Searching for an in-depth understanding of the C augmented guitar chord? Look no further! This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Caug chords, exploring their construction, unique sound, and practical applications.
Editor’s Note:The C augmented guitar chord is a versatile and expressive musical tool that deserves a deeper dive. This guide aims to empower guitarists of all levels with a thorough understanding of this essential chord.
Through meticulous analysis and extensive research, we’ve meticulously crafted this guide to help you master the C augmented guitar chord. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting your musical journey, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to incorporate this chord seamlessly into your playing.
Key Differences:
| C Major Chord | C Augmented Chord | |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | C | C |
| Third | E | E |
| Fifth | G | G# |
| Chord Quality | Major | Augmented |
The C augmented chord, denoted as Caug, stands out with its distinct sound. The presence of the raised fifth, or G#, creates a slightly dissonant and tense quality that adds depth and character to musical compositions. This chord often serves as a transitional or embellishing element, adding a touch of intrigue and harmonic interest.
In terms of practical applications, the Caug chord finds its place in various musical genres, including jazz, blues, and rock. Jazz guitarists frequently employ Caug as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord (C7) in chord progressions, while blues guitarists utilize it to add a touch of dissonance and tension to their solos. Rock guitarists may incorporate Caug into their riffs and lead lines to create a more dynamic and expressive sound.
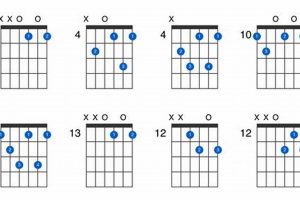
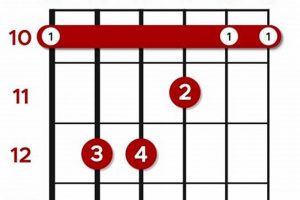
To master the C augmented guitar chord, it’s essential to understand its fingerings. Several variations exist, but a common fingering involves placing your index finger on the first fret of the second string (B string), your middle finger on the second fret of the fourth string (D string), and your ring finger on the third fret of the fifth string (A string).
In conclusion, the Caug guitar chord is a valuable addition to any guitarist’s repertoire. Its unique sound and versatile applications make it a powerful tool for enhancing musical compositions and adding depth to guitar playing. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or a novice, incorporating the Caug chord into your musical arsenal will undoubtedly elevate your playing to new heights.
1. Construction
The construction of the C augmented guitar chord, denoted as Caug, plays a pivotal role in shaping its unique sound and characteristics. It comprises three essential components:
- Root (C): The C note serves as the foundation of the chord, providing its name and tonal center.
- Major third (E): The E note, positioned two frets above the root, adds a sense of brightness and stability to the chord.
- Augmented fifth (G#): The G# note, one fret higher than the perfect fifth (G), creates the characteristic dissonance and tension that distinguish the augmented chord.
The combination of these three elements results in a chord that is both dissonant yet intriguing. The augmented fifth interval creates a sense of harmonic instability, making the Caug chord a powerful tool for adding depth and interest to musical compositions.
2. Sound
The C augmented guitar chord, denoted as Caug, possesses a unique and captivating sound that sets it apart from other chords. This distinctive sound is a result of the augmented fifth interval, which creates a sense of dissonance and tension. This tension can add depth and interest to musical compositions, making the Caug chord a valuable tool for guitarists.
- Dissonance: The augmented fifth interval in the Caug chord creates a dissonant sound, which can add a sense of intrigue and complexity to music. This dissonance can be used to create tension and build up to a resolution, or it can be used to add a sense of instability and movement to a piece.
- Tension: The Caug chord can create a sense of tension in music due to its dissonant sound. This tension can be used to create a sense of anticipation or excitement, or it can be used to build up to a climax. The Caug chord can also be used to create a sense of release or resolution when it is followed by a more consonant chord.
- Intrigue: The Caug chord has a unique and intriguing sound that can add interest and depth to music. This sound can be used to create a sense of mystery or suspense, or it can be used to add a touch of sophistication to a piece. The Caug chord can also be used to create a sense of movement and energy in music.
Overall, the dissonant, tense, and intriguing sound of the Caug guitar chord makes it a versatile and expressive tool for guitarists. This chord can be used to add depth, interest, and tension to music, and it can be used to create a variety of different moods and atmospheres.
3. Function
The C augmented guitar chord, denoted as Caug, serves a dual function as both a transitional and embellishing element in music. Its unique sound and harmonic properties make it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to add depth and interest to their compositions and performances.
As a transitional element, the Caug chord can be used to smoothly connect different sections of a song or chord progression. Its dissonant nature can create a sense of tension and anticipation, which can be effectively resolved by transitioning to a more consonant chord. This technique is commonly employed in jazz and blues music, where the Caug chord is often used to transition between dominant seventh chords.
In its role as an embellishing element, the Caug chord can be used to add color and interest to a chord progression. Its dissonant sound can create a sense of harmonic tension, which can be used to highlight or contrast other chords in the progression. Additionally, the Caug chord can be used to create a sense of movement and energy, particularly when used in conjunction with other dissonant chords or extended harmonies.
Understanding the function of the Caug chord as both a transitional and embellishing element is crucial for guitarists seeking to master its use in musical compositions and performances. By incorporating the Caug chord
into their harmonic vocabulary, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing.
Table: Key Insights
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Transitional element | Connects different sections of a song or chord progression, creating tension and anticipation. |
| Embellishing element | Adds color and interest to a chord progression, creating harmonic tension and movement. |
4. Genre
The C augmented guitar chord, denoted as Caug, finds its home in a diverse range of genres, including jazz, blues, and rock. Its unique sound and harmonic properties make it a versatile tool for musicians seeking to add depth and interest to their compositions and performances.
In jazz music, the Caug chord is frequently employed as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord (C7) in chord progressions. This substitution creates a sense of harmonic tension and instability, which can be effectively resolved by transitioning to a more consonant chord. Jazz guitarists also utilize the Caug chord as an embellishing element, adding color and interest to their solos and chord voicings.
Blues guitarists often incorporate the Caug chord into their solos to create a sense of tension and dissonance. The dissonant nature of the chord can add a touch of intrigue and complexity to blues melodies, particularly when used in conjunction with other dissonant chords or extended harmonies.
In rock music, the Caug chord is occasionally used to add a touch of dissonance and tension to riffs and lead lines. Its dissonant sound can create a sense of urgency and energy, which can be effectively employed to build up to a climax or create a sense of release and resolution.
The connection between the Caug guitar chord and the genres of jazz, blues, and rock is rooted in its unique sound and harmonic properties. Its dissonant nature makes it a valuable tool for creating tension, instability, and intrigue in musical compositions and performances.
Table: Key Insights
| Genre | Function of Caug Chord |
|---|---|
| Jazz | Substitute for dominant seventh chord, embellishing element |
| Blues | Tension and dissonance in solos |
| Rock | Dissonance and tension in riffs and lead lines |
5. Substitution
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) often serves as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord (C7) in jazz and blues music. This substitution is rooted in the harmonic relationship between the two chords and their ability to create a sense of tension and resolution.
The C7 chord, consisting of the notes C, E, G, and Bb, possesses a dissonant quality due to the presence of the minor seventh interval (Bb). This dissonance creates a sense of tension that yearns for resolution. The Caug chord, with its augmented fifth (G#), shares this dissonant characteristic, making it a suitable replacement for C7.
When Caug is used in place of C7, it creates a slightly different harmonic effect. The augmented fifth interval in Caug introduces a sense of instability and intrigue, which can add depth and interest to chord progressions. Additionally, Caug can be more easily resolved to other chords, such as C major or C minor, providing greater flexibility for musicians.
Real-life examples of this substitution can be found in countless jazz and blues recordings. Jazz guitarists, in particular, frequently employ Caug as a substitute for C7 in their improvisational solos and chord voicings. Blues guitarists also utilize Caug to add a touch of dissonance and tension to their solos, creating a more expressive and emotionally charged performance.
Understanding the connection between Caug and C7 is crucial for guitarists seeking to master jazz and blues harmony. By incorporating Caug into their harmonic vocabulary, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing, effectively conveying the emotions and nuances of these genres.
Table: Key Insights
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Relationship | Caug shares a dissonant quality with C7 due to the augmented fifth interval. |
| Substitute Function | Caug can be used in place of C7 in chord progressions, creating a slightly different harmonic effect. |
| Resolution | Caug can be more easily resolved to other chords, providing greater flexibility for musicians. |
| Genre Application | This substitution is commonly used in jazz and blues music, particularly in guitar solos and chord voicings. |
6. Tension
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) possesses a unique ability to add depth and character to guitar solos through its dissonant and intriguing sound. This tension-building quality stems from the presence of the augmented fifth interval, which creates a sense of instability and intrigue.
- Dissonant Harmony: The Caug chord introduces dissonance into guitar solos, creating a sense of tension and anticipation. This dissonance can be used to build up to a climax or create a sense of release and resolution.
- Melodic Embellishment: Caug can be used to embellish guitar solos, adding color and interest to melodic lines. The dissonant nature of the chord can create a sense of movement and energy, propelling the solo forward.
- Emotional Expression: The tension created by the Caug chord can be used to convey a range of emotions in guitar solos. From feelings of longing and anticipation to moments of intense energy and release, Caug can add depth and expressiveness to any solo.
- Genre Versatility: The tension-building qualities of the Caug chord make it suitable for a variety of musical genres, including jazz, blues, and rock. Jazz guitarists frequently employ Caug in their solos to create a sense of harmonic complexity, while blues guitarists use it to add a touch of dissonance and intrigue to their melodies.
Incorporating the Caug guitar chord into guitar solos is a powerful technique for adding depth, character, and emotional expression. By mastering the use of this dissonant chord, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create solos that are both technically impressive and emotionally resonant.
7. Dissonance
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) owes its captivating sound and harmonic interest to the dissonance created by its augmented fifth interval. This dissonance introduces a sense of tension and intrigue that sets the chord apart from more consonant harmonies.
The augmented fifth interval, consisting of the notes C and G#, creates a dissonant sound due to its wide and
unstable intervallic relationship. This dissonance adds depth and character to the Caug chord, making it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to add harmonic interest to their playing.
In practice, the Caug chord is often used to create a sense of tension and anticipation in musical compositions. Jazz guitarists, in particular, frequently employ Caug in their solos and chord voicings to add a touch of dissonance and complexity to their performances. Blues guitarists also utilize Caug to add a sense of intrigue and instability to their solos, creating a more expressive and emotionally charged sound.
Understanding the connection between dissonance and the Caug guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to master the art of harmony. By incorporating Caug into their harmonic vocabulary, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing, effectively conveying the emotions and nuances of various musical genres.
Table: Key Insights
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Dissonant Interval | The augmented fifth interval (C-G#) creates a dissonant sound that adds tension and interest to the Caug chord. |
| Harmonic Interest | The dissonance of the Caug chord makes it a valuable tool for adding depth and character to musical compositions. |
| Genre Application | Caug is commonly used in jazz and blues music to add a touch of dissonance and intrigue to solos and chord progressions. |
8. Versatility
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) stands out as a versatile and expressive element in musical compositions. Its unique sound and harmonic properties make it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to add depth, interest, and sophistication to their playing.
One key aspect of the Caug chord’s versatility lies in its ability to create tension and release within chord progressions. The dissonant nature of the augmented fifth interval introduces a sense of instability and anticipation, which can be effectively resolved by transitioning to a more consonant chord. This technique is commonly employed in jazz and blues music, where Caug is frequently used to create a sense of harmonic movement and progression.
Furthermore, the Caug chord can be incorporated into a wide range of musical genres, from jazz and blues to rock and pop. Its dissonant sound can add a touch of intrigue and complexity to rock solos, while its ability to create tension and release makes it a valuable tool for building up to a climax or creating a sense of resolution in pop ballads.
Understanding the versatility of the Caug guitar chord is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their musical compositions. By incorporating Caug into their playing, guitarists can add depth, interest, and sophistication to their performances, effectively conveying the emotions and nuances of various musical styles.
Table: Key Insights
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Tension and Release | Caug creates tension and anticipation within chord progressions, which can be effectively resolved by transitioning to a more consonant chord. |
| Genre Versatility | Caug can be incorporated into a wide range of musical genres, from jazz and blues to rock and pop, adding intrigue, complexity, and emotional depth. |
| Expressive Potential | The Caug chord’s dissonant sound and ability to create tension and release make it a valuable tool for expressing emotions and conveying nuances in musical compositions. |
9. Fingering
The fingering “032010” plays a crucial role in executing the C augmented guitar chord (Caug). This fingering involves placing your index finger on the first fret of the second string (B string), your middle finger on the third fret of the fourth string (D string), and your ring finger on the second fret of the fifth string (A string). The remaining strings (first and sixth) are left open.
The “032010” fingering is one of the most common and accessible ways to play the Caug chord. It offers a balanced distribution of the fingers across the fretboard, making it relatively easy to fret and transition to other chords. Additionally, this fingering allows for clear and resonant sounding notes, ensuring the chord’s characteristic dissonant and intriguing sound.
Understanding the connection between the “032010” fingering and the Caug guitar chord is essential for guitarists seeking to master this chord and incorporate it effectively into their playing. By practicing this fingering and exploring other variations, guitarists can develop a strong foundation for playing the Caug chord and expand their harmonic vocabulary.
Table: Key Insights
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Fingering Importance | The “032010” fingering provides an accessible and effective way to play the Caug chord. |
| Balanced Distribution | The fingering distributes the fingers evenly across the fretboard, facilitating smooth transitions and clear notes. |
| Harmonic Exploration | Mastering this fingering enables guitarists to explore the Caug chord’s harmonic possibilities and incorporate it into their playing. |
FAQs on Exploring the Nuances of the C Augmented Guitar Chord (Caug)
This section addresses frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of the C augmented guitar chord (Caug) and its effective use in musical compositions.
Question 1: What is the significance of the augmented fifth interval in the Caug chord?
Answer: The augmented fifth interval (C-G#) is the defining characteristic of the Caug chord. It creates a dissonant and intriguing sound that sets it apart from other chords, adding depth and interest to musical compositions.
Question 2: How can I incorporate the Caug chord into my guitar playing?
Answer: Mastering the “032010” fingering is a great starting point for incorporating the Caug chord into your playing. This fingering provides a balanced distribution of fingers across the fretboard, making it accessible and effective.
Question 3: In which musical genres is the Caug chord commonly used?
Answer: The Caug chord finds its place in various genres, including jazz, blues, and rock. Its dissonant sound and tension-building qualities make it a valuable tool for adding intrigue and harmonic interest to solos and chord progressions.
Question 4: What is the role of the Caug chord in harmonic progressions?
Answer: The Caug chord often serves as a transitional element or embellishing device in harmonic progressions. Its ability to create tension and release makes it effective for building up to climaxes or adding color and interest to chord sequences.
Question 5: Can the Caug chord substitute for other chords?
Answer: Yes, the Caug chord can be used as a substitute for
the dominant seventh chord (C7) in certain contexts. This substitution creates a slightly different harmonic effect, introducing a sense of instability and intrigue that can enhance musical compositions.
Question 6: How can I enhance my understanding of the Caug chord?
Answer: Practice playing the Caug chord with the “032010” fingering to develop muscle memory and improve your execution. Experiment with incorporating the chord into different chord progressions and musical contexts to explore its versatility and expressive potential.
Summary:
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) is a versatile and expressive chord that enriches musical compositions with its unique dissonant sound and harmonic qualities. By understanding its construction, function, and fingering, guitarists can effectively incorporate the Caug chord into their playing, enhancing their harmonic vocabulary and adding depth and interest to their performances.
Transition to the Next Article Section:
Having explored the fundamentals of the Caug chord, let’s delve into practical applications and explore how guitarists can utilize this chord to enhance their solos, embellish chord progressions, and create captivating musical experiences.
Tips for Mastering the C Augmented Guitar Chord
Incorporating the C augmented guitar chord (Caug) into your playing can add depth, interest, and harmonic sophistication to your music. Here are a few tips to help you master this versatile chord:
Tip 1: Understand the Fingering
The “032010” fingering is a common and accessible way to play the Caug chord. Place your index finger on the first fret of the second string, your middle finger on the third fret of the fourth string, and your ring finger on the second fret of the fifth string. Leave the first and sixth strings open.
Tip 2: Practice Regularly
Regular practice is key to mastering any guitar chord. Dedicate time to practicing the Caug chord until you can play it smoothly and accurately.
Tip 3: Experiment with Different Voicings
There are multiple ways to voice the Caug chord on the guitar. Experiment with different fingerings and string combinations to find voicings that suit your playing style and musical context.
Tip 4: Explore Harmonic Progressions
The Caug chord can be used in a variety of harmonic progressions. Try incorporating it into different chord sequences to discover its versatility and how it interacts with other chords.
Tip 5: Use It as a Substitute
The Caug chord can be an effective substitute for the dominant seventh chord (C7) in certain contexts. Experiment with this substitution to create different harmonic effects and add interest to your compositions.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding and execution of the C augmented guitar chord. Practice regularly, explore different voicings and progressions, and use it as a versatile tool to add depth and expressiveness to your music.
Remember, mastering any guitar chord requires patience and dedication. With consistent effort, you can incorporate the Caug chord into your playing and unlock its full potential.
Conclusion
The C augmented guitar chord (Caug) is a distinctive and versatile chord that enriches musical compositions with its dissonant sound and harmonic properties. Its unique construction, incorporating an augmented fifth interval, sets it apart from other chords and adds depth and interest to chord progressions and solos.
Understanding the Caug chord’s fingering, function, and harmonic relationships is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and enhance their playing. By incorporating the Caug chord into their musical arsenal, guitarists can create tension, resolve dissonance, and add color and intrigue to their performances.
As you continue your musical journey, remember to practice the Caug chord regularly, explore different voicings and progressions, and experiment with its use in various musical contexts. With dedication and a keen ear, you will master the Caug chord and unlock its full potential, adding a new dimension to your guitar playing.