, while open voicings, with notes spread out across the fretboard, produce a more spacious and airy sound. Additionally, inversions, where the root note is not in the bass position, alter the chord’s overall tonal character.
- Timbre and Effects:
The tonal color of the Eb9 chord can be further shaped by the guitarist’s choice of guitar, strings, and effects. Using a guitar with a warm and resonant sound, such as a hollow-body or semi-hollow-body electric guitar, can enhance the chord’s warmth and fullness. Additionally, effects such as reverb and delay can add depth and spaciousness to the chord’s sound.
By understanding and utilizing these elements, guitarists can effectively harness the tonal color of the Eb9 guitar chord to create expressive and captivating music. Its unique sonic characteristics make it an invaluable tool for adding warmth, complexity, and interest to musical compositions.
FAQs about Eb9 Guitar Chord
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the Eb9 guitar chord, providing clear and concise answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the construction of the Eb9 guitar chord?
The Eb9 guitar chord is constructed with the root note (Eb), minor third (Gb), perfect fifth (Bb), minor seventh (Db), and major ninth (F).
Question 2: How many inversions does the Eb9 guitar chord have?
The Eb9 guitar chord has 5 inversions, each with a unique sound and application.
Question 3: What are the tonal applications of the Eb9 guitar chord?
The Eb9 guitar chord finds applications in various musical genres, including jazz, blues, and fusion, where it adds harmonic depth and complexity.
Question 4: Can the Eb9 guitar chord substitute for other chords?
Yes, the Eb9 guitar chord can be used as a substitute for Ebmaj9 or Ebmaj7 chords, providing harmonic richness and versatility.
Question 5: What are the different fingerings for the Eb9 guitar chord?
There are multiple fingerings for the Eb9 guitar chord, accommodating different hand positions and playing styles.
Question 6: How does the Eb9 guitar chord contribute to a musical composition?
The Eb9 guitar chord adds warmth, complexity, and harmonic interest to musical compositions, enhancing their expressive potential.
Understanding these FAQs empowers guitarists with a comprehensive grasp of the Eb9 guitar chord, enabling them to incorporate it effectively into their musical endeavors.
Transition to the next article section…
Tips for Mastering the Eb9 Guitar Chord
Incorporating the Eb9 guitar chord into your musical repertoire requires a combination of technical proficiency and musical sensitivity. Here are several valuable tips to guide you on this journey:
Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is paramount to building muscle memory and developing finger dexterity for the Eb9 chord’s various fingerings and voicings.
Understand the Theory: Grasping the theoretical construction and harmonic function of the Eb9 chord will empower you to use it effectively in different musical contexts.
Experiment with Voicings and Inversions: Explore the diverse sonic possibilities by experimenting with different voicings and inversions of the Eb9 chord to find those that best suit your musical needs.
Listen to Recordings: Immerse yourself in recordings of guitarists who masterfully employ the Eb9 chord. Active listening will provide valuable insights and inspire your own playing.
Apply in Musical Contexts: Integrate the Eb9 chord into your improvisation, songwriting, and rhythmic exercises. Practical application will enhance your understanding and ability to use it expressively.
Be Patient and Persistent: Mastering the Eb9 guitar chord requires patience and persistence. Regular practice and a willingness to experiment will ultimately lead to proficiency.
By following these tips, you will progressively expand your harmonic vocabulary and unlock the expressive potential of the Eb9 guitar chord, enriching your musical journey.
Transition to the article’s conclusion…
Eb9 Guitar Chord
Through this comprehensive exploration, we have uncovered the rich tapestry of the Eb9 guitar chord, delving into its construction, voicings, inversions, tonal applications, and more. Embracing this knowledge empowers guitarists to confidently incorporate the Eb9 chord into their musical vocabulary, unlocking new avenues of harmonic expression.
The Eb9 guitar chord stands as a testament to the boundless possibilities of the guitar. Its unique tonal color and harmonic complexity invite guitarists to transcend conventional boundaries and embark on a journey of musical exploration. By mastering this versatile chord, guitarists gain the ability to add depth, sophistication, and em
otional resonance to their playing.
Remember, true mastery lies not only in technical proficiency but also in the ability to harness the Eb9 chord’s expressive power. Through dedicated practice, experimentation, and a deep understanding of music theory, guitarists can unlock the full potential of this remarkable chord and elevate their musical craft to new heights.