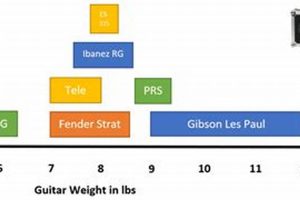
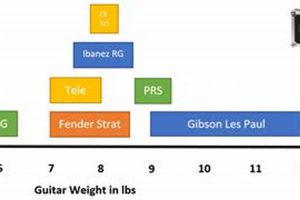
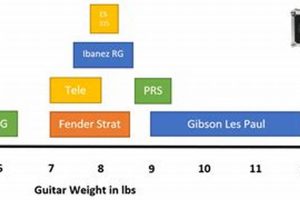
When it comes to playing the electric guitar, there are a lot of different terms that you need to know. These terms can relate to the different parts of the guitar, the different techniques that you can use to play it, and the different sounds that you can create. In this article, we will explore some of the most important electric guitar terms that you need to know.
Editor’s Note:Electric guitar terms are important to learn because they will help you to better understand how your guitar works and how to play it. By knowing the correct terminology, you will be able to communicate more effectively with other guitarists and you will be able to find the information that you need to improve your playing.
We’ve done the analysis, dug into the information, and put together this electric guitar terms guide to help you make the right decision.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Body | The main part of the guitar that produces the sound. |
| Neck | The long, thin part of the guitar that connects the body to the headstock. |
| Headstock | The part of the guitar that contains the tuning pegs. |
| Pickups | The devices that convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. |
| Amplifier | The device that amplifies the electrical signals from the pickups and sends them to the speakers. |
Transition to Main Article Topics
Now that you know some of the most important electric guitar terms, you can start to learn more about how to play the guitar. There are many different resources available online and in libraries that can help you to learn the basics of guitar playing. With a little practice, you’ll be able to play your favorite songs and start writing your own music.
1. Parts of the guitar
The different parts of an electric guitar play a vital role in producing its distinctive sound and allowing for various playing techniques. Understanding the function and terminology of these components is essential for any guitarist.
- Body: The body of the guitar is the main resonant chamber that amplifies the vibrations of the strings. Different body shapes and materials affect the tone and sustain of the instrument.
- Neck: The neck connects the body to the headstock and provides a platform for the strings. It is typically made of wood and features a fretboard where the strings are pressed to change pitch.
- Headstock: The headstock is the part of the guitar that houses the tuning pegs. It also displays the guitar’s brand and model.
- Pickups: Pickups are electromagnetic devices that convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. Different types of pickups produce different tones, from warm and mellow to bright and twangy.
- Bridge: The bridge is the part of the guitar that supports the strings and allows for intonation adjustment. It can be fixed or floating, affecting the guitar’s playing feel and sound.
- Strings: The strings are the vibrating elements of the guitar that produce the sound. They come in different gauges and materials, each with its unique tonal characteristics.
By understanding the different parts of the electric guitar and their functions, guitarists can make informed decisions about their instrument’s setup, maintenance, and modifications. This knowledge empowers them to tailor their guitars to their specific playing style and desired sound.
2. Types of guitars
The type of guitar you choose will have a significant impact on its sound and playability. There are three main types of electric guitars: solid-body, hollow-body, and semi-hollow-body.
Solid-body guitars have a solid body that does not resonate as much as hollow or semi-hollow guitars. This gives them a brighter, more focused sound with less feedback. Solid-body guitars are popular for rock, blues, and country music.
Hollow-body guitars have a hollow body that resonates more than solid-body guitars. This gives them a warmer, more mellow sound with more sustain. Hollow-body guitars are popular for jazz, blues, and rockabilly music.
Semi-hollow-body guitars have a body that is partially hollow and partially solid. This gives them a sound that is a cross between a solid-body and a hollow-body guitar. Semi-hollow-body guitars are popular for jazz, blues, and rock music.
The type of guitar you choose will depend on your personal preferences and the type of music you play. If you are unsure which type of guitar is right for you, it is a good idea to try out different types at a guitar store.
Key Insights:
- The type of guitar you choose will have a significant impact on its sound and playability.
- Solid-body guitars have a brighter, more focused sound with less feedback.
- Hollow-body guitars have a warmer, more mellow sound with more sustain.
- Semi-hollow-body guitars have a sound that is a cross between a solid-body and a hollow-body guitar.
Table: Comparison of Guitar Types
| Type | Body | Sound | Popular Music Styles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-body | Solid | Bright, focused, less feedback | Rock, blues, country |
| Hollow-body | Hollow | Warm, mellow, more sustain | Jazz, blues, rockabilly |
| Semi-hollow-body | Partially hollow, partially solid | Cross between solid-body and hollow-body | Jazz, blues, rock |
3. Guitar electronics
Electric guitar electronics are a crucial aspect of the instrument’s sound and functionality. Understanding their components and how they work will enhance your ability to shape your guitar’s tone and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Here are three essential components of guitar electronics and their significance in the context of electric guitar terms:
- Pickups
Pickups are transducers that convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. The type of pickups used in a guitar has a significant impact on its sound. Single-coil pickups are known for their bright, twangy tone, while humbuck
ers are known for their fuller, warmer sound. - Potentiometers
Potentiometers, also known as pots, are variable resistors that control the volume and tone of the guitar’s signal. The volume pot controls the overall output level, while the tone pot adjusts the balance between high and low frequencies.
- Capacitors
Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical energy. They are used in guitar electronics to filter out unwanted frequencies and smooth out the signal. Different values of capacitors can be used to create different tonal effects.
By understanding the role of these components in guitar electronics, you can make informed decisions about the sound of your instrument and how to maintain it. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced player, having a grasp of guitar electronics will empower you to customize your guitar and achieve your desired tone.
4. Guitar amplifiers
Guitar amplifiers are an essential part of an electric guitar’s sound. They take the electrical signals from the guitar’s pickups and amplify them, creating the sound that is heard through speakers. There are three main types of guitar amplifiers: tube amplifiers, solid-state amplifiers, and hybrid amplifiers.
- Tube amplifiers
Tube amplifiers use (electron tubes) to amplify the signal. They are known for their warm, natural sound. However, they are also more expensive and require more maintenance than other types of amplifiers.
- Solid-state amplifiers
Solid-state amplifiers use transistors to amplify the signal. They are more affordable and reliable than tube amplifiers, and they can produce a wide range of sounds. However, they may not have the same warm, natural sound as tube amplifiers.
- Hybrid amplifiers
Hybrid amplifiers combine both tube and solid-state technology. They offer the best of both worlds, with the warm, natural sound of tube amplifiers and the affordability and reliability of solid-state amplifiers.
The type of amplifier you choose will depend on your personal preferences and the type of music you play. If you are unsure which type of amplifier is right for you, it is a good idea to try out different types at a guitar store.
5. Guitar effects
Electric guitar effects are devices that modify the sound of an electric guitar. They can be used to create a wide range of sounds, from subtle changes to drastic transformations. Distortion, reverb, and delay are three of the most common and versatile guitar effects.
Distortion is an effect that adds a crunchy, overdriven sound to the guitar’s signal. It is often used to create a heavy, distorted sound for rock and metal music. Reverb is an effect that simulates the natural reverberation of a room. It can be used to add depth and ambience to the guitar’s sound. Delay is an effect that creates a delayed copy of the guitar’s signal. It can be used to create a variety of effects, from subtle echoes to long, spacious delays.
These three effects are essential components of many electric guitarists’ rigs. They can be used to create a wide range of sounds, from clean and pristine to heavy and distorted. Understanding how these effects work and how to use them effectively is essential for any guitarist who wants to expand their sonic palette.
Table: Guitar Effects: Distortion, Reverb, Delay
| Effect | Description | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Distortion | Adds a crunchy, overdriven sound to the guitar’s signal. | Rock, metal, blues |
| Reverb | Simulates the natural reverberation of a room. | Jazz, ambient, rock |
| Delay | Creates a delayed copy of the guitar’s signal. | Rock, pop, country |
6. Guitar playing techniques
Guitar playing techniques are an essential part of electric guitar terminology. They allow guitarists to create a wide range of sounds and effects, from subtle nuances to dramatic flourishes. Bending, vibrato, and hammer-ons are three of the most common and versatile guitar playing techniques.
Bending is a technique that involves bending the string sideways to change its pitch. This can be used to create a variety of effects, from subtle pitch changes to wide, expressive bends. Bending is often used in blues, rock, and country music.
Vibrato is a technique that involves rapidly shaking the string to create a vibrato effect. This can be used to add depth and expression to the guitar’s sound. Vibrato is often used in jazz, blues, and rock music.
Hammer-ons are a technique that involves hitting the string with the fretting hand to create a note. This can be used to create a variety of effects, from percussive sounds to legato passages. Hammer-ons are often used in rock, metal, and funk music.
These three guitar playing techniques are essential components of electric guitar terminology. They allow guitarists to create a wide range of sounds and effects, and they are used in a variety of musical genres. Understanding how to use these techniques is essential for any guitarist who wants to expand their playing skills.
Table: Guitar Playing Techniques: Bending, Vibrato, Hammer-Ons
| Technique | Description | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Bending | Bending the string sideways to change its pitch | Blues, rock, country |
| Vibrato | Rapidly shaking the string to create a vibrato effect | Jazz, blues, rock |
| Hammer-ons | Hitting the string with the fretting hand to create a note | Rock, metal, funk |
7. Guitar chords
Guitar chords are a fundamental aspect of electric guitar terminology. They are the building blocks of rhythm and harmony, and they allow guitarists to create a wide range of sounds and styles. Major chords, minor chords, and seventh chords are three of the most common and versatile types of guitar chords.
- Major chords
Major chords are characterized by their bright, happy sound. They are typically used in pop, rock, and country music. Major chords are built on the root, third, and fifth notes of the major scale.
- Minor chords
Minor chords are characterized by their darker, more somber sound. They are typically used in blues, jazz, and rock music. Minor chords are built on the root, third, and fifth notes of the minor scale.
- Seventh chords
Seventh chords are characterized by their riche
r, more complex sound. They are typically used in jazz, blues, and rock music. Seventh chords are built on the root, third, fifth, and seventh notes of the major or minor scale.
Understanding how to play and use guitar chords is essential for any guitarist who wants to expand their playing skills. Major chords, minor chords, and seventh chords are a great place to start, as they are relatively easy to learn and can be used in a wide variety of songs.
8. Guitar scales
Guitar scales are an essential part of electric guitar terminology. They are the building blocks of solos and melodies, and they allow guitarists to create a wide range of sounds and styles. Major scales, minor scales, and pentatonic scales are three of the most common and versatile types of guitar scales.
- Major scales
Major scales are characterized by their bright, happy sound. They are typically used in pop, rock, and country music. Major scales are built on the root, third, fifth, and seventh notes of the major scale.
- Minor scales
Minor scales are characterized by their darker, more somber sound. They are typically used in blues, jazz, and rock music. Minor scales are built on the root, third, fifth, and seventh notes of the minor scale.
- Pentatonic scales
Pentatonic scales are characterized by their simple, five-note structure. They are typically used in blues, rock, and country music. Pentatonic scales are built on the root, second, third, fifth, and sixth notes of the major or minor scale.
Understanding how to play and use guitar scales is essential for any guitarist who wants to expand their playing skills. Major scales, minor scales, and pentatonic scales are a great place to start, as they are relatively easy to learn and can be used in a wide variety of songs.
9. Guitar tablature
Guitar tablature is a system of musical notation specifically designed for the guitar. It represents the fretboard of the guitar, with each horizontal line representing a string and the numbers indicating which fret to play on that string. This system is widely used by guitarists of all levels, as it is a relatively easy and intuitive way to learn and play guitar music.
Guitar tablature is an essential component of electric guitar terminology because it provides a clear and concise way to communicate guitar-specific information. For example, tablature can be used to indicate the fingering for a particular chord or scale, or to provide a complete transcription of a song. This makes it possible for guitarists to share and learn music with each other, regardless of their skill level or musical background.
In addition to its practical applications, guitar tablature also has a number of educational benefits. For example, it can help guitarists to visualize the fretboard and to understand how different notes and chords are constructed. This can lead to a deeper understanding of guitar theory and technique.
Overall, guitar tablature is a valuable tool for guitarists of all levels. It is a versatile system that can be used for a variety of purposes, from learning new songs to developing new guitar techniques.
Table: Guitar Tablature vs. Standard Notation
| Characteristic | Guitar Tablature | Standard Notation |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of learning | Easier for beginners | More difficult for beginners |
| Flexibility | Can be used for any type of guitar | Limited to classical guitar |
| Versatility | Can be used to indicate fingering, chords, and scales | Primarily used for melodies |
10. Guitar maintenance
Guitar maintenance is an essential part of electric guitar terminology because it ensures that your guitar is in good playing condition. A well-maintained guitar will stay in tune, produce a clear sound, and be comfortable to play. Neglecting guitar maintenance can lead to a variety of problems, including:rust and corrosion on the strings and metal parts, dirt and grime on the fretboard and body, and a loss of intonation.
There are three main types of guitar maintenance tasks: cleaning, restringing, and setting up.
- Cleaning involves wiping down the guitar’s body, neck, and fretboard with a soft cloth to remove dirt and grime.
- Restringing involves replacing the old strings with new ones.
- Setting up involves adjusting the guitar’s intonation, string height, and truss rod to ensure that it plays optimally.
Each of these tasks is important for maintaining the playability and sound of your guitar. Cleaning removes dirt and grime that can build up over time and interfere with the guitar’s finish and sound. Restringing replaces old strings that have become worn or damaged, which can improve the guitar’s intonation and sound. Setting up ensures that the guitar’s intonation, string height, and truss rod are properly adjusted, which can make the guitar more comfortable to play and improve its sound.
By understanding the importance of guitar maintenance and how to perform these tasks, you can keep your guitar in good playing condition for years to come.
Table: Guitar Maintenance Tasks
| Task | Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | Monthly | Prevents dirt and grime buildup, protects the finish |
| Restringing | Every 3-6 months | Improves intonation and sound, prevents string breakage |
| Setting up | Every 6-12 months | Ensures optimal playability and sound, prevents neck and fretboard damage |
FAQs on Electric Guitar Terminology
Understanding the terminology associated with electric guitars is essential for effective communication and knowledge acquisition in the world of electric guitar playing. This FAQ section addresses some common questions and misconceptions surrounding electric guitar terms, providing clear and informative answers to enhance your understanding.
Question 1: What is the difference between a solid-body and a hollow-body electric guitar?
Answer: Solid-body electric guitars have a solid body that does not resonate as much as hollow-body guitars, resulting in a brighter, more focused sound with less feedback. Hollow-body electric guitars have a hollow body that resonates more, producing a warmer, more mellow sound with more sustain.
Question 2: What is the function of a pickup in an electric guitar?
Answer: Pickups are electromagnetic devices that convert the vibrations of the strings into electrical signals. Different types of pickups produce different tones, allowing guitarists to achieve a wide range of sounds.
Question 3: What is the difference between a tube amplifier and a solid-state amplifier?
Answer: Tube amplifiers use vacuum tubes to amplify the guitar’s signal, resulting in a warm, natural sound. Solid-state amplifiers use transistors to amplify the signal, producing a more affordable, reliable, and versatile sound.
Question 4: What is the purpose of guitar effects?
Answer: Guitar effects are devices that modify the sound of an electric guitar, allowing guitarists to create a vast array of tones and sonic textures. Common effects include distortion, reverb, and delay.
Question 5: What is the difference between major and minor chords?
Answer: Major chords have a bright, happy sound and are commonly used in pop, rock, and country music. Minor chords have a darker, more somber sound and are often found in blues, jazz, and rock music.
Question 6: What is the benefit of learning guitar scales?
Answer: Learning guitar scales provides guitarists with a structured framework for understanding and creating melodies and solos. Scales help guitarists improve their dexterity, finger coordination, and overall musicality.
Summary: Understanding electric guitar terminology is crucial for guitarists to effectively communicate, acquire knowledge, and expand their playing abilities. The FAQs addressed in this section provide a solid foundation for comprehending essential electric guitar terms and concepts.
Transition: To delve deeper into the world of electric guitar terminology, explore the additional sections of this comprehensive guide, where we cover a wide range of topics related to electric guitar terms.
Tips on Electric Guitar Terms
Understanding the terminology associated with electric guitars is essential for effective communication, knowledge acquisition, and overall improvement as a guitarist. Here are several tips to help you master electric guitar terminology:
Tip 1: Immerse Yourself in Guitar-Related Content
Surround yourself with electric guitar resources such as books, websites, magazines, and online forums. By regularly engaging with guitar-related content, you will naturally absorb and retain new terms.
Tip 2: Attend Workshops and Masterclasses
Participating in workshops and masterclasses led by experienced electric guitarists provides an opportunity to learn directly from experts. These sessions often focus on specific guitar techniques and terminologies, allowing you to gain a deeper understanding.
Tip 3: Analyze Song Structures and Guitar Parts
When listening to electric guitar music, pay attention to the guitar parts and how they contribute to the overall sound. Identify the different guitar techniques, effects, and tones used, and research the corresponding terminology.
Tip 4: Collaborate with Other Guitarists
Engaging with other guitarists provides a platform for exchanging knowledge and expanding your vocabulary. Discuss guitar-related topics, share experiences, and learn from each other’s perspectives.
Tip 5: Utilize Online Resources and Dictionaries
Take advantage of the wealth of online resources and dictionaries dedicated to electric guitar terminology. These resources offer comprehensive explanations, examples, and interactive tools to enhance your understanding.
Tip 6: Practice Regularly and Experiment with Different Sounds
Regular practice is essential for solidifying your knowledge of electric guitar terms. Experiment with different guitar techniques, effects, and amplifier settings to hear how they impact the sound. This hands-on experience will deepen your understanding and practical application of guitar terminology.
Summary: By implementing these tips, you can effectively expand your knowledge of electric guitar terminology, enhance your communication skills within the guitar community, and elevate your overall playing abilities.
Transition: Continue exploring the subsequent sections of this comprehensive guide to further enhance your understanding of electric guitar terminology and its significance in the world of electric guitar playing.
Electric Guitar Terms
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored the diverse and essential world of electric guitar terminology, providing a thorough understanding of the components, techniques, and concepts that shape the electric guitar experience. From the fundamental parts of the guitar to the intricacies of guitar electronics, amplifiers, and effects, we have covered a wide range of topics to equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the world of electric guitar playing.
Understanding electric guitar terminology is not merely about memorizing definitions; it is about gaining a deeper appreciation for the instrument’s capabilities and unlocking your potential as a guitarist. By mastering these terms, you can communicate effectively with other guitarists, explore new musical possibilities, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise with your gear. Ultimately, a solid grasp of electric guitar terminology will empower you to fully embrace the joys and rewards of electric guitar playing.