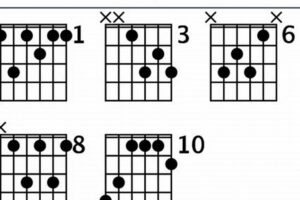
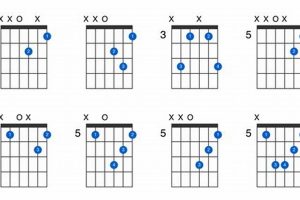
Wondering what an ab13 guitar chord is? You’re in the right place! This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about this versatile and expressive chord, empowering you to enhance your guitar playing skills.
Editor’s Note:Understanding the ab13 guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore new sonic possibilities. This guide will serve as your ultimate resource, providing a deep dive into its construction, voicings, and practical applications.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve crafted this ab13 guitar chord guide to help you master this essential chord and elevate your musical journey.
Key Differences:
| ab13 | |
|---|---|
| Root Note: | A |
| Intervals: | 1, 3, b5, 6, 9, 13 |
| Voicings: | Multiple voicings available, each with a unique character |
Main Article Topics:
- Construction and Theory of the ab13 Guitar Chord
- Exploring Different Voicings and Inversions
- Practical Applications in Various Musical Contexts
- Tips for Effective Use in Improvisation and Composition
- Additional Resources and Learning Materials
1. Construction
Understanding the construction of the ab13 guitar chord is crucial as it determines its unique sound and harmonic characteristics. As an extended chord, the ab13 incorporates intervals beyond the basic triad (root, third, and fifth), specifically adding the 9th and 13th intervals.
- 9th Interval: Adds a dissonant quality to the chord, creating a sense of tension and resolving to the root.
- 13th Interval: Extends the chord further, providing a rich and complex harmonic texture, often resolving to the 5th or 7th of the scale.
- Voicings: The ab13 guitar chord can be played in various voicings, inverting the order of notes to emphasize different intervals and create distinct sounds.
- Extended Family: The ab13 chord belongs to a family of extended chords, including 9th, 11th, and 13th chords, each with its own unique harmonic properties.
By understanding the construction of the ab13 guitar chord, guitarists can effectively use it to create sophisticated and expressive harmonies. It provides a wealth of options for improvisation, composition, and exploring different musical genres.
2. Harmony
The ab13 guitar chord’s unique harmonic properties stem from the combination of extended intervals, namely the 9th and 13th. These intervals add complexity and richness to the chord, creating a dissonant yet intriguing sound that sets it apart from basic triads.
- Dissonance and Resolution: The 9th interval introduces dissonance to the chord, creating tension that resolves to the root. This interplay of dissonance and resolution adds depth and emotional impact to the music.
- Extended Harmonic Texture: The 13th interval further extends the harmonic texture, providing a rich and complex sound. It often resolves to the 5th or 7th of the scale, adding harmonic sophistication to chord progressions.
- Distinctive Character: The combination of the 9th and 13th intervals gives the ab13 guitar chord a distinctive character that can enhance solos, improve chord melodies, and add harmonic interest to any musical context.
- Improvisational Potential: The dissonant nature of the ab13 chord provides ample opportunities for improvisation. Guitarists can explore different melodic lines that interact with the chord’s extended intervals, creating unique and expressive solos.
In summary, the harmony created by the ab13 guitar chord’s extended intervals is integral to its expressive and versatile nature. It adds richness, dissonance, and harmonic complexity, making it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to expand their musical vocabulary and create captivating music.
3. Inversions
Inversions are a fundamental aspect of the ab13 guitar chord, allowing guitarists to explore different voicings and harmonic possibilities while maintaining the chord’s essential structure.
- Root Position: The root position of the ab13 chord places the root note (A) in the bass, followed by the 3rd, 9th, 13th, b5, and 6th intervals.
- First Inversion: The first inversion moves the 3rd interval (C) to the bass, followed by the root, 9th, 13th, b5, and 6th intervals. This inversion emphasizes the C note and creates a slightly different harmonic character.
- Second Inversion: The second inversion places the 9th interval (G) in the bass, followed by the root, 3rd, 13th, b5, and 6th intervals. This inversion highlights the G note and adds a more dissonant and complex sound.
- Third Inversion: The third inversion moves the 13th interval (E) to the bass, followed by the root, 3rd, 9th, b5, and 6th intervals. This inversion emphasizes the E note and creates a more resolved and stable sound.
By understanding and utilizing inversions, guitarists can create a wide range of harmonic colors and textures using the ab13 guitar chord. Each inversion offers a unique sound that can enhance chord progressions, add interest to solos, and expand the overall musical vocabulary.
4. Voicings
The ab13 guitar chord offers a rich array of voicings, ranging from simple and accessible to complex and sophisticated. These voicings provide guitarists with a versatile palette of harmonic colors and textures to explore.
Simple voicings, typically utilizing open strings or fewer extended intervals, are ideal for beginners or those seeking a more straightforward sound. As guitarists progress, they can delve into more complex voicings that incorporate extended intervals, such as the 9th and 13th, adding depth and harmonic interest to their playing.
The choice of voicing depends on the desired harmonic effect and the overall musical context. Simple voicings can provide a stable and clear harmonic foundation, while complex voicings can add intrigue and sophistication to chord progressions and solos.
Understanding and mastering different voicings of the ab13 guitar chord empower
s guitarists to express themselves musically and create a wide range of harmonic possibilities.
Here’s a table summarizing the key points:
| Simple Voicings | Complex Voicings | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Fewer extended intervals, open strings | Incorporate extended intervals (9th, 13th), sophisticated sound |
| Suitability | Beginners, straightforward sound | Advanced players, harmonic interest |
| Effect | Stable harmonic foundation | Intrigue and sophistication |
5. Function
The ab13 guitar chord serves as a versatile substitute for dominant 7th chords, offering a unique blend of harmonic tension and resolution. Understanding this function opens up a range of possibilities for guitarists in various musical contexts.
- Harmonic Substitution: The ab13 chord shares a similar harmonic function to dominant 7th chords, acting as a strong indicator of impending resolution. This substitution allows guitarists to introduce harmonic interest and variation while maintaining the overall chord progression’s direction.
- Tension and Release: The extended intervals in the ab13 chord, particularly the 9th and 13th, create a sense of harmonic tension that resolves naturally to the root. This interplay of tension and release adds depth and emotional impact to chord progressions, making them more engaging and expressive.
- 5 Interval: The inclusion of the 5 interval in the ab13 chord contributes to its distinct sound. This interval provides a dissonant element that adds character and harmonic intrigue, setting it apart from traditional dominant 7th chords.
- Improvisation and Soloing: The ab13 chord’s rich harmonic structure offers a fertile ground for improvisation and soloing. Guitarists can explore different melodic lines that interact with the extended intervals, creating unique and expressive solos that enhance the overall musical performance.
In summary, the ab13 guitar chord’s function as a substitute for dominant 7th chords provides guitarists with a powerful tool for harmonic exploration. Its unique blend of tension, resolution, and extended intervals makes it an essential chord for expanding musical vocabulary and enhancing improvisation and composition.
6. Resolution
The ab13 guitar chord’s resolution to a major or minor chord is a crucial aspect that defines its harmonic function and musical impact. Understanding this resolution is essential for guitarists seeking to use the chord effectively in various musical contexts.
The ab13 chord, with its extended intervals, creates a sense of tension and instability. This tension naturally seeks resolution to a more stable and consonant chord, typically a major or minor chord. The specific resolution depends on the harmonic context and the intended musical effect.
For instance, in a jazz context, the ab13 chord often resolves to a dominant 7th chord, which then resolves to a major chord. This creates a strong sense of harmonic movement and progression. In a blues context, the ab13 chord may resolve to a minor chord, adding a touch of melancholy and emotional depth to the music.
The resolution of the ab13 chord is not limited to specific chord types. Guitarists can experiment with different resolutions based on their musical taste and the desired harmonic effect. This flexibility makes the ab13 chord a versatile tool for creating diverse and expressive chord progressions.
| Resolution | Effect |
|---|---|
| Major chord | Strong sense of harmonic movement and progression |
| Minor chord | Touch of melancholy and emotional depth |
Understanding the resolution of the ab13 guitar chord empowers guitarists to make informed decisions about its usage in their music. By considering the harmonic context and the intended musical effect, guitarists can effectively harness the ab13 chord’s expressive potential.
7. Improvisation
The ab13 guitar chord’s unique harmonic structure and extended intervals make it a fertile ground for improvisation. Guitarists can explore a vast array of melodic possibilities that interact with the chord’s rich harmonic tapestry.
- Melodic Embellishments: The ab13 chord’s extended intervals offer ample opportunities for melodic embellishments. Guitarists can incorporate chromatic passing tones, trills, and arpeggios to add melodic interest and create a sense of movement.
- Intervallic Exploration: The intervals within the ab13 chord provide a framework for intervallic exploration. Guitarists can experiment with different intervallic combinations, such as leaps, sequences, and contrary motion, to create unique and expressive melodies.
- Harmonic Tension and Release: The ab13 chord’s inherent tension and resolution create a dynamic platform for improvisation. Guitarists can explore melodic lines that build tension against the chord’s dissonance and then resolve to the more stable intervals, creating a sense of musical drama.
- Chord Tone Outlining: The ab13 chord’s distinct intervals can serve as reference points for chord tone outlining. Guitarists can improvise melodies that emphasize the root, 3rd, 5th, 9th, and 13th intervals, creating a strong sense of harmonic connection.
These facets of improvisation highlight the ab13 guitar chord’s versatility and expressive potential. By understanding the harmonic structure and melodic possibilities of the chord, guitarists can unlock a wealth of creative options for improvising melodies and solos that enhance their musical performances.
8. Composition
The ab13 guitar chord’s harmonic richness and extended intervals make it a powerful tool for composers seeking to create complex and sophisticated chord progressions. Its unique sound and ability to generate harmonic tension and resolution provide a fertile ground for musical exploration and innovation.
One key aspect of the ab13 chord’s compositional potential is its ability to add depth and complexity to chord progressions. By incorporating extended intervals, composers can create progressions that move beyond traditional major and minor chords, introducing new harmonic colors and textures. This expanded harmonic palette allows for more expressive and nuanced musical compositions.
Furthermore, the ab13 chord’s inherent tension and resolution can be used to create a sense of harmonic movement and progression. Composers can juxtapose the ab13 chord with more stable chords, such as major or minor chords, to create a dynamic interplay of tension and release. This interplay adds depth and interest to chord progressions, keeping listeners engaged and involved in the musical journey.
In prac
tice, the ab13 guitar chord has been used by countless composers to create iconic and memorable chord progressions. For instance, jazz composer and pianist Bill Evans frequently employed the ab13 chord in his compositions, adding harmonic sophistication and depth to his music. Similarly, guitarists such as George Benson and Pat Metheny have utilized the ab13 chord to enhance their improvisational solos and create harmonically rich and engaging performances.
Understanding the compositional potential of the ab13 guitar chord empowers musicians to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create sophisticated and expressive chord progressions. By incorporating this chord into their compositions, they can add depth, complexity, and harmonic movement to their music, captivating audiences and leaving a lasting impression.
9. Genre
The ab13 guitar chord finds its home in a variety of musical genres, each with its unique characteristics and harmonic approaches.
- Jazz:
In jazz, the ab13 chord is a staple, adding harmonic complexity and sophistication to improvisational solos and chord progressions. Jazz guitarists often employ the ab13 chord as a substitute for dominant 7th chords, creating a rich and dissonant sound that enhances the improvisational nature of the genre.
- Fusion:
Fusion music, which blends elements of jazz, rock, and funk, frequently incorporates the ab13 guitar chord. The chord’s extended intervals and dissonant qualities contribute to the genre’s complex and harmonically adventurous sound.
- Contemporary styles:
Contemporary guitarists in various genres, including pop, rock, and R&B, have embraced the ab13 chord for its ability to add a modern and sophisticated touch to their music. The chord’s unique harmonic structure and versatility make it a valuable tool for creating memorable and engaging chord progressions.
Overall, the ab13 guitar chord’s presence in jazz, fusion, and contemporary styles highlights its adaptability and expressive potential. Guitarists across genres have recognized the chord’s ability to enhance harmonic sophistication, create tension and release, and add a touch of modernity to their music.
10. Difficulty
The ab13 guitar chord presents a unique challenge for guitarists due to its extended intervals, particularly the 9th and 13th. These intervals introduce dissonance and harmonic complexity, requiring guitarists to develop precise finger positioning and coordination to execute the chord accurately.
Mastering the ab13 chord involves dedicated practice to overcome the technical demands it presents. Guitarists must train their fingers to reach and fret the extended intervals comfortably while maintaining proper intonation. Additionally, understanding the chord’s construction and theory helps guitarists visualize the intervals and their relationship to the root note.
Overcoming the difficulty associated with the ab13 chord is essential for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore advanced musical concepts. It unlocks a wealth of creative possibilities, allowing guitarists to add sophistication and expressiveness to their playing.
11. Notation
The notation of the ab13 guitar chord Abmaj13, Abmaj9/13, or simply Ab13 holds significant importance in understanding and utilizing this versatile chord. These notations represent the chord’s construction and provide valuable information for guitarists.
- Chord Structure:
The notation Abmaj13 indicates that the chord consists of the root note (A), followed by a major 3rd (C), perfect 5th (E), major 7th (G), major 9th (B), and major 13th (E). The maj13 suffix denotes the inclusion of both the major 9th and major 13th intervals.
- Alternative Notation:
Abmaj9/13 is an alternative notation that emphasizes the presence of the major 9th and major 13th intervals. This notation is often used to differentiate the ab13 chord from other extended chords that may have different 9th or 13th intervals.
- Simplified Notation:
The notation Ab13 is a simplified form that combines the major 9th and major 13th intervals into a single symbol. This notation is commonly used in lead sheets and chord charts to simplify the representation of the chord.
- Implications for Playing:
Understanding the notation of the ab13 chord is essential for accurately playing the chord on the guitar. The notation provides a clear indication of the intervals and their relationship to the root note, guiding the guitarist’s finger placement and fretting.
In summary, the various notations of the ab13 guitar chord Abmaj13, Abmaj9/13, and Ab13 serve as valuable tools for guitarists to comprehend the chord’s structure, visualize its intervals, and execute it accurately on the instrument. Understanding these notations is crucial for mastering this advanced and expressive chord, unlocking its potential in musical compositions and performances.
12. Related Chords
The ab13 guitar chord bears a close relationship to several other extended chords, namely the A13, Ab9, and Abmaj7 chords. Understanding these related chords provides valuable insights into the ab13 chord’s construction, harmonic function, and practical applications.
- A13 Chord:
The A13 chord is closely related to the ab13 chord, as it shares the same root note (A) and incorporates both the major 9th and major 13th intervals. The primary difference lies in the inclusion of a major 7th interval in the A13 chord, giving it a more stable and consonant sound compared to the ab13 chord.
- Ab9 Chord:
The Ab9 chord is another closely related chord, sharing the same root note (Ab) and the major 9th interval. However, the Ab9 chord lacks the major 13th interval, resulting in a less complex and dissonant sound. This chord is often used as a substitute for the ab13 chord in situations where a less harmonically adventurous sound is desired.
- Abmaj7 Chord:
The Abmaj7 chord shares the same root note (Ab) with the ab13 chord and incorporates the major 7th interval. However, it lacks both the major 9th and major 13th intervals, resulting in a more consonant and less dissonant sound. This chord is frequently used in jazz and blues contexts, where its stable and pleasant sound complements the improvisational nature of these genres.
By studying these related chords, guitarists can gain a deeper understanding of the ab13 chord’s unique harmonic characteristics and its place within the broader family of extended chords. This knowledge enables guitarists to make informed choices when incorporating the ab13 chord into their musical compositions and improvisations, allowing them to create a wider range of harmonic colors and textures.
FAQs about ab13 Guitar Chord
Here are answers to freque
ntly asked questions about the ab13 guitar chord:
Question 1: What is the construction of an ab13 guitar chord?
Answer: The ab13 chord comprises the root note (A), followed by a major 3rd (C), perfect 5th (E), major 7th (G), major 9th (B), and major 13th (E). It is an extended chord that incorporates both the major 9th and major 13th intervals.
Question 2: How do I play an ab13 guitar chord?
Answer: There are multiple ways to play the ab13 chord on the guitar. One common fingering involves using the index finger on the root note (A) on the 5th string, the middle finger on the major 3rd (C) on the 4th string, the ring finger on the perfect 5th (E) on the 5th string, the pinky finger on the major 7th (G) on the 6th string, and the thumb on the major 9th (B) on the 6th string. The major 13th (E) is typically omitted due to its high position on the neck.
Question 3: What is the difference between an ab13 and an A13 chord?
Answer: The ab13 and A13 chords share the same root note (A) and incorporate both the major 9th and major 13th intervals. However, the A13 chord additionally includes a major 7th interval, resulting in a more stable and consonant sound compared to the ab13 chord.
Question 4: When is it appropriate to use an ab13 guitar chord?
Answer: The ab13 chord is commonly found in jazz, fusion, and contemporary styles of music. It adds harmonic complexity and richness to chord progressions and solos, and can be used as a substitute for dominant 7th chords to create tension and resolution.
Question 5: How can I practice playing the ab13 guitar chord effectively?
Answer: Regular practice is key to mastering the ab13 guitar chord. Start by slowly practicing the chord shape and fingering, focusing on accuracy and proper fretting. Gradually increase the speed and incorporate the chord into different chord progressions and musical contexts to improve your proficiency.
Question 6: Are there any online resources available for learning more about the ab13 guitar chord?
Answer: Yes, there are numerous online resources that provide lessons, tutorials, and interactive exercises on the ab13 guitar chord. These resources can be helpful for both beginners and experienced guitarists seeking to expand their knowledge and skills.
Summary: The ab13 guitar chord is a versatile and expressive chord that adds harmonic richness and sophistication to music. Understanding its construction, voicings, and practical applications is crucial for guitarists seeking to enhance their playing. Regular practice and exploration of online resources will enable guitarists to master this chord and incorporate it effectively into their musical endeavors.
Transition to the next article section: For further exploration of advanced guitar chords, refer to the comprehensive guide on “Exploring Extended Guitar Chords: A Journey Beyond the Basics”.
Tips for Mastering the ab13 Guitar Chord
Incorporating the ab13 guitar chord into your playing requires dedication and practice. Here are some valuable tips to guide you on your journey:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is paramount for developing muscle memory and improving finger coordination. Dedicate time each day to practicing the ab13 chord in different positions and contexts.
Tip 2: Understand the Theory: Grasping the construction and theory behind the ab13 chord will enhance your understanding of its structure and how it interacts with other chords. Study the intervals and their relationships to the root note.
Tip 3: Explore Different Voicings: Experiment with various voicings of the ab13 chord to discover its tonal possibilities. Experimenting with different fingerings and inversions will expand your harmonic vocabulary and provide diverse sound options.
Tip 4: Use a Metronome: Practicing with a metronome helps develop a steady rhythm and improve your timing. Start slowly and gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable with the chord.
Tip 5: Listen to Recordings: Active listening to recordings of professional guitarists who utilize the ab13 chord can provide valuable insights into its practical application. Analyze their techniques, voicings, and how they incorporate the chord into musical contexts.
Tip 6: Experiment in Different Musical Styles: Explore the ab13 chord’s versatility by experimenting with it in various musical styles. Apply it in jazz, fusion, or contemporary genres to understand its diverse harmonic capabilities.
Tip 7: Seek Guidance from a Guitar Teacher: Consider seeking guidance from an experienced guitar teacher who can provide personalized instruction, feedback, and support. They can help you refine your technique and overcome challenges.
Summary: Mastering the ab13 guitar chord requires dedication, practice, and a thorough understanding of its theory and applications. By incorporating these tips into your practice routine, you can effectively enhance your guitar playing skills and expand your musical horizons.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Embracing the ab13 guitar chord opens up a world of harmonic possibilities. Dedicate yourself to mastering this versatile chord, and you will unlock a new level of musical expression and creativity.
Conclusion
The ab13 guitar chord, with its extended intervals and rich harmonic structure, offers guitarists a powerful tool for creating sophisticated and expressive music. Its versatility allows it to enhance chord progressions, add depth to solos, and contribute to a wide range of musical genres.
Mastering the ab13 guitar chord requires dedication, practice, and a thorough understanding of its construction and applications. Embracing this chord opens up a world of harmonic possibilities, allowing guitarists to expand their musical vocabulary and elevate their playing to new heights. Whether used as a substitute for dominant 7th chords, to create tension and resolution, or to add a touch of modern sophistication, the ab13 guitar chord is an indispensable tool for guitarists seeking to explore the boundaries of their musical expression.