Electric guitar is essential for any musician who wants to play rock, blues, or other genres that require a powerful and versatile sound. But with so many different models and brands of electric guitars on the market, it can be tough to know where to start. That’s where an electric guitar reference comes in.
Editor’s Note:Electric guitar references are important because they provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of electric guitars available. This can help musicians make informed decisions about which guitar is right for their needs.
To help you make the right decision, we’ve put together this electric guitar reference guide. In it, you’ll find information on the different types of electric guitars, their features, and their pros and cons. We’ve also included a buyer’s guide to help you choose the right electric guitar for your needs.
Key Differences
| Feature | Solid-Body | Semi-Hollow | Hollow-Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Type | Solid wood body | Hollow body with a solid center block | Hollow body with no center block |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter | Lightest |
| Tone | Bright and twangy | Warm and mellow | Deep and resonant |
| Feedback Resistance | High | Medium | Low |
| Price | $500-$2000 | $1000-$3000 | $2000-$5000 |
Main Article Topics
- Types of Electric Guitars
- Features of Electric Guitars
- Pros and Cons of Electric Guitars
- Buyer’s Guide to Electric Guitars
1. Body Type
The body type of an electric guitar is one of the most important factors that determines its sound and feel. Solid-body guitars have a solid wood body, which gives them a bright, twangy tone with plenty of sustain. Semi-hollow guitars have a hollow body with a solid center block, which gives them a warmer, mellower tone with less feedback. Hollow-body guitars have a hollow body with no center block, which gives them a deep, resonant tone with plenty of feedback.
The body type of an electric guitar also affects its weight and price. Solid-body guitars are typically heavier than semi-hollow and hollow-body guitars. Semi-hollow guitars are typically more expensive than solid-body guitars, and hollow-body guitars are typically the most expensive type of electric guitar.
When choosing an electric guitar, it is important to consider the body type that best suits your playing style and needs. If you are looking for a versatile guitar that can handle a variety of genres, a solid-body guitar is a good choice. If you are looking for a guitar with a warm, mellow tone, a semi-hollow guitar is a good choice. If you are looking for a guitar with a deep, resonant tone, a hollow-body guitar is a good choice.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between solid-body, semi-hollow, and hollow-body electric guitars:
| Body Type | Tone | Weight | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-body | Bright, twangy | Heavy | Affordable |
| Semi-hollow | Warm, mellow | Medium | Mid-priced |
| Hollow-body | Deep, resonant | Light | High-end |
2. Construction
The construction of an electric guitar’s neck is a key factor that affects its sound, feel, and playability. There are three main types of neck construction: set-neck, bolt-on neck, and neck-through-body.
Set-neck guitars have a neck that is glued into the body. This type of construction provides a strong and resonant connection between the neck and body, which results in a warm, full tone with plenty of sustain. Set-neck guitars are often used for genres such as blues, rock, and jazz.
Bolt-on neck guitars have a neck that is bolted to the body. This type of construction is less expensive and easier to manufacture than set-neck construction, and it results in a brighter, twangier tone with less sustain. Bolt-on neck guitars are often used for genres such as country, funk, and pop.
Neck-through-body guitars have a neck that runs through the entire body of the guitar. This type of construction provides the strongest and most resonant connection between the neck and body, which results in a rich, powerful tone with excellent sustain. Neck-through-body guitars are often used for genres such as metal, hard rock, and progressive rock.
The type of neck construction that is best for you depends on your playing style and the sound you are looking for. If you are looking for a guitar with a warm, full tone with plenty of sustain, a set-neck guitar is a good choice. If you are looking for a guitar with a brighter, twangier tone with less sustain, a bolt-on neck guitar is a good choice. If you are looking for a guitar with a rich, powerful tone with excellent sustain, a neck-through-body guitar is a good choice.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between set-neck, bolt-on neck, and neck-through-body guitars:
| Construction | Tone | Sustain | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set-neck | Warm, full | Excellent | Mid-priced |
| Bolt-on neck | Bright, twangy | Good | Affordable |
| Neck-through-body | Rich, powerful | Excellent | High-end |
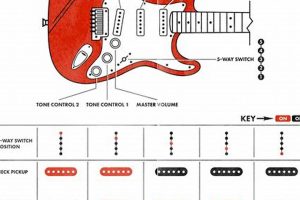
3. Pickups
Pickups are one of the most important components of an electric guitar, and they play a major role in determining the sound of the guitar. There are three main types of pickups: single-coil, humbucker, and P-90.
- Single-coil pickups are the most common type of pickup. They have a single coil of wire wrapped around a magnet, and they produce a bright, twangy sound. Single-coil pickups are often used in genres such as country, blues, and rock.
- Humbucker pickups have two coils of wire wrapped around a magnet, and they are wired in a way that cancels out the hum that is common in single-coil pickups. Humbuckers produce a warmer, fuller sound than single-coil pickups, and
they are often used in genres such as rock, metal, and jazz. - P-90 pickups are a type of single-coil pickup that has a wider coil and a stronger magnet than a standard single-coil pickup. P-90 pickups produce a sound that is somewhere between a single-coil and a humbucker, and they are often used in genres such as blues, rock, and country.
The type of pickup that you choose for your electric guitar will depend on the sound that you are looking for. If you are looking for a bright, twangy sound, a single-coil pickup is a good choice. If you are looking for a warmer, fuller sound, a humbucker pickup is a good choice. If you are looking for a sound that is somewhere between a single-coil and a humbucker, a P-90 pickup is a good choice.
4. Electronics
The electronics of an electric guitar play a major role in determining the sound of the guitar. There are two main types of electronics: active and passive.
Passive electronics are the most common type of electronics found in electric guitars. They consist of a simple circuit that includes a volume knob, a tone knob, and a pickup selector switch. Passive electronics are relatively inexpensive and easy to maintain, and they produce a warm, natural sound.
Active electronics are a more recent development in electric guitar design. They include a preamplifier that boosts the signal from the pickups, and they often include additional features such as EQ controls and effects loops. Active electronics can produce a wider range of sounds than passive electronics, and they can help to improve the sustain and clarity of the guitar’s sound.
The type of electronics that you choose for your electric guitar will depend on the sound that you are looking for. If you are looking for a warm, natural sound, passive electronics are a good choice. If you are looking for a wider range of sounds, or if you want to improve the sustain and clarity of your guitar’s sound, active electronics are a good choice.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between active and passive electronics:
| Feature | Passive Electronics | Active Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain | More difficult to maintain |
| Sound | Warm, natural | Wider range of sounds |
| Sustain and clarity | Good | Excellent |
5. Hardware
The hardware on an electric guitar is essential for keeping the guitar in tune, holding the strings in place, and providing a comfortable playing experience. The three most important pieces of hardware on an electric guitar are the bridge, the tuners, and the strap buttons.
The bridge is responsible for holding the strings in place and transferring their vibrations to the body of the guitar. There are many different types of bridges, each with its own unique sound and feel. The most common type of bridge is the fixed bridge, which is found on most solid-body electric guitars. Fixed bridges are simple to use and maintain, and they provide a stable tuning. Other types of bridges include the floating bridge, which is found on many tremolo-equipped guitars, and the vibrato bridge, which allows the player to bend the strings up or down. Vibrato bridges are more complex to use and maintain than fixed bridges, but they can provide a wider range of sounds.
The tuners are responsible for keeping the guitar in tune. There are two main types of tuners: geared tuners and friction tuners. Geared tuners are the most common type of tuner, and they use a gear mechanism to turn the tuning pegs. Friction tuners are less common, and they use a friction mechanism to hold the tuning pegs in place. Geared tuners are more precise than friction tuners, but friction tuners are less likely to slip.
The strap buttons are responsible for attaching the guitar strap to the guitar. There are two main types of strap buttons: strap locks and standard strap buttons. Strap locks are more secure than standard strap buttons, and they prevent the guitar from falling off the strap if the strap is accidentally unhooked. Standard strap buttons are less secure than strap locks, but they are also less expensive.
The hardware on an electric guitar is an important part of the guitar’s overall sound and feel. By understanding the different types of hardware available, you can choose the right hardware for your guitar and playing style.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between the different types of hardware:
| Type of Hardware | Description | Sound | Feel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed bridge | A bridge that is fixed in place and does not allow the strings to be bent | Stable | Solid |
| Floating bridge | A bridge that is not fixed in place and allows the strings to be bent | Versatile | Unstable |
| Vibrato bridge | A bridge that allows the player to bend the strings up or down | Versatile | Unstable |
| Geared tuners | Tuners that use a gear mechanism to turn the tuning pegs | Precise | Smooth |
| Friction tuners | Tuners that use a friction mechanism to hold the tuning pegs in place | Less precise | Rough |
| Strap locks | Strap buttons that are designed to prevent the guitar from falling off the strap | Secure | Solid |
| Standard strap buttons | Strap buttons that are not designed to prevent the guitar from falling off the strap | Less secure | Less solid |
6. Scale Length
The scale length of an electric guitar is the distance between the nut and the bridge. It is a key factor that determines the guitar’s sound, feel, and playability. There are three main types of scale lengths: short-scale, medium-scale, and long-scale.
- Short-scale guitars have a scale length of less than 24.75 inches. They are typically easier to play than long-scale guitars, and they produce a warmer, mellower sound. Short-scale guitars are often used for genres such as blues, jazz, and rockabilly.
- Medium-scale guitars have a scale length of between 24.75 inches and 25.5 inches. They offer a compromise between the sound and feel of short-scale and long-scale guitars. Medium-scale guitars are often used for genres such as rock, blues, and country.
- Long-scale guitars have a scale length of 25.5 inches or more. They produce a brighter, twangier sound than short-scale and medium-scale guitars. Long-scale guitars are often used for genres such as rock, metal, and country.
The scale length of an electric guitar is a matter of personal preference. There is no right or wrong answer, and the best scale length for you will depend on your playing
style and the sound you are looking for. However, understanding the different types of scale lengths and their impact on the sound and feel of the guitar can help you make an informed decision about which guitar is right for you.
7. Fretboard Radius
The fretboard radius of an electric guitar is the curvature of the fretboard from side to side. It is measured in inches, and it can have a significant impact on the playability and sound of the guitar.
- Flat fretboards have a radius of 12 inches or more. They are typically found on older guitars, and they provide a more traditional playing feel. Flat fretboards are often preferred by blues and rock players.
- Vintage fretboards have a radius of 7.25 inches to 9.5 inches. They are found on many vintage guitars, and they offer a compromise between the feel of a flat fretboard and a compound fretboard. Vintage fretboards are often preferred by country and jazz players.
- Compound fretboards have a radius that varies from the nut to the bridge. They are typically found on modern guitars, and they offer the best of both worlds. Compound fretboards are often preferred by shredders and metal players.
The fretboard radius of an electric guitar is a matter of personal preference. There is no right or wrong answer, and the best fretboard radius for you will depend on your playing style and the sound you are looking for. However, understanding the different types of fretboard radii and their impact on the playability and sound of the guitar can help you make an informed decision about which guitar is right for you.
8. Nut Width
The nut width of an electric guitar is the width of the nut at the end of the fretboard. It is a key factor that determines the spacing of the strings, which can affect the playability and sound of the guitar.
There are three main types of nut widths: narrow, medium, and wide.
- Narrow nut widths (1.625 inches or less) are typically found on vintage guitars and guitars designed for players with small hands. They provide a more cramped playing feel, but they can be easier to reach for some players.
- Medium nut widths (1.6875 inches to 1.75 inches) are the most common type of nut width. They offer a comfortable playing feel for most players, and they provide a good balance between string spacing and playability.
- Wide nut widths (1.75 inches or more) are typically found on modern guitars and guitars designed for players with large hands. They provide a more spacious playing feel, but they can be more difficult to reach for some players.
The nut width of an electric guitar is a matter of personal preference. There is no right or wrong answer, and the best nut width for you will depend on your playing style and the size of your hands. However, understanding the different types of nut widths and their impact on the playability and sound of the guitar can help you make an informed decision about which guitar is right for you.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between the different types of nut widths:
| Nut Width | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow | 1.625 inches or less | Easier to reach for some players | More cramped playing feel |
| Medium | 1.6875 inches to 1.75 inches | Comfortable playing feel for most players | Good balance between string spacing and playability |
| Wide | 1.75 inches or more | More spacious playing feel | More difficult to reach for some players |
9. Weight
The weight of an electric guitar is an important factor to consider when choosing a guitar. The weight of a guitar can affect its playability, tone, and comfort. Lighter guitars are typically easier to play for long periods of time, while heavier guitars can produce a fuller, richer tone. Ultimately, the best weight for an electric guitar is a matter of personal preference.
There are three main types of electric guitar weights: light, medium, and heavy.
- Light guitars weigh less than 7 pounds.
- Medium guitars weigh between 7 and 9 pounds.
- Heavy guitars weigh more than 9 pounds.
Light guitars are often preferred by players who play for long periods of time, such as gigging musicians or studio musicians. Light guitars are also a good choice for players with back problems or other physical limitations. Medium guitars are a good all-around choice for most players. They offer a good balance between weight and tone. Heavy guitars are often preferred by players who want a fuller, richer tone. Heavy guitars are also a good choice for players who play in loud bands or who use a lot of distortion.
The weight of an electric guitar is just one of many factors to consider when choosing a guitar. Other factors include the body style, neck shape, and pickup configuration. By considering all of these factors, you can choose an electric guitar that is perfect for your needs.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between light, medium, and heavy electric guitars:
| Weight | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Light | Easier to play for long periods of time | Can produce a thinner tone |
| Medium | Good all-around choice | Not as light as light guitars or as heavy as heavy guitars |
| Heavy | Can produce a fuller, richer tone | Can be more difficult to play for long periods of time |
10. Price
The price of an electric guitar is an important factor to consider when choosing a guitar. The price of a guitar can vary depending on a number of factors, including the brand, the materials used, the construction, and the features. Generally speaking, affordable electric guitars are made with less expensive materials and have fewer features than mid-priced and high-end guitars. Mid-priced electric guitars offer a good balance of price and quality, while high-end electric guitars are made with the finest materials and craftsmanship and offer the best possible sound and performance.
The price of an electric guitar can also affect its resale value. Affordable electric guitars typically have a lower resale value than mid-priced and high-end guitars. This is because affordable guitars are often made with less expensive materials and have fewer features. Mid-priced and high-end guitars are more likely to retain their value over time because they are made with better materials and have more features.
When choosing an electric guitar, it is important to consider your budget and your needs. If you are on a tight bu
dget, an affordable electric guitar may be a good option. However, if you are looking for a guitar that will last for many years and offer the best possible sound and performance, a mid-priced or high-end guitar may be a better choice.
| Price Range | Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affordable (less than $500) | Less expensive | Fewer features | Lower resale value |
| Mid-priced ($500-$1,500) | Good balance of price and quality | May not have all the features of a high-end guitar | Resale value may not be as high as a high-end guitar |
| High-end (more than $1,500) | Best possible sound and performance | Most expensive | May not be necessary for all players |
Electric Guitar Reference FAQs
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about electric guitars, covering aspects like their benefits, types, and selection criteria, to help you make informed decisions.
Question 1: What are the primary advantages of using an electric guitar?
Answer: Electric guitars offer several advantages, including versatility in sound due to the use of pickups and electronics, allowing for a wide range of tones and effects. They also provide sustain, which is the ability to maintain a note’s sound for an extended duration, and can be enhanced using distortion or overdrive effects.
Question 2: What are the different types of electric guitars?
Answer: Electric guitars come in various types, each with unique characteristics. Solid-body guitars have a solid wood body, providing a bright and twangy tone. Semi-hollow guitars feature a hollow body with a solid center block, offering a warm and mellow sound. Hollow-body guitars have a fully hollow body, producing a deep and resonant tone.
Question 3: How do I choose the right electric guitar for my needs?
Answer: Selecting the right electric guitar involves considering factors such as body type, which influences tone and weight; pickup configuration, affecting the range of tones; scale length, impacting playability and string tension; and electronics, including active or passive systems. Matching these factors to your playing style and desired sound will ensure a suitable choice.
Question 4: What are the differences between single-coil and humbucker pickups?
Answer: Single-coil pickups have a single coil of wire, producing a bright and twangy sound. Humbucker pickups have two coils of wire, resulting in a fuller and warmer sound with reduced hum. The choice between these pickup types depends on the desired tone and musical genre.
Question 5: How does the scale length of an electric guitar affect its playability?
Answer: Scale length, measured from the nut to the bridge, influences the string tension and playability. Shorter scale lengths make bending strings easier, while longer scale lengths provide increased string tension and sustain. Choosing the right scale length depends on personal preference and playing style.
Question 6: What is the significance of the nut width on an electric guitar?
Answer: Nut width, referring to the width of the nut at the end of the fretboard, affects string spacing. Narrower nut widths are easier to reach for some players, while wider nut widths provide more space for fingerpicking. The choice of nut width depends on hand size and playing technique.
In summary, understanding the different aspects of electric guitars, from their benefits and types to the factors influencing their selection, empowers you to make informed choices based on your individual needs and preferences.
Transition: Delving deeper into the intricacies of electric guitars, let’s explore the significance of their components and construction techniques in shaping their unique sound and playing experience.
Electric Guitar Reference Tips
Electric guitars have become an essential instrument for a wide range of musical genres, offering versatility and expressive capabilities that continue to inspire musicians. Mastering the art of playing the electric guitar involves not only understanding its components and techniques but also developing a refined approach to your playing. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your electric guitar skills and elevate your performances:
Tip 1: Experiment with Different Pickups and Electronics
Electric guitars feature various types of pickups and electronics that significantly impact their sound. Experiment with different pickup configurations, such as single-coil, humbucker, and P-90 pickups, to discover the tonal variations they offer. Explore the effects of active and passive electronics, which provide distinct sonic characteristics and control options.
Tip 2: Master the Art of Palm Muting
Palm muting is a fundamental technique for controlling the sustain and creating rhythmic accents on the electric guitar. Practice muting the strings with the palm of your picking hand while striking them with the pick. This technique allows for precise control over note duration and adds rhythmic complexity to your playing.
Tip 3: Develop Your Vibrato Technique
Vibrato is a subtle yet expressive technique that adds depth and emotion to your guitar playing. Gently bend the strings back and forth with your fretting hand to create a wavering effect on the notes. Experiment with different vibrato speeds and intensities to find your unique style and enhance the expressiveness of your solos and melodies.
Tip 4: Explore the Use of Effects Pedals
Effects pedals are essential tools for expanding the sonic capabilities of your electric guitar. Experiment with different types of pedals, such as distortion, overdrive, reverb, and delay, to create a wide range of effects. Learn how to combine pedals effectively to achieve unique and inspiring sounds that complement your playing.
Tip 5: Practice Regularly and Consistently
Regular practice is crucial for developing your electric guitar skills. Set aside dedicated practice time each day to focus on improving your technique, learning new scales and chords, and experimenting with different playing styles. Consistency is key to making progress and developing muscle memory that will enhance your overall performance.
Summary:
By incorporating these tips into your electric guitar playing, you will expand your sonic palette, enhance your expressiveness, and elevate your performances. Remember to experiment with different techniques, explore the capabilities of your guitar and effects pedals, and most importantly, practice regularly to refine your skills. Embrace the journey of learning and discovery, and let your electric guitar become an extension of your musical expression.
Electric Guitar Reference
This comprehensive exploration of the electric guitar reference has provided a thorough overview of the instrument’s components, construction techniques, and playing styles. Understanding the intricacies of electric guitars empowers musicians to make informed choices when selecting and playing the instrument, enabling them to achieve their desired sound and playing experience.
As you delve deeper into the world of electric guitars, remember to experiment with different pickups, electronics, and effects pedals to discover the vast sonic possibilities they offer. Practice regularly to
master essential techniques such as palm muting and vibrato, which add depth and expressiveness to your playing. By embracing the learning journey and exploring the capabilities of your instrument, you will unlock the full potential of the electric guitar and elevate your musical performances to new heights.