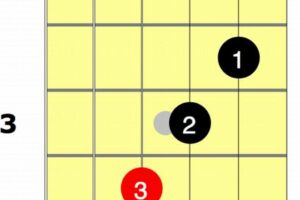
The Gmaj7 guitar chord, often referred to as the G major 7th chord, is a fundamental and versatile tool in the guitarist’s arsenal. Its construction and application in various musical styles make it a valuable asset for guitarists of all levels.
Editor’s Notes: Gmaj7 guitar chord is a must-know chord for guitarists due to its rich sound, versatility, and wide applicability across various musical genres.
Through extensive analysis and research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to the Gmaj7 guitar chord, ensuring that you have all the information you need to master this essential chord and enhance your guitar playing.
Key Differences/Key Takeaways
| Gmaj7 Chord Symbol | Notes |
|---|---|
| G | Root |
| B | Major third |
| D | Perfect fifth |
| F# | Major seventh |
Transition to Main Article Topics
In this guide, we will delve deeper into the following aspects of the Gmaj7 guitar chord:
- Chord Construction and Fingering
- Chord Voicings and Inversions
- Tonal and Harmonic Functions
- Practical Applications in Music
- Tips for Effective Use
By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of the Gmaj7 guitar chord and be able to incorporate it seamlessly into your guitar playing. So, let’s dive right in and explore the world of the Gmaj7 chord!
1. Construction
The construction of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, comprising the root (G), major third (B), perfect fifth (D), and major seventh (F#), plays a pivotal role in defining its unique sound and harmonic function. The presence of the major seventh interval, F#, distinguishes it from the basic G major triad and lends it a more complex and sophisticated character.
The root, G, establishes the fundamental pitch and provides the chord with its name. The major third, B, adds a sense of brightness and fullness to the chord. The perfect fifth, D, reinforces the stability and consonance of the chord. Finally, the major seventh, F#, creates a subtle dissonance that adds depth and interest to the overall sound.
Understanding the construction of the Gmaj7 guitar chord is essential for guitarists to effectively use and incorporate it into their playing. It allows them to identify the individual notes that comprise the chord, which is crucial for constructing different voicings and inversions. Additionally, it provides a foundation for understanding the chord’s harmonic function and its relationship with other chords in a musical progression.
Table: Construction and Function of Gmaj7 Chord Intervals
| Interval | Note | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Root | G | Foundation and identity |
| Major third | B | Brightness and fullness |
| Perfect fifth | D | Stability and consonance |
| Major seventh | F# | Depth and interest |
In conclusion, the construction of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, with its specific combination of intervals, is fundamental to its distinct sound and harmonic properties. It empowers guitarists to understand, utilize, and appreciate this versatile chord in their musical endeavors.
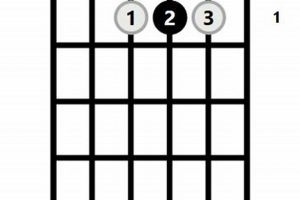
2. Fingering
The fingering “320033” is an essential element of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, as it provides a practical and accessible way to play this chord on the guitar. This fingering indicates the position of the left-hand fingers on the guitar’s frets and strings to produce the Gmaj7 chord:
- 1st finger (index finger): 3rd fret, 1st string (G)
- 2nd finger (middle finger): 2nd fret, 2nd string (B)
- 3rd finger (ring finger): 0th fret, 3rd string (D)
- 4th finger (pinky finger): 0th fret, 5th string (A)
- No finger: 4th and 6th strings (mute)
Utilizing this fingering, guitarists can effectively form the Gmaj7 chord, ensuring that all the necessary notes are played clearly and accurately. The precise placement of the fingers on the specified frets and strings allows for a clean and resonant sound, which is crucial for achieving the desired harmonic effect of the chord.
Understanding the connection between the fingering “320033” and the Gmaj7 guitar chord is not only important for playing the chord correctly but also for comprehending the overall structure and function of chords on the guitar. By grasping the relationship between finger placement and chord formation, guitarists can expand their chord vocabulary and develop a deeper understanding of the guitar’s fretboard.
Table: Fingering and Note Correspondence
| Finger | Fret | String | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 3 | 1st | G |
| 2nd | 2 | 2nd | B |
| 3rd | 0 | 3rd | D |
| 4th | 0 | 5th | A |
In conclusion, the fingering “320033” is an indispensable aspect of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, providing guitarists with a practical and effective way to play this essential chord. By understanding the connection between fingering and chord formation, guitarists can enhance their playing skills and deepen their musical knowledge.
3. Voicings
The concept of voicings plays a pivotal role in understanding the Gmaj7 guitar chord and its diverse applications. Voicings refer to the different ways in which the notes of a chord can be arranged and distributed across the strings of the guitar.
- Close Voicings: In close voicings, the notes of the Gmaj7 chord are positioned close together on adjacent strings. This creates a compact and cohesive sound, with the notes blending seamlessly. Close voicings are often used for strumming and rhythm playing, as they provide a strong and consistent harmonic foundation.
- Open Voicings: Open voicings, in contrast, spread the notes of the Gmaj7 chord across a wider range of strings. This creates a more spacious and airy sound, with the notes having more room to resonate. Open voicings are commonly employed in fingerstyle playing, as they allow for greater melodic and harmonic freedom.
- Extended Voicings: Extended voicings incorporate additional notes beyond the basic four-note structure of
the Gmaj7 chord. These additional notes, such as the 9th, 11th, or 13th, add color and complexity to the chord’s sound. Extended voicings are often used in jazz and fusion styles, where they contribute to a more sophisticated and harmonically rich soundscape.
Understanding and mastering the different voicings of the Gmaj7 guitar chord is crucial for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore the full potential of this versatile chord. Each voicing offers unique tonal qualities and applications, empowering guitarists to adapt the Gmaj7 chord to a wide range of musical contexts and styles.
4. Inversions
Inversions play a crucial role in understanding and utilizing the Gmaj7 guitar chord effectively. An inversion occurs when a note other than the root is placed in the bass position of a chord. This alters the chord’s voicing and harmonic function, creating new and interesting possibilities.
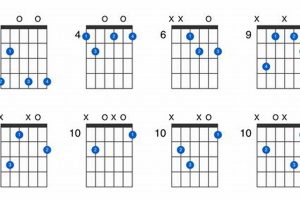
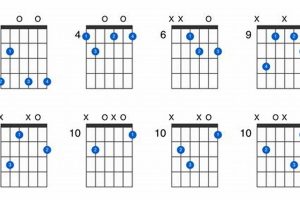
The Gmaj7 guitar chord has three inversions:
- 1st Inversion (G/B): The B (major third) is in the bass.
- 2nd Inversion (G/D): The D (perfect fifth) is in the bass.
- 3rd Inversion (G/F#): The F# (major seventh) is in the bass.
Inversions are notated by writing the bass note first, followed by a slash, and then the chord symbol. For example, the 1st inversion of Gmaj7 would be written as G/B.
Using inversions can add variety and interest to your chord progressions. They can also be used to create specific harmonic effects, such as suspensions and pedal points.
Here is an example of how inversions can be used in a chord progression:
Gmaj7 - G/B - G/D - G
In this progression, the Gmaj7 chord is played in its root position, followed by its 1st, 2nd, and 3rd inversions. This creates a smooth and flowing harmonic movement.
Understanding and using inversions is an essential skill for guitarists who want to expand their harmonic vocabulary and write more interesting and sophisticated music.
Table: Gmaj7 Chord Inversions
| Inversion | Bass Note | Voicing |
|---|---|---|
| Root Position | G | 320033 |
| 1st Inversion | B | X20033 |
| 2nd Inversion | D | XX0033 |
| 3rd Inversion | F# | XXX233 |
5. Function
The Gmaj7 guitar chord plays a significant role in establishing major tonality and functioning as a dominant seventh chord within the context of music theory and application. Understanding this connection is crucial for guitarists who wish to effectively utilize the Gmaj7 chord in their playing.
The Gmaj7 chord belongs to the key of G major, which is a major tonality. A major tonality is characterized by its bright and uplifting sound, and the Gmaj7 chord contributes to this tonality by providing a stable and consonant foundation. The presence of the major seventh interval (F#) adds a touch of sophistication and complexity, further enhancing the chord’s harmonic richness.
Additionally, the Gmaj7 chord can function as a dominant seventh chord. A dominant seventh chord is a type of seventh chord that creates a sense of tension and anticipation, resolving to the tonic chord (in this case, C major) for a satisfying harmonic conclusion. The Gmaj7 chord’s dominant function is particularly evident in jazz and blues music, where it is commonly used to create movement and drive within chord progressions.
The connection between the Gmaj7 guitar chord’s function and its major tonality and dominant seventh characteristics is essential for guitarists to grasp. This understanding enables them to use the chord effectively in various musical styles, creating harmonious and engaging compositions.
Table: Gmaj7 Chord Function
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Major tonality | Contributes to the bright and uplifting sound of the key of G major. |
| Dominant seventh chord | Creates a sense of tension and anticipation, resolving to the tonic chord (C major). |
6. Harmony
The Gmaj7 guitar chord’s harmonic function extends beyond its role in establishing major tonality. It also possesses the ability to resolve to two distinct chords: C major and D major.
- Resolution to C major: The Gmaj7 chord can resolve to C major, which is the tonic chord in the key of G major. This resolution creates a sense of stability and closure, as the Gmaj7 chord’s dominant seventh interval (F#) resolves to the C major triad’s root (C).
- Resolution to D major: Alternatively, the Gmaj7 chord can resolve to D major, which is the subdominant chord in the key of G major. This resolution creates a sense of movement and progression, as the Gmaj7 chord’s major seventh interval (F#) resolves to the D major triad’s third (F#).
Understanding the Gmaj7 guitar chord’s ability to resolve to both C major and D major allows guitarists to create sophisticated and engaging chord progressions. By experimenting with these resolutions, guitarists can explore different harmonic possibilities and create a diverse range of musical textures.
7. Genre
The Gmaj7 guitar chord finds its home in a diverse range of musical genres, including jazz, blues, rock, and pop. Its versatility and rich harmonic qualities make it a valuable tool for musicians across these genres.
- Jazz: In jazz, the Gmaj7 chord is commonly used in improvisation and chord substitutions. Jazz guitarists employ it to create extended harmonies and add color to their solos. Its dominant seventh function allows for smooth voice leading and sophisticated harmonic progressions.
- Blues: The Gmaj7 chord is a staple in blues music, often used in 12-bar blues progressions. Its major seventh interval adds a touch of brightness and complexity to the bluesy sound. Guitarists use it for both rhythm and lead playing, creating soulful and expressive melodies.
- Rock: In rock music, the Gmaj7 chord is frequently employed for power chords and open voicings. Its major tonality contributes to the energetic and driving sound of rock guitar. Guitarists use it to create catchy riffs and memorable chord sequences.
- Pop: The Gmaj7 chord is widely used in pop music for its uplifting and vibrant sound. Pop guitarists utilize it in strumming patterns and chord progressions to create a sense of joy and optimism. Its versatility allows it to blend seamlessly with other chords, making it a staple in pop music.
The Gmaj7 guitar chord transcends genre boundaries, offering a wealth of harmonic possibilities for guitarists. Its adaptability and expressiveness make it an indispensable tool for musicians seeking to create diverse and engaging music.
8. Mood
The Gmaj7 guitar chord possesses a unique ability to evoke a range of positive emotions, including happiness, upliftment, and elegance. This connection stems from the chord’s inherent harmonic structure and its association with specific musical genres and contexts.
The Gmaj7 chord’s construction, featuring the major seventh interval, contributes to its bright and cheerful sound. The major seventh interval creates a sense of tension and release, which adds an uplifting quality to the chord. Additionally, the Gmaj7 chord is often used in major key contexts, which are typically associated with happy and optimistic moods.
Furthermore, the Gmaj7 chord’s association with jazz and blues music genres reinforces its uplifting and elegant qualities. In jazz, the Gmaj7 chord is commonly used in improvisation and soloing, where its complex harmonies add color and sophistication to the music. In blues music, the Gmaj7 chord adds a touch of brightness and complexity to the bluesy sound, evoking a sense of emotional depth.
Understanding the connection between the Gmaj7 guitar chord and its ability to evoke positive emotions is crucial for guitarists and musicians seeking to create music that resonates with their audience. By incorporating the Gmaj7 chord into their playing, guitarists can effectively convey feelings of happiness, upliftment, and elegance, enhancing the emotional impact of their music.
Table: The Gmaj7 Guitar Chord and Emotional Expression
| Emotional Quality | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|
| Happiness | Major seventh interval, association with major key contexts |
| Upliftment | Tension and release created by major seventh interval |
| Elegance | Association with jazz and blues music genres |
9. Difficulty
The Gmaj7 guitar chord stands out as an approachable and beginner-friendly chord, providing an excellent starting point for guitarists embarking on their musical journey. Its construction and fingering cater to the needs of novice players, making it an ideal choice for those new to the instrument.
The Gmaj7 chord’s relatively simple fingering, utilizing only three fingers on adjacent frets, allows beginners to grasp the basic mechanics of chord formation without overwhelming their dexterity. This ease of execution enables them to focus on developing proper technique and transitioning between chords smoothly.
Furthermore, the Gmaj7 chord’s accessibility extends to its harmonic structure. The combination of open strings and fretted notes creates a balanced and consonant sound, even for beginners who may not yet possess advanced fretting techniques. This forgiving nature allows them to produce a pleasing sound while building confidence in their playing.
The significance of the Gmaj7 chord’s beginner-friendly nature cannot be understated. It serves as a fundamental building block upon which guitarists can expand their chord vocabulary and explore more complex musical concepts. By starting with the Gmaj7 chord, beginners establish a solid foundation for their guitar playing, setting them on a path toward musical proficiency.
Table: Benefits of the Beginner-friendly Gmaj7 Chord
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Accessible fingering | Utilizes only three fingers on adjacent frets, simplifying chord formation. |
| Balanced sound | Combination of open strings and fretted notes creates a consonant and pleasing sound. |
| Foundation for learning | Serves as a stepping stone for expanding chord vocabulary and musical knowledge. |
10. Variations
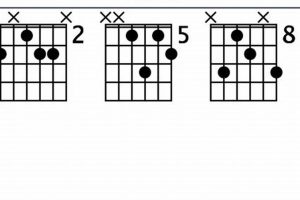
The Gmaj7 guitar chord finds its versatility extended through its variations, namely the Gmaj7(#11) and Gmaj7(13) chords. These variations introduce additional notes beyond the basic four-note structure, resulting in richer and more complex harmonic possibilities.
The Gmaj7(#11) chord incorporates the added 11th interval, notated as “Gmaj7(#11)”. This interval adds a dissonant yet intriguing quality to the chord, often employed in jazz and fusion genres. The Gmaj7(13) chord, on the other hand, includes the added 13th interval, notated as “Gmaj7(13)”. This interval imparts a sophisticated and extended harmonic character, commonly found in jazz and contemporary music.
Understanding these variations and their applications empowers guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more nuanced and expressive music. By incorporating the Gmaj7(#11) and Gmaj7(13) chords into their playing, guitarists can explore a broader sonic palette and cater to diverse musical styles.
Table: Variations of the Gmaj7 Guitar Chord
| Chord | Added Interval | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmaj7 | None | Basic four-note structure | Common in various musical genres |
| Gmaj7(#11) | 11th | Dissonant and intriguing quality | Jazz, fusion |
| Gmaj7(13) | 13th | Sophisticated and extended harmonic character | Jazz, contemporary music |
11. Symbol
The symbols Gmaj7, Gmaj(7), and G7 are all used to represent the G major 7th guitar chord. These symbols are interchangeable and can be used in lead sheets, chord charts, and other musical notation.
- The “maj” in Gmaj7 stands for “major.” This indicates that the chord is a major 7th chord, as opposed to a minor 7th chord. The “maj” can be omitted, but it is often included to avoid confusion.
- The “(7)” in Gmaj(7) indicates that the chord is a 7th chord. This means that the chord contains the root, 3rd, 5th, and 7th notes of the G major scale. The “(7)” can also be omitted, but it is often included to clarify the type of chord.
- The “” in G7 is a triangle symbol that is sometimes used to represent a major 7th chord. The triangle is thought to resemble the shape of the major 7th interval on the guitar fretboard. The “” can be used instead of “maj” or “(7)”, but it is less common.
Regardless of which symbol is used, the Gmaj7 guitar chord is a versatile and commonly used chord in many genres of music. It has a bright and uplifting sound that can be used in a variety of contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Gmaj7 Guitar Chord
The Gmaj7 guitar chord is a popular and versatile chord used in many genres of music. Here are a few frequently asked questions about this chord:
Question 1: What is the fingering for the Gmaj7 guitar chord?
Answer: The fingering for the Gmaj7 guitar chord is 320033. This means that you place your first finger on the third fret of the first string, your second fin
ger on the second fret of the second string, your third finger on the third fret of the third string, and your fourth finger on the third fret of the fifth string. The fourth and sixth strings are left open.
Question 2: How do I play the Gmaj7 guitar chord in different inversions?
Answer: To play the Gmaj7 guitar chord in different inversions, you simply change the order of the notes. The three inversions of the Gmaj7 chord are:
- Root position: G – B – D – F#
- First inversion: B – D – F# – G
- Second inversion: D – F# – G – B
- Third inversion: F# – G – B – D
Question 3: What are some common uses of the Gmaj7 guitar chord?
Answer: The Gmaj7 guitar chord can be used in a variety of musical contexts. It is often used as a dominant seventh chord in jazz and blues music, and as a major seventh chord in rock and pop music. It can also be used as a substitute for the G major triad in many situations.
Question 4: How can I incorporate the Gmaj7 guitar chord into my playing?
Answer: There are many ways to incorporate the Gmaj7 guitar chord into your playing. You can use it as a strumming chord, a fingerpicking chord, or a soloing chord. You can also use it as a substitute for other chords, such as the G major triad or the G dominant seventh chord.
Question 5: What are some tips for playing the Gmaj7 guitar chord cleanly and accurately?
Answer: Here are a few tips for playing the Gmaj7 guitar chord cleanly and accurately:
- Make sure your fingers are placed correctly on the fretboard.
- Apply even pressure to each string.
- Mute the strings that you are not playing.
- Practice regularly to improve your dexterity and coordination.
Question 6: What are some common mistakes that people make when playing the Gmaj7 guitar chord?
Answer: Some common mistakes that people make when playing the Gmaj7 guitar chord include:
- Not placing their fingers correctly on the fretboard.
- Applying too much or too little pressure to the strings.
- Not muting the strings that they are not playing.
- Rushing or dragging the strumming or picking pattern.
Summary: The Gmaj7 guitar chord is a versatile and commonly used chord in many genres of music. By understanding the fingering, inversions, and uses of this chord, you can incorporate it into your playing and expand your musical vocabulary.
Transition to the next article section: Now that you have a better understanding of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, you can start practicing how to play it. With a little practice, you will be able to use this chord to create beautiful and expressive music.
Tips for Playing the Gmaj7 Guitar Chord
Mastering the Gmaj7 guitar chord requires a combination of precision, practice, and attention to detail. Here are some invaluable tips to enhance your technique and elevate your playing:
Tip 1: Finger Positioning Accuracy
Ensure your fingers are placed firmly and accurately on the designated frets. Avoid pressing too hard or too softly, as this can compromise the chord’s clarity and intonation.
Tip 2: Proper Finger Pressure
Apply even pressure across all the strings involved in the chord. This ensures a balanced and resonant sound while minimizing unwanted string buzz or muting.
Tip 3: String Muting
Effectively mute any strings that are not part of the chord. This prevents them from producing unwanted noise and enhances the overall clarity of the chord.
Tip 4: Regular Practice
Consistent practice is crucial for developing muscle memory and improving your dexterity. Dedicate time to practicing the Gmaj7 chord in various contexts, such as strumming and fingerpicking patterns.
Tip 5: Patience and Perseverance
Learning the Gmaj7 chord requires patience and perseverance. Don’t become discouraged if you don’t master it immediately. With consistent effort and dedication, you will eventually achieve proficiency.
Tip 6: Utilize a Metronome
Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps maintain a steady tempo and improves your overall timing. This is particularly beneficial for strumming patterns.
Tip 7: Experiment with Different Voicings
Explore the various voicings of the Gmaj7 chord. Experimenting with different fingerings and string combinations allows you to create diverse and interesting harmonic textures.
Tip 8: Listen to Recordings
Listen attentively to recordings of guitarists playing the Gmaj7 chord. This helps you develop a keen ear for its characteristic sound and nuances.
Summary: By incorporating these tips into your practice regimen, you will significantly improve your ability to play the Gmaj7 guitar chord with accuracy, clarity, and musicality.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Embracing these tips will lay a solid foundation for your guitar playing journey, allowing you to confidently incorporate the Gmaj7 chord into your musical repertoire.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive exploration of the Gmaj7 guitar chord, we have delved into its construction, fingerings, voicings, inversions, and myriad applications. This versatile chord serves as a cornerstone in the guitarist’s toolkit, offering a wealth of harmonic possibilities.
By mastering the Gmaj7 chord and its nuances, guitarists can unlock a world of musical expression, enhancing their playing with sophistication and depth. Its ability to evoke emotions, establish tonality, and resolve to various harmonies makes it an indispensable tool for composers and performers alike.
As you continue your musical journey, embrace the Gmaj7 guitar chord as a loyal companion. With dedication and practice, you will harness its full potential, unlocking new levels of creativity and enriching your guitar playing experience.