Unveiling the d#dim7 Guitar Chord: A Comprehensive Guide
Editor’s Note:The d#dim7 guitar chord is an essential tool for any guitarist looking to expand their harmonic vocabulary. This guide will provide an in-depth exploration of this versatile chord, including its construction, voicings, and musical applications.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve compiled this comprehensive guide to empower guitarists with the knowledge and skills to master the d#dim7 chord. This guide will delve into the intricacies of this chord, providing a solid foundation for musical exploration and expression.
Key Takeaways:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Construction | Explores the notes that comprise the d#dim7 chord and their relationship to the d# harmonic minor scale. |
| Voicings | Presents various fingerings and voicings for the d#dim7 chord, catering to different playing styles and preferences. |
| Musical Applications | Demonstrates the practical use of the d#dim7 chord in various musical contexts, including jazz, blues, and rock. |
Delving into the Main Article Topics:
1. Construction
The construction of the d#dim7 guitar chord, a diminished seventh chord built on the root d#, is a fundamental aspect that shapes its unique sound and harmonic function. This construction entails stacking diminished intervals, specifically three minor thirds, upon the root note d#.
- Intervallic Structure: The d#dim7 chord comprises the following intervals: d# (root), f (minor third), a (diminished fifth), and c (double diminished seventh). This intervallic structure creates a dissonant and unresolved sound, contributing to the chord’s characteristic tension.
- Tonal Context: The d#dim7 chord can exist in various tonal contexts, but it commonly functions as a pre-dominant chord, leading to a dominant chord and ultimately resolving to a tonic chord. This progression creates a sense of harmonic movement and resolution.
- Harmonic Function: As a diminished seventh chord, d#dim7 often serves as a connector or transition chord between other harmonies. Its dissonant nature adds tension and instability, propelling the music forward and creating a sense of anticipation.
- Voicings: The construction of the d#dim7 chord allows for multiple voicings on the guitar. Different voicings can emphasize specific intervals or create different harmonic effects, catering to the guitarist’s desired sound and musical context.
In summary, the construction of the d#dim7 guitar chord, built on the root d# and comprising diminished intervals, gives rise to its dissonant and unresolved sound. This construction influences the chord’s tonal context, harmonic function, and the availability of various voicings, making it a versatile tool for guitarists to explore and utilize in their musical endeavors.
2. Voicings
The d#dim7 guitar chord offers a diverse array of voicings, each with its unique character and utility. These voicings arise from the multiple fingerings possible on the guitar, allowing guitarists to tailor the chord to their playing style and the desired harmonic effect.
- Tonal Flexibility: Different voicings can emphasize specific notes within the d#dim7 chord, such as the root, third, fifth, or seventh. This tonal flexibility enables guitarists to highlight particular melodic lines or create specific harmonic tensions.
- Inversional Possibilities: Inversions of the d#dim7 chord, such as d#dim7/f or d#dim7/a, offer alternative voicings with distinct harmonic implications. These inversions can alter the chord’s root position, creating different melodic contours and harmonic progressions.
- Playing Comfort and Accessibility: The availability of multiple voicings caters to different hand sizes and playing styles. Some voicings may be more comfortable or accessible for certain guitarists, allowing them to play the d#dim7 chord with greater ease and efficiency.
- Stylistic Versatility: Different voicings can evoke diverse musical styles. For instance, close voicings may lend a jazzier sound, while open voicings can create a more spacious and atmospheric effect. Guitarists can choose voicings that align with the desired musical genre or mood.
In summary, the multiple fingerings and voicings available for the d#dim7 guitar chord empower guitarists with a wide range of tonal, harmonic, and stylistic possibilities. By understanding and utilizing these voicings effectively, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance the expressiveness of their playing.
3. Inversions
Inversions of the d#dim7 guitar chord play a significant role in shaping its harmonic functionality and expressive potential. Inversions involve reordering the notes of the chord, placing a different note as the bass note. This technique allows guitarists to create diverse harmonic effects and voice leading possibilities.
The d#dim7 chord has three inversions, each with its unique sound and application:
- d#dim7 (root position): This is the standard voicing of the chord, with d# as the bass note.
- d#dim7/f (first inversion): With f as the bass note, this inversion emphasizes the minor third interval and can create a more dissonant sound.
- d#dim7/a (second inversion): This inversion, with a as the bass note, highlights the diminished fifth interval and often provides a smoother transition to other chords.
By utilizing inversions, guitarists can achieve various harmonic effects:
- Harmonic Tension and Release: Inversions can create a sense of tension and release within a chord progression. For instance, moving from a root position d#dim7 to a first inversion d#dim7/f can intensify the dissonance, which can then be resolved by moving to a more consonant chord.
- Voice Leading: Inversions allow for smoother voice leading between chords. By carefully choosing the inversion of the d#dim7 chord, guitarists can create melodic lines that flow naturally and avoid awkward leaps.
- Stylistic Versatility: Different inversions can evoke different musical styles. Root position chords often provide a strong and stable foundation, while inversions can add a more nuanced and sophisticated harmonic color.
Understanding and utilizing inversions of the d#dim7 guitar chord is essential for expand
ing harmonic possibilities and enhancing musical expression. By incorporating inversions into their playing, guitarists can create more dynamic and engaging chord progressions, add depth and color to their harmonies, and explore a wider range of musical styles.
Table: Harmonic Effects of d#dim7 Inversions
| Inversion | Bass Note | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Root Position | d# | Standard voicing, strong and stable |
| First Inversion | f | Emphasizes minor third, creates dissonance |
| Second Inversion | a | Highlights diminished fifth, smoother transitions |
4. Harmonic Function
The d#dim7 guitar chord plays a vital harmonic function, serving as a dissonant chord that creates tension and resolves to major or minor chords. This dissonance arises from the diminished intervals within the chord, particularly the diminished fifth and double diminished seventh intervals.
The d#dim7 chord’s dissonant nature makes it an effective tool for creating harmonic tension and movement within a chord progression. When used judiciously, it can add depth, interest, and a sense of anticipation to the music. By resolving the dissonance to a more consonant chord, such as a major or minor chord, guitarists can create a sense of release and harmonic satisfaction.
Furthermore, the d#dim7 chord can also function as a pre-dominant chord, leading to a dominant chord and ultimately resolving to a tonic chord. This harmonic progression is commonly found in jazz, blues, and other musical genres, and it creates a strong sense of harmonic movement and resolution.
In summary, the harmonic function of the d#dim7 guitar chord as a dissonant chord is crucial for creating tension and movement within chord progressions. By understanding and utilizing this harmonic function effectively, guitarists can enhance the expressiveness and impact of their music.
Table: Harmonic Function of the d#dim7 Chord
| Function | Effect |
|---|---|
| Dissonant chord | Creates tension and anticipation |
| Pre-dominant chord | Leads to a dominant chord and resolves to a tonic chord |
5. Musical Applications
The d#dim7 guitar chord finds its home in a diverse range of musical genres, each utilizing its unique harmonic properties to create distinct moods and atmospheres. Let’s explore its multifaceted applications:
- Jazz: In the improvisational world of jazz, the d#dim7 chord adds tension and complexity to chord progressions. Its dissonant nature provides a platform for soloists to explore melodic possibilities and create intricate lines that resolve to more consonant chords.
- Blues: The d#dim7 chord adds a touch of harmonic sophistication to blues music. Its diminished intervals create a sense of longing and melancholy, enhancing the emotional depth of blues compositions.
- Rock: While less common in traditional rock music, the d#dim7 chord can add a touch of dissonance and intrigue to rock solos and chord progressions. Its unexpected sound can create moments of tension and release, adding depth and interest to the music.
The versatility of the d#dim7 guitar chord stems from its ability to create tension and resolve to a variety of other chords. This makes it a valuable tool for musicians seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more expressive and dynamic music.
6. Improvisation
The d#dim7 guitar chord stands out as a versatile tool for improvisation, offering a vast landscape of melodic possibilities. Its dissonant nature provides a fertile ground for exploration, allowing guitarists to create intricate and expressive solos.
- Tonal Flexibility: The d#dim7 chord’s diminished intervals create a unique and malleable harmonic environment. Guitarists can explore different melodic lines that resolve to various tonal centers, creating a sense of harmonic freedom and endless possibilities.
- Dissonant Counterpoint: The dissonant intervals within the d#dim7 chord lend themselves well to creating dissonant counterpoint lines. By playing melodic lines that clash with the chord’s harmony, guitarists can generate tension and release, adding depth and interest to their solos.
- Chromatic Embellishments: The chromatic notes found within the d#dim7 chord provide ample opportunities for chromatic embellishments. Guitarists can incorporate chromatic passing tones, leading tones, and appoggiaturas to create melodic lines that are both harmonically rich and technically challenging.
- Outside Playing: The d#dim7 chord’s dissonant nature encourages guitarists to explore “outside” playing, venturing beyond the traditional scales and arpeggios associated with the chord. This approach can lead to innovative and unexpected melodic ideas that push the boundaries of conventional harmony.
In conclusion, the d#dim7 guitar chord’s versatility in improvisation stems from its dissonant intervals and harmonic ambiguity. It provides a platform for guitarists to explore a wide range of melodic possibilities, from tonal flexibility to dissonant counterpoint, chromatic embellishments, and outside playing. By mastering this chord, guitarists can unlock a new level of creativity and expression in their solos.
7. Tonal Center
The d#dim7 guitar chord possesses a remarkable ability to establish or imply different tonal centers when used in chord progressions. This characteristic stems from its inherent harmonic ambiguity and dissonant nature.
- Modulation: The d#dim7 chord can act as a pivot chord, enabling smooth modulation between different keys. Its dissonant intervals allow it to resolve to multiple tonal centers, creating a sense of harmonic movement and progression.
- Tonicization: When used in a non-diatonic context, the d#dim7 chord can temporarily establish a new tonal center. This technique, known as tonicization, adds harmonic depth and interest to chord progressions.
- Harmonic Suspension: The d#dim7 chord can create a sense of harmonic suspension, delaying the resolution to a more consonant chord. This creates tension and anticipation, enhancing the impact of the eventual resolution.
- Polytonality: In advanced musical contexts, the d#dim7 chord can contribute to the creation of polytonal passages, where multiple tonal centers coexist simultaneously. This technique adds a layer of harmonic complexity and intrigue to the music.
In summary, the d#dim7 guitar chord’s ability to establish or imply different tonal centers is a testament to its versatility and harmonic power. By understanding and utilizing this char
acteristic effectively, guitarists can create chord progressions that are both harmonically rich and expressively captivating.
8. Chord Substitutions
The d#dim7 guitar chord’s versatility extends to its interchangeable relationship with other diminished seventh chords, such as c#dim7 and fdim7. This interchangeability stems from the inherent symmetry and shared harmonic function among diminished seventh chords.
In music theory, diminished seventh chords are constructed using a specific intervallic pattern: root, minor third, diminished fifth, and double diminished seventh. This pattern creates a dissonant and unstable sound that resolves naturally to a major or minor chord. As a result, diminished seventh chords often serve as transitional chords in chord progressions, adding tension and harmonic movement.
The d#dim7, c#dim7, and fdim7 chords all share this diminished seventh structure. Therefore, they can be substituted for each other in many musical contexts without significantly altering the harmonic progression. This interchangeability allows guitarists to explore different voicings and harmonic possibilities while maintaining the overall harmonic function of the chord.
For instance, in a jazz improvisation, a guitarist might choose to substitute d#dim7 with c#dim7 to create a smoother voice leading or to avoid awkward fingerings on the guitar. Similarly, in a rock or blues context, substituting d#dim7 with fdim7 can add a slightly different harmonic color while still providing the necessary dissonant tension.
Understanding and utilizing chord substitutions is a valuable skill for guitarists. It allows them to expand their harmonic vocabulary, enhance their improvisational abilities, and create more dynamic and interesting chord progressions.
Table: Chord Substitutions for d#dim7
| Original Chord | Substituted Chord |
|---|---|
| d#dim7 | c#dim7 |
| d#dim7 | fdim7 |
9. Voice Leading
Voice leading plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and logical chord transitions, especially when dealing with dissonant chords like d#dim7. Voice leading refers to the movement of individual voices (melodic lines) within a chord progression, and it aims to create a sense of coherence and flow in the music.
When transitioning to or from a d#dim7 chord, it’s essential to consider the voice leading of each note within the chord. The dissonant intervals in d#dim7 (the diminished fifth and double diminished seventh) can create tension and instability if not handled carefully.
To achieve smooth voice leading, follow these principles:
- Avoid parallel fifths and octaves: When moving from one chord to another, ensure that no two voices move in parallel fifths or octaves. This can create a harsh and dissonant sound.
- Resolve dissonant intervals: The dissonant intervals in d#dim7 should be resolved to consonant intervals in the following chord. For example, the diminished fifth can resolve to a perfect fifth or fourth, and the double diminished seventh can resolve to a major or minor third.
- Maintain voice ranges: Keep the voices within a reasonable range to avoid awkward leaps or voice crossings. This helps maintain a smooth melodic flow.
Understanding and applying these voice leading principles is essential for guitarists who want to incorporate d#dim7 and other dissonant chords into their playing. It allows for seamless and musical chord transitions, enhancing the overall sound and expressiveness of their music.
Example:
Consider the following chord progression: d#dim7 – Gmaj7
- The d#dim7 chord can be voiced as: d# (root), f (minor third), a (diminished fifth), and c (double diminished seventh).
- To transition smoothly to Gmaj7, the dissonant intervals (a and c) should be resolved. The a can resolve down to g (perfect fifth), and the c can resolve up to d (major third).
- The voice leading could be as follows: d# (d#dim7) – g (Gmaj7), f (d#dim7) – e (Gmaj7), a (d#dim7) – g (Gmaj7), c (d#dim7) – d (Gmaj7).
By following the principles of voice leading, the transition from d#dim7 to Gmaj7 becomes smooth and logical, enhancing the overall musicality of the progression.
Conclusion:
Understanding voice leading is crucial for effective use of the d#dim7 guitar chord and other dissonant chords. By applying the principles of parallel motion, interval resolution, and voice range maintenance, guitarists can create smooth and musical chord transitions that enhance the overall impact of their playing.
10. Extended Chords
Extending the d#dim7 guitar chord leads to the creation of more complex and dissonant harmonies, enriching the sonic possibilities for guitarists. By adding additional notes to the basic d#dim7 structure, extended chords offer a wider range of harmonic colors and textures to explore.
Two common extensions for the d#dim7 chord are d#dim7(add9) and d#dim7(b5):
- d#dim7(add9): This extended chord adds a major ninth (f##) to the basic d#dim7 structure. The addition of the ninth interval creates a more dissonant and unresolved sound, adding tension and interest to chord progressions.
- d#dim7(b5): This extended chord replaces the perfect fifth (a) in the d#dim7 structure with a diminished fifth (ab). The diminished fifth interval intensifies the dissonance and creates a darker, more somber harmonic color.
Extended chords like d#dim7(add9) and d#dim7(b5) are valuable tools for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and expressive music. Understanding how to utilize these extended chords effectively can open up new avenues for musical exploration and creativity.
In practice, extended chords are commonly used in jazz, fusion, and other genres where harmonic complexity and experimentation are valued. They can add depth and sophistication to chord progressions, create dissonant tension, and provide a platform for improvisational exploration.
To master the use of extended chords, guitarists should focus on understanding their construction, practicing different voicings, and experimenting with their application in various musical contexts. By incorporating extended chords into their playing, guitarists can elevate their harmonic knowledge and enhance the expressiveness of their music.
Table: Extended d#dim7 Chords
| Extended Chord | Added Note | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| d#dim7(add9) | Major ninth (f) | Adds dissonance and unresolved sound |
| d#dim7(b5) | Diminished fifth (ab) | Intensifies dissonance, creates a darker harmonic color |
11. Diatonic Context
The diatonic context of the d#dim7 guitar chord significantly influences its function and sound within a musical piece. The diatonic context refers to the collection of seven notes that make up a particular key or scale. When a chord is used within its diatonic context, it has a specific harmonic relationship to the other chords in that key and can evoke certain emotional responses.
The d#dim7 chord, for example, can have different functions and implications depending on its diatonic context:
- In the key of D# major: The d#dim7 chord is the vii7 chord, which typically functions as a pre-dominant chord leading to the dominant chord (G#maj7) and ultimately resolving to the tonic chord (D#maj7). In this context, the d#dim7 chord creates a sense of tension and anticipation, propelling the music forward.
- In the key of E major: The d#dim7 chord is the iii7 chord, which can be used as a substitute for the tonic chord (Emaj7). It adds a touch of dissonance and complexity to the progression, creating a more sophisticated and nuanced harmonic color.
- In the key of B minor: The d#dim7 chord is the viio7 chord, which is commonly used as a leading chord to resolve to the tonic chord (Bmin7). In this context, the d#dim7 chord intensifies the sense of harmonic movement and provides a strong sense of resolution.
Understanding the diatonic context of the d#dim7 chord is essential for guitarists to use it effectively and expressively. By considering the harmonic relationships and emotional implications of the chord within different keys, guitarists can make informed choices about when and how to incorporate it into their music.
Table: Diatonic Context and Function of the d#dim7 Chord
| Key | Diatonic Function | Emotional Implication |
|---|---|---|
| D# major | vii7 | Tension, anticipation |
| E major | iii7 | Dissonance, complexity |
| B minor | viio7 | Intensified harmonic movement, strong resolution |
12. Aural Recognition
The ability to recognize the d#dim7 chord by ear is a fundamental skill for guitarists and musicians alike. Aural recognition plays a vital role in developing musical proficiency and enhancing overall musicianship. Here’s why it matters:
Enhanced Ear Training: Recognizing the d#dim7 chord by ear requires a trained ear that can identify its unique sonic characteristics, such as its dissonant intervals and overall harmonic tension. This ear training translates to improved recognition of other chords and musical patterns, fostering a deeper understanding of music theory and harmony.
Improvisation and Soloing: The ability to recognize the d#dim7 chord by ear is crucial for improvisation and soloing. Guitarists who can quickly identify this chord can seamlessly incorporate it into their solos, creating melodic lines that navigate its harmonic complexity and adding depth to their improvisational vocabulary.
Ensemble Playing: In ensemble settings, recognizing the d#dim7 chord by ear enables guitarists to follow chord changes more effectively. This skill is particularly important in jazz and other genres where complex chord progressions are common. By being able to aurally identify the d#dim7 chord, guitarists can adapt and respond to musical cues from their fellow musicians, contributing to a cohesive and dynamic ensemble performance.
Transcription and Analysis: Musicians often need to transcribe or analyze music by ear. The ability to recognize the d#dim7 chord is essential for accurately transcribing and understanding chord progressions, melodies, and harmonic structures found in recorded music or live performances.
Developing a Musical Ear: Aural recognition of the d#dim7 chord is a stepping stone towards developing a well-rounded musical ear. By training themselves to identify this specific chord, guitarists lay the groundwork for recognizing a wider range of chords, intervals, and harmonic progressions, enhancing their overall musical comprehension and appreciation.
In summary, developing the ability to recognize the d#dim7 chord by ear is an invaluable skill for guitarists and musicians. It enhances ear training, facilitates improvisation and soloing, improves ensemble playing, aids in transcription and analysis, and contributes to the development of a strong musical ear.
Table: Benefits of Aural Recognition of the d#dim7 Chord
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Ear Training | Develops the ability to identify unique sonic characteristics of the d#dim7 chord and other musical patterns. |
| Improved Improvisation and Soloing | Enables guitarists to incorporate the d#dim7 chord into solos, adding depth and complexity to their melodic lines. |
| Effective Ensemble Playing | Allows guitarists to follow chord changes in ensemble settings, contributing to a cohesive performance. |
| Accurate Transcription and Analysis | Facilitates accurate transcription and analysis of music by ear, including chord progressions and harmonic structures. |
| Development of a Musical Ear | Contributes to the development of a well-rounded musical ear, enhancing overall musical comprehension and appreciation. |
Frequently Asked Questions about the d#dim7 Guitar Chord
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the d#dim7 guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to enhance your understanding.
Question 1: What is the construction of the d#dim7 guitar chord?
Answer: The d#dim7 chord is a diminished seventh chord built on the root note d#. It consists of four notes: d# (root), f (minor third), a (diminished fifth), and c (double diminished seventh).
Question 2: How can I identify the d#dim7 chord by ear?
Answer: The d#dim7 chord has a distinctive dissonant sound characterized by its diminished fifth (a) and double diminished seventh (c) intervals. Training your ear to recognize these intervals is crucial for aural recognition.
Question 3: What are some common voicings for the d#dim7 chord on the guitar?
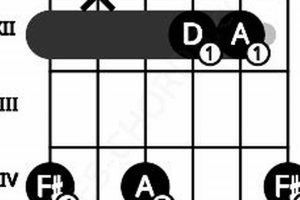
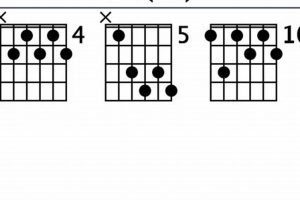
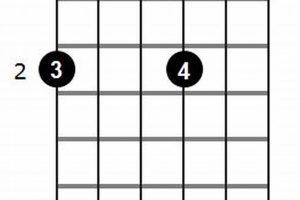
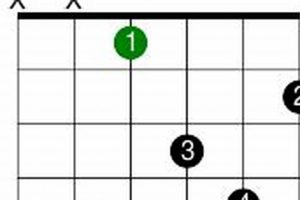
Answer: There are multiple voicings for the d#dim7 chord on the guitar. Some common voicings include:
- x46454
- x65454
- x43211
- x20212
Question 4: How is the d#dim7 chord typically used in music?
Answer: The d#dim7 chord is commonly used as a dissonant chord to create tension and resolve to major or minor chords. It often functions as a pre-dominant chord, leading to a dominant chord and ultimately resolving to a tonic chord.
Question 5: Can the d#dim7 chord be substituted for other diminished seventh chords?
Answer: Yes, the d#dim7 chord can be substituted for other diminished seventh chords, such as c#dim7 or fdim7, due to their shared diminished seventh structure and harmonic function.
Question 6: What is the importance of voice leading when using the d#dim7 chord?
Answer: Voice leading is crucial for smooth chord transitions involving the d#dim7
chord. Proper voice leading ensures that dissonant intervals are resolved smoothly, avoiding awkward voice crossings and maintaining a coherent melodic flow.
Summary: Understanding the construction, voicings, uses, and harmonic implications of the d#dim7 guitar chord is essential for guitarists. By incorporating this versatile chord into your playing, you can add depth, complexity, and expressiveness to your music.
Transition to the next article section: Explore the practical applications of the d#dim7 guitar chord in various musical contexts, including jazz, blues, and rock.
Tips for Mastering the d#dim7 Guitar Chord
Incorporating the d#dim7 guitar chord into your playing requires careful consideration and practice. Here are some essential tips to guide you:
Tip 1: Understand its Construction and Voicings:Grasp the construction of the d#dim7 chord and explore various fingerings (voicings) to find those that suit your playing style and the desired harmonic effect.
Tip 2: Practice Voice Leading:Pay attention to voice leading when transitioning to or from the d#dim7 chord. Resolve dissonant intervals smoothly to avoid awkward melodic jumps.
Tip 3: Explore Harmonic Substitutions:Become familiar with other diminished seventh chords, such as c#dim7 and fdim7, which can be interchanged with d#dim7 in certain contexts.
Tip 4: Experiment with Extended Chords:Expand the harmonic possibilities by experimenting with extended chords like d#dim7(add9) and d#dim7(b5).
Tip 5: Consider the Diatonic Context:Understand the diatonic context in which you use the d#dim7 chord. Its function and sound can vary depending on the key or scale.
Tip 6: Develop Aural Recognition:Train your ear to recognize the distinctive sound of the d#dim7 chord, enabling you to use it effectively in improvisation and ensemble playing.
Tip 7: Apply in Different Musical Styles:Explore the versatility of the d#dim7 chord by incorporating it into various musical styles, including jazz, blues, and rock.
Summary: By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding and application of the d#dim7 guitar chord. Practice regularly, experiment with different voicings and harmonic contexts, and develop a keen ear to master this versatile and expressive chord.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: With dedication and practice, the d#dim7 guitar chord will become a valuable tool in your musical arsenal, adding depth and sophistication to your playing.
Conclusion
The d#dim7 guitar chord, with its unique construction and dissonant sound, offers a versatile tool for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary. Its ability to create tension, resolve to different tonal centers, and substitute for other diminished seventh chords makes it a valuable asset in various musical genres.
Mastering the d#dim7 chord requires understanding its construction, practicing different voicings, considering diatonic context, and developing aural recognition. By incorporating these techniques into their playing, guitarists can unlock the full potential of this chord and add depth and sophistication to their music.