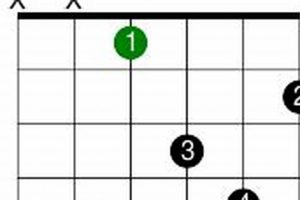
What is a Dominant 7th Chord on Guitar? Have you been wondering about this interesting yet essential chord? Well, it’s time to dive into the captivating world of music theory and explore the fascinating universe of dominant 7th chords on the guitar.
Editor’s Note:Understanding dominant 7th chords is not just crucial for guitarists but also beneficial for musicians across various skill levels. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of dominant 7th chords on the guitar, empowering you to enhance your musical prowess.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve meticulously crafted this in-depth guide to dominant 7th chords on the guitar. Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential musical element, enabling you to confidently incorporate it into your playing and unlock a wider range of harmonic possibilities.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
(Presented in an informative table format)
Transition to Main Article Topics:
- Unveiling the Structure and Anatomy of Dominant 7th Chords
- Exploring Inversions and Voicings for Harmonic Versatility
- Discovering the Magic of Dominant 7th Chords in Major and Minor Keys
- Unveiling the Power of Dominant 7th Chords in Chord Progressions
- Mastering the Art of Using Dominant 7th Chords in Real-World Musical Scenarios
- Additional Tips and Tricks for Enhancing Your Dominant 7th Chord Prowess
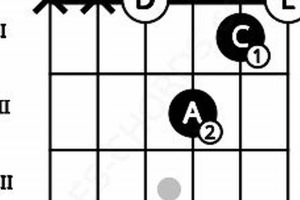
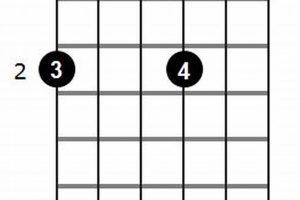
1. Construction
At the heart of dominant 7th chords on the guitar lies their distinct construction. This unique structure sets them apart from other chord types and defines their characteristic sound and function within harmonic progressions.
- Components:
Dominant 7th chords consist of four notes: the root, third, perfect fifth, and a flat seventh interval. This specific combination creates a dissonant yet stable sound that yearns for resolution.
- Intervallic Relationship:
The arrangement of intervals in a dominant 7th chord is crucial. The major third interval between the root and third, along with the minor seventh interval between the root and seventh, produces a characteristic tension and harmonic richness.
- Tonal Function:
Dominant 7th chords fulfill a specific tonal function within the harmonic structure of music. They are typically used as dominant chords, creating a sense of anticipation and leading towards a resolution to the tonic chord.
- Common Notations:
In guitar tablature, dominant 7th chords are often denoted with the root note followed by “7” or “maj7” (e.g., “C7” or “Cmaj7”). In chord diagrams, they are represented with a circle containing the letter “7” (e.g., C7).
Understanding the construction of dominant 7th chords is essential for guitarists to effectively utilize them in their playing. By grasping the unique combination of intervals and their tonal function, guitarists can harness the power of these chords to create sophisticated and expressive music.
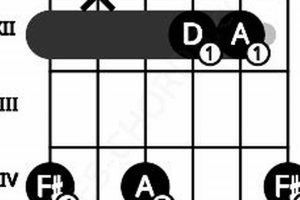
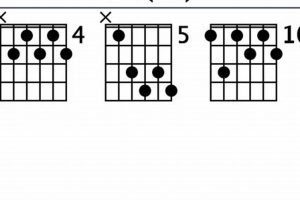
2. Inversions
In the realm of “dom 7 chord guitar,” inversions play a pivotal role in expanding harmonic possibilities and enhancing musical expression. By understanding and utilizing inversions, guitarists can create richer and more sophisticated chord voicings, adding depth and color to their playing.
- Unveiling Inversions:
Inversions occur when the root note of a chord is not the lowest note played. This technique allows guitarists to rearrange the notes of a dominant 7th chord, creating different voicings with unique harmonic qualities.
- First Inversion:
The first inversion of a dominant 7th chord places the third of the chord in the bass. This voicing creates a smoother and less dissonant sound, often used for creating flowing chord progressions.
- Second Inversion:
In the second inversion, the fifth of the chord becomes the lowest note. This inversion produces a more open and spacious sound, adding harmonic interest to chord sequences.
- Third Inversion:
The third inversion, with the seventh of the chord in the bass, creates a dissonant and unstable sound. This inversion is often used to build tension and lead into chord resolutions.
By incorporating inversions into their playing, guitarists can add harmonic depth and variety to their music, creating more engaging and expressive performances.
3. Major and Minor Keys
In the realm of “dom 7 chord guitar,” understanding the connection to major and minor keys is essential for unlocking a world of musical expression. Dominant 7th chords play distinct roles within different key contexts, shaping the harmonic landscape and creating unique emotional atmospheres.
- In Major Keys:
Dominant 7th chords serve as pillars of harmonic tension and resolution within major keys. They create a sense of anticipation and drive, propelling the music towards the tonic resolution. Their dissonant nature adds depth and richness to major key progressions.
- In Minor Keys:
In minor keys, dominant 7th chords take on a more complex character. They can function as leading chords, intensifying the harmonic tension and creating a sense of urgency. Additionally, they can provide a contrasting element, adding brightness and dissonance to the darker tonality of minor keys.
- Interplay and Contrast:
The interplay between dominant 7th chords in major and minor keys creates a dynamic and expressive range of possibilities. Guitarists can explore the contrasting effects of these chords, using them to create sections of tension and release, light and dark.
- Expanded Harmonic Vocabulary:
Understanding the roles of dominant 7th chords in both major and minor keys broadens a guitarist’s harmonic vocabulary. It allows for more sophisticated and nuanced chord progressions, enhancing the depth and emotional impact of their music.
By mastering the connection between “dom 7 chord guitar” and major and minor keys, guitarists unlock a gateway to a vast and expressive musical universe. These chords become powerful tools for crafting evocative melodies, creating harmonic tension and resolution, and adding depth and intrigue to their compositions.
4. Chord Progressions
In the realm of “dom 7 chord guitar,” chord progressions take center stage, highlighting the transformative power of dominant 7th chords in creating dynamic and expressive musical landscapes.
- Functional Role:
Dominant 7th chords play a pivotal functional role in chord progressions, acting as a catalyst for movement and resolution. Their inherent tension drives the music forward, creating a sense of anticipation and propelling the progression towards a satisfying resolution.
- Harmonic Movement:
The inclusion of dominant 7th chords in chord progressions introduces harmonic movement and variety. They can be used to create smooth transitions between chords, add and depth, and generate a sense of harmonic momentum.
- Cadential Patterns:
Dominant 7th chords are commonly employed in cadential patterns, such as the V-I cadence (dominant 7th chord resolving to the tonic chord). These cadences provide a strong sense of closure and finality, contributing to the overall structure and coherence of the music.
- Jazz and Blues Progressions:
In jazz and blues music, dominant 7th chords are an integral part of the harmonic language. They form the foundation of common progressions like the ii-V-I progression, adding harmonic sophistication and creating a driving rhythmic feel.
Understanding the power of dominant 7th chords in chord progressions empowers guitarists to craft more engaging and dynamic music. By incorporating these chords into their playing, they can create a wider range of harmonic possibilities, add depth and interest to their compositions, and master the art of creating satisfying musical resolutions.
5. Common Progressions
The connection between “Common Progressions: Identifying and mastering typical chord progressions involving dominant 7th chords” and “dom 7 chord guitar” lies in the fundamental role that dominant 7th chords play in creating sophisticated and engaging chord progressions. Understanding and mastering these progressions is essential for guitarists seeking to enhance their harmonic vocabulary and expand their musical expression.
Importance of Common Progressions: Common progressions involving dominant 7th chords, such as the ii-V-I progression, provide a solid foundation for improvisation and composition in various musical genres. By mastering these progressions, guitarists gain a deeper understanding of harmonic movement and can create more dynamic and expressive music.
Real-Life Examples: One of the most iconic examples of a common progression involving dominant 7th chords is the blues progression. This 12-bar progression, typically played in the key of E, uses dominant 7th chords on the IV (IV7), V (V7), and I (I7) chords. By understanding the functional relationships within this progression, guitarists can create compelling blues solos and chord melodies.
Practical Significance: Understanding common progressions involving dominant 7th chords empowers guitarists to:
- Craft more sophisticated and engaging chord progressions in their own compositions
- Communicate more effectively with other musicians during improvisation sessions
- Deepen their understanding of music theory and expand their harmonic vocabulary
Key Insights:
- Common progressions involving dominant 7th chords provide a roadmap for creating dynamic and expressive music
- Mastering these progressions enhances harmonic understanding, improvisation skills, and overall musicianship
- The ii-V-I progression is a fundamental building block for many musical genres and a valuable tool for guitarists to explore
Table of Common Progressions:
| Progression | Description |
|---|---|
| ii-V-I | Common in jazz, blues, and pop music, creates a strong sense of resolution |
| IV-V-I | Also known as the “authentic cadence,” found in many classical and folk melodies |
| I-vi-IV-V | A common progression in pop and rock music, provides a sense of movement and release |
| vi-ii-V-I | Often used in jazz and blues, creates a sophisticated and unexpected harmonic journey |
6. Jazz and Blues
The connection between “Jazz and Blues: Exploring the prominence in jazz and blues genres” and “dom 7 chord guitar” lies in the fundamental role that dominant 7th chords play in the harmonic language of these genres. Understanding and mastering the use of dominant 7th chords is essential for guitarists seeking to play jazz and blues authentically and expressively.
- Harmonic Foundation:
In jazz and blues, dominant 7th chords form the backbone of harmonic progressions, providing a rich and complex harmonic foundation. Their dissonant nature creates tension and movement, driving the music forward and giving it a distinctive rhythmic feel.
- Improvisation and Soloing:
Dominant 7th chords are essential for improvisation and soloing in jazz and blues. Guitarists use the chord tones and tensions of these chords to create melodic lines that are both harmonically sophisticated and emotionally expressive.
- Comping and Chord Melodies:
In jazz, guitarists often play comping patterns that accompany soloists, using dominant 7th chords to create rhythmic and harmonic interest. Additionally, dominant 7th chords can be used to create beautiful and memorable chord melodies.
- Historical Significance:
The use of dominant 7th chords in jazz and blues has a long and rich history. These chords were first used in New Orleans jazz in the early 20th century, and they have since become an integral part of the harmonic language of both genres.
Mastering the use of dominant 7th chords on the guitar is essential for any guitarist who wants to play jazz or blues authentically and expressively. These chords provide a solid foundation for improvisation, soloing, and comping, and they have a rich and storied history in these genres.
7. Function and Resolution
The connection between “Function and Resolution: Understanding their functional role and resolution tendencies” and “dom 7 chord guitar” lies in the essential role that dominant 7th chords play in creating harmonic movement and resolving tension in music. Understanding the functional role and resolution tendencies of dominant 7th chords is crucial for guitarists seeking to master the art of chord progressions and create expressive and engaging music.
Functional Role:
In music theory, chords are often categorized based on their function within a chord progression. Dominant 7th chords primarily serve as dominant chords, meaning they create a sense of tension and anticipation that resolves to a tonic chord. This functional role is rooted in the dissonant interval between the root and the flat seventh, which creates a strong pull towards resolution.
Resolution Tendencies:
The resolution tendencies of dominant 7th chords are d
etermined by the leading tone created by the flat seventh interval. This leading tone has a strong tendency to resolve up by a half step to the tonic note, creating a satisfying sense of closure. The other notes in the dominant 7th chord (the root, third, and fifth) typically resolve down by step to the corresponding notes in the tonic chord.
Real-Life Examples:
One of the most common examples of a dominant 7th chord resolution is the V-I cadence (also known as the “perfect cadence”). In this cadence, a dominant 7th chord (e.g., G7) resolves to the tonic chord (e.g., Cmaj7). This cadence is widely used in Western music to create a strong sense of finality and closure.
Practical Significance:
Understanding the functional role and resolution tendencies of dominant 7th chords empowers guitarists to:
- Craft more sophisticated and effective chord progressions
- Create a stronger sense of harmonic movement and resolution in their music
- Communicate more effectively with other musicians during improvisation and composition
Key Insights:
- Dominant 7th chords play a crucial functional role in creating harmonic tension and resolving to tonic chords.
- The flat seventh interval in a dominant 7th chord creates a leading tone that resolves up to the tonic note.
- Understanding the resolution tendencies of dominant 7th chords is essential for creating satisfying and effective chord progressions.
8. Extended Chords
The connection between “Extended Chords: Expanding harmonic possibilities with extended dominant 7th chords” and “dom 7 chord guitar” lies in the expanded sonic palette and harmonic sophistication that extended dominant 7th chords offer to guitarists. By incorporating extended chords into their playing, guitarists can create more complex and interesting chord voicings, enhance their improvisational vocabulary, and explore new and uncharted harmonic territories.
Extended dominant 7th chords are created by adding additional notes beyond the basic four-note structure of a dominant 7th chord (root, third, fifth, and flat seventh). These additional notes can include the ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth intervals, resulting in chords such as the dominant 9th (add9), dominant 11th (add11), and dominant 13th (add13).
The inclusion of these extended intervals adds richness, depth, and harmonic color to the basic dominant 7th chord. Extended chords can be used to create lush and sophisticated chord progressions, add tension and release to harmonic structures, and explore new and innovative soundscapes.
In jazz guitar, extended dominant 7th chords are a staple of the harmonic language. Guitarists such as Wes Montgomery, Pat Martino, and George Benson have made extensive use of extended chords in their playing, creating a distinctive and harmonically sophisticated style.
Understanding and mastering extended dominant 7th chords is essential for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of the instrument. These chords provide a gateway to a world of harmonic possibilities, allowing guitarists to create music that is both beautiful and intellectually stimulating.
Key Insights:
- Extended dominant 7th chords expand the harmonic possibilities available to guitarists.
- These chords can be used to create lush and sophisticated chord progressions.
- Extended dominant 7th chords are a staple of the jazz guitar harmonic language.
- Understanding and mastering these chords is essential for guitarists who want to explore the full potential of the instrument.
9. Improvisation
The connection between “Improvisation: Unlocking improvisational freedom through dominant 7th chord voicings” and “dom 7 chord guitar” lies in the central role that dominant 7th chords play in jazz and blues improvisation. Understanding and mastering the art of dominant 7th chord voicings is essential for guitarists who want to develop their improvisational skills and create expressive and spontaneous solos.
- Voicings and Inversions:
Dominant 7th chords can be voiced and inverted in a variety of ways, each with its own unique sound and harmonic implications. By exploring different voicings, guitarists can create improvised lines that are both melodically interesting and harmonically sophisticated.
- Target Notes:
When improvising over dominant 7th chords, guitarists often target specific notes within the chord, such as the root, third, fifth, or seventh. These target notes provide a harmonic framework for the improvisation and help to ensure that the lines are musically coherent.
- Scales and Arpeggios:
Scales and arpeggios derived from dominant 7th chords provide a valuable resource for improvising. By practicing these scales and arpeggios, guitarists can develop the fingerboard fluency and harmonic knowledge necessary for creating fluid and expressive improvised lines.
- Real-Life Examples:
Countless jazz and blues guitarists have mastered the art of dominant 7th chord improvisation. Some notable examples include:
- Wes Montgomery
- Pat Martino
- George Benson
- John Scofield
In conclusion, the study of dominant 7th chord voicings is essential for guitarists who want to develop their improvisational skills. By understanding the different ways to voice and invert these chords, targeting specific notes, and practicing scales and arpeggios, guitarists can unlock the full potential of dominant 7th chords and create improvised lines that are both musically sophisticated and emotionally expressive.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dominant 7th Chords on Guitar
This section addresses commonly asked questions and misconceptions surrounding dominant 7th chords on the guitar, providing clear and informative answers to enhance your understanding and playing.
Question 1: What is the difference between a dominant 7th chord and a major 7th chord?
A dominant 7th chord includes a flat seventh interval, creating a dissonant sound that resolves to the tonic chord. In contrast, a major 7th chord has a major seventh interval, resulting in a more stable and consonant sound.
Question 2: How do I construct a dominant 7th chord on the guitar?
To construct a dominant 7th chord, start with the root note, then add the major third, perfect fifth, and flat seventh intervals. For example, to create a G7 chord, you would play the notes G, B, D, and F.
Question 3: What are some common ways to use dominant 7th chords in music?
Dominant 7th chords are frequently used in chord progressions to create a sense of tension and movement. They are also employed in improvisation, providing a harmonic framework for soloing.
Question 4: How can I improve my dominant 7th chord voicings?
Experiment with different voicings and inversions to discover the sounds that best suit your musical style. Practice transitioning smoothly between voicings to enhance your harmonic vocabulary.
Question 5: What are some tips for playing dominant 7th chords effectively on guitar?
Ensure your fingers are properly positioned and that you are using the correct fretting t
echnique. Practice regularly to improve your finger coordination and overall dexterity.
Summary:
Understanding dominant 7th chords on the guitar is crucial for expanding your harmonic knowledge and enhancing your playing abilities. By incorporating these chords into your playing, you can add depth, sophistication, and expressive potential to your music.
Transition:
Now that we have explored the fundamentals of dominant 7th chords on the guitar, let’s delve into more advanced concepts and techniques to further your understanding and playing skills.
Tips for Mastering Dominant 7th Chords on Guitar
Incorporating dominant 7th chords into your guitar playing opens up a world of harmonic possibilities. Here are some essential tips to help you master these versatile chords:
Tip 1: Understand Their Construction
Dominant 7th chords consist of the root, major third, perfect fifth, and flat seventh intervals. This unique structure creates their characteristic dissonant yet stable sound.
Tip 2: Practice Different Voicings
Experiment with various voicings and inversions of dominant 7th chords. This will enhance your harmonic vocabulary and allow you to create diverse and interesting chord progressions.
Tip 3: Target Specific Notes
When improvising or soloing over dominant 7th chords, learn to target specific notes within the chord, such as the root, third, fifth, or seventh. This will help you create melodically coherent and harmonically sophisticated lines.
Tip 4: Use Dominant 7th Chord Extensions
Adding extensions to dominant 7th chords, such as the ninth, eleventh, or thirteenth intervals, can further enrich your harmonic palette. Explore these extended chords to create lush and complex sounds.
Tip 5: Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is key to mastering dominant 7th chords on the guitar. Dedicate time to practicing scales, arpeggios, and chord progressions that incorporate these chords.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding and playing of dominant 7th chords on the guitar. Embrace the harmonic possibilities they offer to add depth, sophistication, and expressiveness to your music.
Transition:
As you continue your journey with dominant 7th chords, discover how they interact with other chords and how you can utilize them effectively in various musical contexts.
Conclusion
The exploration of dominant 7th chords on the guitar has unveiled a treasure trove of harmonic possibilities. These chords, with their unique construction and inherent tension, have become an indispensable tool for guitarists seeking to expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their playing.
By understanding the construction, voicings, and functional roles of dominant 7th chords, guitarists can unlock a universe of harmonic colors and expressive potential. Incorporating these chords into chord progressions, improvisational solos, and various musical styles allows for the creation of sophisticated and emotionally resonant music.
The journey with dominant 7th chords is an ongoing one, filled with opportunities for exploration and growth. As guitarists delve deeper into the intricacies of these chords, they will continue to discover new ways to harness their power and create music that captivates and inspires.