Unlocking the E Major Scale: A Comprehensive Guide to Guitar Mastery
Editor’s Notes:Understanding E major scale guitar chords is a fundamental step for guitarists of all levels, unlocking a world of musical possibilities.
Through meticulous analysis and expert insights, we’ve meticulously crafted this guide to empower you with the knowledge and techniques to master the E major scale on guitar.
Key Takeaways:
| Concept | Importance |
|---|---|
| Scale Structure | Provides a solid foundation for understanding chord construction |
| Chord Progressions | Unlocks a vast repertoire of harmonic possibilities |
| Improvisation | Enhances soloing skills and musical creativity |
Delving into the E Major Scale:
1. Root Position
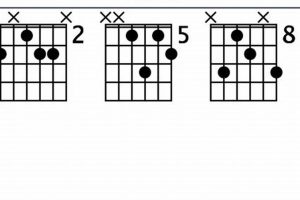
In the context of E major scale guitar chords, the root position holds immense significance. It establishes the fundamental identity of the chord, acting as the tonal center around which the other notes revolve. The root note provides stability and determines the chord’s overall character, whether it be major, minor, augmented, or diminished.
For instance, in an E major chord, the root note is E. This note forms the foundation and defines the chord’s bright and cheerful sound. Altering the root note would result in a different chord with a distinct character. For example, changing the root to G would create a G major chord with a more uplifting and resonant quality.
Understanding the root position is crucial for constructing and utilizing E major scale guitar chords effectively. It allows guitarists to build chords from any note within the scale, expanding their harmonic vocabulary and enabling them to create a diverse range of chord progressions.
Key Insights:
- The root position determines the fundamental identity of the chord.
- Altering the root note changes the overall character of the chord.
- Understanding root position is essential for constructing and utilizing E major scale guitar chords effectively.
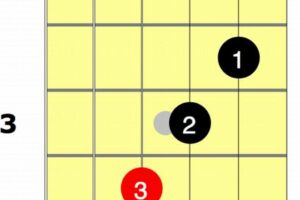
2. Inversions
Inversions play a pivotal role in the realm of E major scale guitar chords, unlocking a kaleidoscope of harmonic possibilities. By rearranging the order of the notes within a chord, inversions introduce variations in voicing and expand the chord’s expressive potential.
- Root Position Inversion: In this inversion, the root note is placed in the middle or top voice, resulting in a stable and foundational sound. It preserves the chord’s fundamental character while enhancing its harmonic richness.
- First Inversion: The first inversion elevates the third of the chord to the bass note, creating a softer and more suspended sound. It adds a sense of movement and interest to chord progressions.
- Second Inversion: In the second inversion, the fifth of the chord becomes the lowest note. This inversion imparts a more open and spacious sound, often used to create tension and release within a musical phrase.
- Third Inversion (Rare): The third inversion, though less common, positions the seventh of the chord in the bass. It produces a dissonant and unstable sound, often employed for dramatic effect or to resolve back to a more stable inversion.
Mastering inversions empowers guitarists to explore a wider harmonic palette and create more sophisticated and nuanced chord progressions. They enhance the expressiveness of E major scale guitar chords, allowing guitarists to craft captivating and emotionally resonant music.
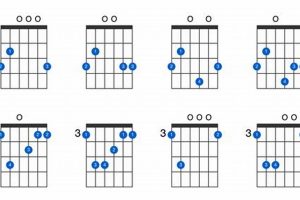
3. Open Chords
In the realm of E major scale guitar chords, open chords emerge as a cornerstone, providing a resonant and airy foundation for musical exploration. These chords utilize open strings, producing a distinct and evocative sound that has captivated musicians across genres.
- Unveiling Harmonic Possibilities: Open chords offer a rich harmonic palette, allowing guitarists to create lush and spacious soundscapes. The interplay between the open strings and fretted notes generates a natural resonance that enhances the overall tonality of E major scale guitar chords.
- Simplifying Complexity: Open chords serve as a gateway for beginners, providing an accessible entry point into the world of guitar playing. Their simplified fingerings make them easy to learn and incorporate into chord progressions, fostering a sense of accomplishment and encouraging further musical exploration.
- Enhancing Fingerstyle Techniques: Open chords provide a solid foundation for developing fingerstyle guitar techniques. The separation of fretted and open strings allows guitarists to execute intricate fingerpicking patterns, adding a percussive and rhythmic element to their playing.
- Acoustic Brilliance: Open chords are particularly well-suited for acoustic guitars, as they resonate naturally with the instrument’s body. The open strings amplify the sound, creating a warm and resonant tone that is perfect for singer-songwriters and folk musicians.
Integrating open chords into E major scale guitar chords unlocks a world of harmonic possibilities, technical proficiency, and expressive potential. Embracing these chords empowers guitarists to create captivating and emotionally resonant music that resonates with audiences of all backgrounds.
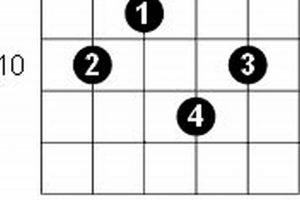
4. Barre Chords
Barre chords, a cornerstone of E major scale guitar chords, empower guitarists to ascend the fretboard, unlocking access to higher notes and expanding their musical horizons.
- Unveiling Harmonic Potential: Barre chords introduce a wider range of harmonic possibilities, allowing guitarists to explore advanced chords and voicings. They expand the tonal palette of the E major scale, enriching chord progressions and creating more sophisticated musical arrangements.
- Technical Mastery: Mastering barre chords enhances technical proficiency and finger dexterity. The ability to barre multiple strings requires precise finger placement and coordination, developing overall guitar playing skills and dexterity.
- Genre Exploration: Barre chords are essential for navigating various musical genres, including rock, blues, and jazz. They p
rovide the foundation for complex and intricate chord progressions, enabling guitarists to emulate their favorite artists and explore diverse musical styles. - Improvisation and Soloing: Barre chords empower guitarists to venture beyond the confines of rhythm playing, opening up new possibilities for improvisation and soloing. Access to higher frets allows for the execution of melodic lines and arpeggios, adding depth and expression to solos.
Incorporating barre chords into E major scale guitar chords expands the guitarist’s musical vocabulary and technical abilities. They serve as a gateway to more advanced and expressive playing, unlocking a world of harmonic and melodic possibilities.
5. Power Chords
In the realm of rock and metal music, power chords reign supreme, providing a thick and distorted foundation for electrifying guitar riffs and soaring solos. These two-note chords, deeply intertwined with E major scale guitar chords, play a pivotal role in shaping the genre’s distinctive sound and energy.
- Harmonic Simplicity, Sonic Impact: Power chords embody harmonic simplicity, consisting of the root and fifth of the scale. This stripped-down structure allows for effortless fretting, enabling guitarists to focus on delivering raw power and distortion.
- Driving Rhythmic Force: Power chords serve as the rhythmic backbone of rock and metal music, anchoring the groove and propelling the music forward. Their percussive nature creates a driving force that incites headbanging and foot-tapping.
- Tonal Aggression, Emotional Catharsis: The distorted sound of power chords adds an aggressive edge to the E major scale, evoking emotions that range from anger and frustration to exhilaration and triumph. They provide a cathartic outlet for intense feelings, resonating with audiences on a visceral level.
- Versatility Across Genres: While primarily associated with rock and metal, power chords have found their way into various genres, including punk, grunge, and even pop. Their versatility stems from their ability to create a sense of urgency and excitement, regardless of the musical context.
Incorporating power chords into E major scale guitar chords expands the guitarist’s sonic arsenal, enabling them to explore the raw and energetic side of the scale. These chords provide a foundation for creating electrifying riffs, driving rhythms, and emotionally charged solos, making them an essential element in the guitarist’s toolkit.
6. Extended Chords
Extended chords, venturing beyond the traditional triad structure, introduce additional notes to the E major scale guitar chords, unlocking a world of harmonic depth and complexity. These chords serve as essential building blocks for constructing sophisticated and emotionally resonant music.
By incorporating extended chords into their playing, guitarists gain access to a broader sonic palette, allowing them to create rich and evocative chord progressions that captivate audiences. These chords add color and character to the E major scale, enabling guitarists to express a wide range of emotions and musical ideas.
Examples of extended chords commonly used within the E major scale include the Emaj7 (E major 7th), Emaj9 (E major 9th), and Emaj11 (E major 11th) chords. Each extended chord adds a unique flavor to the harmony, enhancing the overall musical experience.
Mastering extended chords empowers guitarists to explore advanced musical concepts such as jazz improvisation, where these chords provide a harmonic foundation for intricate solos and chord substitutions. Additionally, extended chords are prevalent in contemporary pop and rock music, adding sophistication and harmonic interest to modern tracks.
Key Insights:
- Extended chords expand the harmonic possibilities of E major scale guitar chords.
- These chords add depth, complexity, and color to chord progressions.
- Mastering extended chords enhances technical proficiency and opens up new avenues for musical expression.
- Extended chords play a vital role in jazz improvisation and contemporary music.
7. Suspensions
Suspensions are a type of chord that creates a sense of tension and anticipation by temporarily omitting a specific note, typically the third or fifth. This omission creates a dissonance that resolves when the missing note returns, adding depth and interest to chord progressions.
In the context of E major scale guitar chords, suspensions are commonly used to create a sense of movement and forward motion. For example, a suspended fourth chord, such as Asus4, omits the third (G#) of the E major triad, creating a dissonant sound that resolves when the G# is played. This technique adds a sense of anticipation and momentum to the chord progression.
Suspensions can also be used to create a sense of space and openness in a chord progression. By omitting a note, suspensions allow the other notes to resonate more freely, creating a more airy and spacious sound. This effect can be particularly effective in fingerstyle guitar playing, where the use of open strings and suspended chords can create a rich and evocative soundscape.
Mastering the use of suspensions is an important aspect of developing a well-rounded guitar playing style. Suspensions add a sense of sophistication and interest to chord progressions, and they can be used to create a wide range of musical effects. By understanding the theory behind suspensions and how to use them effectively, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more expressive and engaging music.
8. Chord Progressions
Chord progressions are a fundamental aspect of music composition, and they play a vital role in the context of E major scale guitar chords. A chord progression is a sequence of chords that create a sense of movement and forward motion in a piece of music. By combining different chords in a logical and effective way, guitarists can create chord progressions that support the melody, create tension and release, and evoke a wide range of emotions.
In the context of E major scale guitar chords, there are a number of common chord progressions that are frequently used. These progressions are often based on the circle of fifths, which is a graphical representation of the relationship between different chords. The circle of fifths can be used to create a variety of chord progressions, including the I-IV-V progression, the I-V-vi-IV progression, and the ii-V-I progression.
These chord progressions are just a starting point, and guitarists can experiment with different combinations of chords to create their own unique progressions. By understanding the principles of chord progressions, guitarists can create more interesting and engaging music that will captivate their audience.
Key Insights:
- Chord progressions are essential for creating movement and forward motion in music.
- Guitarists can experiment with different combinations of chords to create their own unique progressions.
The circle of fifths can be used to create a variety of common chord progressions.
Practical Significance:
- Understanding chord progressions will help guitarists create more interesting and engaging music.
- Guitarists can use chord progressions to support the melody, create tension and release, and evoke a wide range of emotions.
- Chord progressions are a valuable tool for improvisation and songwriting.
9. Chord Embellishments
Chord embellishments are a collection of techniques, such as hammer-ons, pull-offs, and slides, that guitarists employ to add rhythmic and melodic interest to their playing. These techniques involve using the fretting hand to add or remove notes without picking the strings, creating a smooth and fluid sound. When applied to E major scale guitar chords, these embellishments elevate the chords, making them more expressive and dynamic.
Hammer-ons and pull-offs are closely related techniques that involve striking a string with the picking hand and then using the fretting hand to either hammer a note onto the fretboard or pull off a note to create a descending pitch. These techniques allow guitarists to play rapid-fire notes without the need for alternate picking, adding a percussive element to their playing. Slides, on the other hand, involve sliding the fretting finger along the string to create a smooth transition between notes. When used in conjunction with E major scale guitar chords, slides can create a bluesy or soulful sound, adding depth and emotion to the music.
Mastering these embellishments is essential for guitarists who want to add a personal touch to their playing and expand their technical abilities. By incorporating chord embellishments into their E major scale guitar chords, guitarists can create unique and expressive musical passages that captivate their audience.
Examples:
- Adding a hammer-on to the third fret of the high E string while playing an E major chord creates a lively and syncopated rhythm.
- Using a pull-off from the fifth fret to the third fret of the A string within an E major chord adds a descending melodic line, creating a sense of movement and interest.
- Sliding from the second fret to the fourth fret on the D string while playing an E major chord creates a smooth and expressive transition, evoking a bluesy feel.
10. Improvisation
Improvisation, the art of spontaneous musical creation, finds a fertile ground in the E major scale and its associated guitar chords. This interplay offers a framework for guitarists to explore their creativity, express their musicality, and connect with their audience on a deeper level.
- Tonal Center and Harmonic Foundation:
The E major scale provides a stable tonal center, grounding the improvisation within a specific key. Its chords, such as E major, A major, and B minor, serve as harmonic building blocks, offering a rich palette for creating melodic lines and chord progressions.
- Melodic Exploration:
The E major scale provides a framework for melodic exploration, with its distinct intervals and patterns. Guitarists can navigate the fretboard, crafting improvised solos that showcase their technical proficiency and musical imagination. The scale’s familiar melodies can serve as a foundation for creating new and exciting musical ideas.
- Chordal Embellishments:
E major scale guitar chords can be adorned with embellishments such as hammer-ons, pull-offs, and slides, adding rhythmic and melodic interest to improvised passages. These techniques allow guitarists to create fluid and expressive solos that captivate listeners.
- Emotional Expression:
The E major scale, with its bright and uplifting tonality, lends itself well to expressing a wide range of emotions in improvisation. From joyful melodies to introspective solos, guitarists can tap into the emotional power of the scale and chords to communicate their musical message.
By mastering the E major scale and its guitar chords, improvisers gain a powerful tool for spontaneous musical expression. This framework provides a solid foundation for developing improvisation skills, fostering creativity, and connecting with audiences through the universal language of music.
Frequently Asked Questions about E Major Scale Guitar Chords
This section addresses commonly asked questions and misconceptions regarding E major scale guitar chords, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding and dispel any confusion.
Question 1: What is the significance of the E major scale in guitar playing?
The E major scale is a fundamental scale for guitarists, serving as the basis for numerous chords and musical patterns. It provides a solid foundation for developing technical skills, understanding music theory, and creating expressive melodies and chord progressions.
Question 2: How do I build E major scale guitar chords?
To construct E major scale guitar chords, start with the root note, E, and follow the major scale formula: whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, whole step, half step. This pattern will guide you in forming major chords at each note of the scale.
Question 3: What are the most commonly used E major scale guitar chords?
The most frequently employed E major scale guitar chords include: E major (E, G#, B), A major (A, C#, E), B minor (B, D, F#), C#m (C#, E, G#), and F#m (F#, A, C#). These chords form the foundation of many popular songs and chord progressions.
Question 4: How can I practice and improve my E major scale guitar chord playing?
Regular practice is crucial for mastering E major scale guitar chords. Start by practicing each chord individually, focusing on accuracy and clean finger placement. Gradually increase the speed and incorporate chord transitions to enhance your dexterity. Additionally, playing along with songs or backing tracks can help you develop your timing and musicality.
Question 5: What are some tips for using E major scale guitar chords effectively in my playing?
To utilize E major scale guitar chords effectively, consider their harmonic relationships and how they create movement and tension within a song. Experiment with different voicings and inversions of the chords to add variation and interest to your playing. Additionally, practice connecting chords smoothly through transitions to ensure a fluid and professional sound.
Question 6: How can I expand my knowledge and skills beyond E major scale guitar chords?
To broaden your harmonic vocabulary, explore other scales and their associated chords. Learn about chord extensions and alterations to enhance the richness and complexity of your chord progressions. Furthermore, study music theory to gain a deeper understanding of how chords are constructed and function within the context of music.
These questions and answers provide a comprehensive overview of E major scale guitar chords, addressing common concerns and offering guidance for effective practice and application. By embracing these concepts and dedicating yourself t
o consistent practice, you can elevate your guitar playing skills and unlock a world of musical possibilities.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding and Utilizing E Major Scale Guitar Chords
Tips for Utilizing E Major Scale Guitar Chords
Integrating E major scale guitar chords into your playing opens up a vast array of harmonic possibilities. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your technique and musical expression:
Tip 1: Master the Basic Forms:
Begin by practicing the root position, first inversion, and second inversion of each E major scale chord. This will provide you with a solid foundation and enable you to construct chords effortlessly across the fretboard.
Tip 2: Explore Different Voicings:
Experiment with various voicings of E major scale chords to create unique and interesting sounds. By altering the order of the notes within the chord, you can add depth and variety to your playing.
Tip 3: Utilize Inversions for Harmonic Movement:
Inversions allow you to create smooth and logical chord progressions. By inverting chords, you can create a sense of movement and forward momentum within your music.
Tip 4: Practice Chord Transitions:
Smooth chord transitions are essential for creating a polished and professional sound. Practice transitioning between E major scale chords to improve your finger coordination and timing.
Tip 5: Incorporate Embellishments:
Add embellishments such as hammer-ons, pull-offs, and slides to your E major scale guitar chords to enhance their rhythmic and melodic interest. These techniques will add a personal touch to your playing and make your chords more expressive.
Key Takeaways:
- Mastering basic chord forms provides a strong foundation.
- Exploring different voicings adds depth and variety to your playing.
- Inversions create harmonic movement and logical chord progressions.
- Practicing chord transitions improves coordination and timing.
- Embellishments enhance the rhythmic and melodic interest of your chords.
By implementing these tips into your practice routine, you will significantly improve your ability to utilize E major scale guitar chords effectively. These techniques will empower you to create captivating and expressive music that resonates with your audience.
Conclusion
The exploration of E major scale guitar chords has unveiled a world of musical possibilities. Through a comprehensive understanding of the scale’s structure, chord constructions, and practical applications, guitarists can elevate their playing to new heights.
Embracing the tips and techniques outlined in this article will empower you to master E major scale guitar chords, incorporate them seamlessly into your playing, and unlock a vast repertoire of harmonic expressions. By practicing diligently and expanding your musical knowledge, you will transform your guitar playing into a captivating and expressive art form.
Youtube Video: