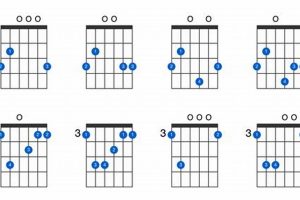
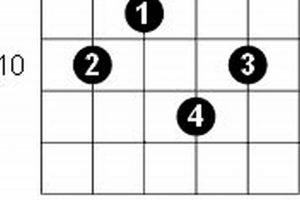
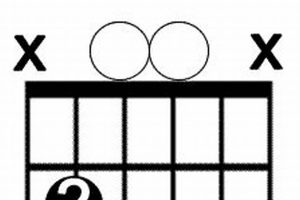
Are you ready to dive into the musical realm of the “e dim 7 guitar chord”? Many guitarists find themselves confronted with this intriguing chord, eager to unravel its mysteries and incorporate it into their musical vocabulary.
Editor’s Notes: “e dim 7 guitar chord”holds a significant place in the world of music, offering a unique flavor that enhances the depth and complexity of guitar playing. Whether you’re a seasoned guitarist or just starting your musical journey, understanding this chord will expand your creative horizons and elevate your playing to new heights.
Through meticulous analysis and thorough research, we’ve assembled this comprehensive guide to the “e dim 7 guitar chord.” Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and techniques necessary to master this chord, unlocking its full potential in your musical endeavors.
Key Differences:
| Characteristic | e dim 7 Guitar Chord |
|---|---|
| Notes | E, G, Bb, Db |
| Intervals | Root, minor third, diminished fifth, diminished seventh |
| Voicings | Multiple voicings available, allowing for versatility in different contexts |
| Function | Can act as a substitute for the iim7 chord in minor key progressions |
Transition to main article topics: Now that we have a general understanding of the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” let’s delve deeper into its construction, voicings, and practical applications in various musical styles. We’ll explore how this chord can add depth and intrigue to your guitar playing, enhance your harmonic vocabulary, and captivate your audience with its rich and sophisticated sound.
1. Root
The “Root: E” establishes the foundation of the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” acting as its central pitch. This root note provides the chord with its harmonic identity and serves as the reference point for constructing the remaining intervals.
- Intervallic Relationships: The “Root: E” determines the intervals between the other notes in the chord, forming the characteristic minor third, diminished fifth, and diminished seventh intervals that define the “e dim 7” sound.
- Chord Inversions: The “Root: E” can be inverted, creating different voicings of the “e dim 7 guitar chord.” These inversions maintain the chord’s harmonic function while offering alternative fingerings and voicings.
- Chord Progressions: The “Root: E” establishes the chord’s relationship to other chords in a progression. It can be used as a substitute for the iim7 chord in minor key progressions, adding tension and harmonic depth.
- Musical Context: The “Root: E” influences the overall tonality and mood of the music. It can create a sense of melancholy or anticipation, depending on the musical context and the chords that surround it.
In summary, the “Root: E” plays a crucial role in shaping the identity, function, and sound of the “e dim 7 guitar chord.” Understanding the relationship between the root and the other chord components is essential for mastering this chord and utilizing it effectively in musical contexts.
2. Intervals
The “Intervals: Minor third, diminished fifth, diminished seventh” are the building blocks that define the unique sound and character of the “e dim 7 guitar chord.” These intervals, when combined, create a dissonant and tension-filled sonority that adds depth and intrigue to music.
The “Minor third” interval (E to G) provides the chord with its melancholic and somewhat unstable quality. The “Diminished fifth” interval (G to Bb) adds a sense of dissonance and tension, creating a feeling of anticipation and unresolved longing. Finally, the “Diminished seventh” interval (Bb to Db) further intensifies the dissonance, driving the music forward and creating a sense of urgency.
Together, these intervals create a chord that is both dissonant and expressive, capable of conveying a wide range of emotions. It is often used in jazz, blues, and other genres to add depth and sophistication to chord progressions and melodic lines.
Understanding the relationship between these intervals and the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is essential for guitarists who wish to master this chord and use it effectively in their playing. By studying the intervals and their interactions, guitarists can gain a deeper understanding of the chord’s structure and how it functions within different musical contexts.
Table: Intervals of the e dim 7 Guitar Chord
| Interval | Notes | Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Root | E | – |
| Minor Third | G | Minor |
| Diminished Fifth | Bb | Diminished |
| Diminished Seventh | Db | Diminished |
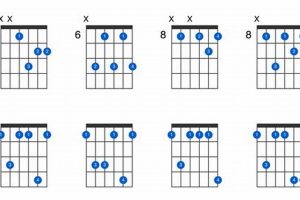
3. Voicings
The “Voicings: Multiple voicings, offering flexibility” aspect of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” highlights the versatility and adaptability of this chord. Unlike some chords with fixed voicings, the “e dim 7 guitar chord” can be played in various voicings, allowing guitarists to choose the most suitable voicing for their musical context and desired sound.
- Inversions: By inverting the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” guitarists can create different voicings that emphasize different chord tones. Inversions involve rearranging the notes of the chord, with the lowest note not always being the root. This technique allows for a wider range of voicings and harmonic possibilities.
- Spread Voicings: Spread voicings involve distributing the chord tones across a wider range of the guitar neck. This creates a more open and spacious sound, often used in jazz and contemporary styles. Spread voicings can also facilitate melodic lines and improvisational passages.
- Close Voicings: Close voicings, on the other hand, keep the chord tones closer together on the fretboard. This results in a thicker and more compact sound, commonly found in rock, blues, and funk music. Close voicings can provide a solid harmonic foundation and support lead guitar lines.
- Partial Voicings: Partial voicings involve omitting one or more notes from the full “e dim 7 guitar chord.” This technique can create unique and interesting sounds, adding color and variation to chord progressions. Partial voicings are often used in jazz and fusion styles.
Understanding and utilizing the multiple voicings of the “e dim
7 guitar chord” empowers guitarists with a vast sonic palette. By exploring different voicings, guitarists can tailor the chord to fit various musical genres, playing styles, and compositional needs. The flexibility offered by multiple voicings makes the “e dim 7 guitar chord” a versatile and expressive tool for guitarists of all levels.
4. Function
The “Function: Substitute for iim7 in minor key progressions” aspect of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” highlights its crucial role in minor key harmony. In minor key progressions, the ii chord (second chord) is often a minor 7th chord (iim7). The “e dim 7 guitar chord” can be used as a substitute for this iim7 chord, creating a unique and expressive harmonic sound.
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” shares similar harmonic properties with the iim7 chord, making it a suitable replacement. Both chords contain the minor third interval, which provides the characteristic minor tonality. Additionally, the diminished fifth and diminished seventh intervals in the “e dim 7 guitar chord” add depth and dissonance, enhancing the harmonic tension and resolution.
Substituting the iim7 chord with the “e dim 7 guitar chord” can create several effects:
- Increased Tension: The diminished fifth and diminished seventh intervals in the “e dim 7 guitar chord” create a stronger sense of tension compared to the iim7 chord. This tension drives the music forward and intensifies the emotional impact.
- Harmonic Coloration: The unique combination of intervals in the “e dim 7 guitar chord” adds a distinctive harmonic color to minor key progressions. It can introduce a sense of mystery, intrigue, or melancholy, depending on the musical context.
- Smooth Resolution: Despite its dissonant nature, the “e dim 7 guitar chord” typically resolves smoothly to a major or minor chord. This resolution creates a satisfying harmonic release and adds depth to the chord progression.
Understanding the “Function: Substitute for iim7 in minor key progressions” of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” empowers guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more expressive and sophisticated minor key progressions. By incorporating this chord substitution, guitarists can add depth, tension, and harmonic interest to their music.
Table: Comparison of iim7 and e dim 7 Chords in Minor Key Progressions
| Chord | Intervals | Function |
|---|---|---|
| iim7 | Root, minor third, perfect fifth, minor seventh | Minor seventh chord, often used as the second chord in minor key progressions |
| e dim 7 | Root, minor third, diminished fifth, diminished seventh | Diminished seventh chord, can be used as a substitute for iim7 in minor key progressions, adding tension and harmonic interest |
5. Dissonance
The “Dissonance: Tension-building quality” of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is a defining characteristic that contributes to its unique sound and expressive potential. Dissonance refers to the clashing or contrasting of musical notes, creating a sense of tension and instability within a chord or musical passage.
- Minor Third Interval: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” features a minor third interval (E to G), which introduces a sense of tension and melancholy. This interval creates a dissonant sound that adds depth and complexity to the chord.
- Diminished Fifth Interval: The diminished fifth interval (G to Bb) further enhances the dissonance of the chord. This interval creates a sense of unresolved tension, driving the music forward and creating a feeling of anticipation.
- Diminished Seventh Interval: The diminished seventh interval (Bb to Db) adds to the dissonance and instability of the chord. This interval creates a strong sense of tension that demands resolution, propelling the music towards a satisfying harmonic release.
- Unresolved Tension: Unlike consonant chords that provide a sense of stability and resolution, the “e dim 7 guitar chord” often leaves a sense of unresolved tension. This tension creates a dynamic and engaging sound that can evoke a range of emotions, from intrigue to anticipation.
The “Dissonance: Tension-building quality” of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” makes it a powerful tool for guitarists seeking to add depth, expressiveness, and harmonic interest to their music. By understanding and utilizing this dissonant quality, guitarists can create captivating chord progressions, enhance melodic lines, and convey a wide range of emotions through their playing.
6. Resolution
The “Resolution: Typically resolves to a major or minor chord” aspect of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” highlights its role in creating dynamic and satisfying harmonic progressions. The “e dim 7 guitar chord,” with its inherent dissonance, often finds resolution in a major or minor chord, creating a sense of harmonic closure and release.
- Tension and Release: The “e dim 7 guitar chord,” with its dissonant intervals, creates a sense of tension and instability within a chord progression. This tension is resolved when the chord progresses to a more stable major or minor chord, providing a sense of harmonic satisfaction.
- Common Resolutions: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” commonly resolves to major or minor chords that share similar harmonic properties. For example, it often resolves to the I (major) chord in major key progressions and the i (minor) chord in minor key progressions.
- Harmonic Movement: The resolution of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” contributes to the overall harmonic movement of a piece of music. By creating tension and then resolving it, this chord helps to drive the music forward and create a sense of harmonic progression.
- Emotional Impact: The resolution of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” can evoke a range of emotions, depending on the musical context. It can create a sense of release, satisfaction, or even surprise, enhancing the emotional impact of the music.
Understanding the “Resolution: Typically resolves to a major or minor chord” aspect of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” empowers guitarists to create more effective and emotionally resonant chord progressions. By utilizing this chord’s dissonant and resolving qualities, guitarists can add depth, tension, and harmonic interest to their music, captivating listeners and enhancing the overall musical experience.
7. Inversions
The “Inversions: Various inversions, expanding harmonic possibilities” aspect of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” highlights the versatility and harmonic richness that can be achieved by rearranging the notes of the chord. Inversions involve changing the order of the notes, with the lowest note not always being the root.
- Root Position: The root position of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is E-G-Bb-Db, with the root note E
as the lowest note. This is the most common inversion and provides a stable and recognizable sound. - First Inversion: The first inversion, also known as the “e dim 7/G” inversion, has G as the lowest note, followed by Bb, Db, and E. This inversion emphasizes the minor third interval and can create a more open and spacious sound.
- Second Inversion: The second inversion, or “e dim 7/Bb,” has Bb as the lowest note, followed by Db, E, and G. This inversion highlights the diminished fifth interval and can add a sense of tension and instability to the chord.
- Third Inversion: The third inversion, or “e dim 7/Db,” has Db as the lowest note, followed by E, G, and Bb. This inversion emphasizes the diminished seventh interval and can create a sense of unresolved tension that drives the music forward.
By utilizing different inversions of the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” guitarists can create a wider range of harmonic possibilities and add depth and interest to their playing. Each inversion offers a unique sound and can be used to create different moods and atmospheres in music.
8. Jazz and Blues
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” holds a prominent place in the worlds of jazz and blues music, two genres renowned for their sophisticated harmonies and expressive melodies. This chord’s unique dissonant and resolving qualities make it a versatile tool for creating tension, depth, and harmonic interest in jazz and blues compositions.
- Harmonic Complexity: Jazz and blues often explore complex harmonic structures, and the “e dim 7 guitar chord” provides a rich harmonic palette for these genres. Its dissonant intervals add tension and intrigue, while its ability to resolve to both major and minor chords creates a sense of harmonic movement and progression.
- Improvisation: Jazz and blues musicians frequently engage in improvisation, and the “e dim 7 guitar chord” offers a fertile ground for exploration. Its dissonant nature provides a platform for creating unique and expressive melodic lines, while its resolving quality provides a sense of structure and direction for improvisational passages.
- Emotional Expression: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” can convey a wide range of emotions in jazz and blues music. Its dissonant intervals can create a sense of tension and longing, while its resolution can provide a sense of release and catharsis. This emotional versatility makes the chord a valuable tool for expressing the nuances of human experience.
- Historical Context: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” has deep roots in the history of jazz and blues music. It was commonly used by early jazz guitarists such as Charlie Christian and Django Reinhardt, and its influence can be heard in the works of countless blues and jazz musicians throughout the decades.
In summary, the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is a fundamental element in the vocabulary of jazz and blues guitarists. Its dissonant and resolving qualities, harmonic complexity, and suitability for improvisation make it a versatile and expressive tool for creating captivating and emotionally resonant music.
9. Emotional Impact
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” possesses a unique ability to evoke a wide spectrum of emotions through its dissonant and resolving qualities. This evocative power stems from the inherent tension and release created by the chord’s structure and its relationship to other chords in a musical context.
The combination of the minor third, diminished fifth, and diminished seventh intervals within the “e dim 7 guitar chord” creates an inherent sense of dissonance and instability. This dissonance generates a feeling of tension and anticipation, which can be musically interpreted as emotions such as melancholy, sadness, or longing.
However, the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is not solely confined to expressing negative emotions. Its resolving nature, often leading to major or minor chords, provides a sense of release and catharsis. This resolution can evoke feelings of hope, anticipation, or even triumph, depending on the musical context and the progression of chords.
The emotional impact of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is not merely theoretical; it has been employed by countless musicians throughout history to convey a range of emotions in their compositions and performances. For instance, jazz guitarist Wes Montgomery frequently utilized the “e dim 7 guitar chord” to create a sense of longing and melancholy in his solos, while blues musicians such as B.B. King used it to express the raw emotions of pain and heartbreak.
Understanding the emotional impact of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is crucial for guitarists seeking to expand their expressive range and connect with their audience on a deeper level. By mastering this chord and its various voicings and inversions, guitarists can effectively convey a multitude of emotions through their playing, enhancing the overall impact and emotional resonance of their music.
Table: Emotional Impact of the “e dim 7 Guitar Chord”
| Musical Context | Emotional Impact |
|---|---|
| Minor key progressions, resolving to a minor chord | Melancholy, sadness, longing |
| Major key progressions, resolving to a major chord | Anticipation, hope, triumph |
| Jazz solos | Longing, introspection |
| Blues progressions | Pain, heartbreak, sorrow |
10. Improvisation
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” stands as a versatile tool for guitarists seeking to explore the realms of improvisation and soloing. Its inherent dissonant qualities provide a fertile ground for creating unique and expressive melodic lines, while its resolving nature offers a sense of structure and direction for improvisational passages.
The dissonant intervals within the “e dim 7 guitar chord” create a sense of tension and instability, which can be effectively harnessed by guitarists to generate innovative and emotionally charged solos. The minor third interval provides a melancholic undertone, while the diminished fifth and diminished seventh intervals add layers of tension and intrigue. This combination of dissonant elements invites guitarists to experiment with unconventional note choices and harmonic progressions, pushing the boundaries of traditional soloing.
Furthermore, the resolving nature of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” provides a sense of structure and direction for improvisational passages. Its tendency to resolve to major or minor chords offers a harmonic framework within which guitarists can navigate and develop their solos. This resolving quality allows guitarists to create a sense of musical coherence and progression, even amidst the exploration and experimentation that characterizes improvisation.
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” has been embraced by countless guitarists throughout history as a catalyst for exceptional soloing and improvisation. Jazz guitarists such as Wes Montgomery and Pat Metheny have utilized this chord to create solos that are both technically impressive and emotionally resonant. Blues guitarists like B.B. K
ing and Eric Clapton have also employed the “e dim 7 guitar chord” to add depth and expressiveness to their solos, evoking a range of emotions from sorrow to joy.
Mastering the “e dim 7 guitar chord” and its various voicings and inversions is essential for guitarists who aspire to elevate their improvisational skills. By incorporating this chord into their solos, guitarists can access a wider harmonic palette, generate more innovative and expressive melodic lines, and create solos that captivate and engage listeners.
Table: Benefits of Using the “e dim 7 Guitar Chord” for Improvisation
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Dissonant qualities | Provides a foundation for creating unique and expressive melodic lines. |
| Resolving nature | Offers a sense of structure and direction for improvisational passages. |
| Wide harmonic palette | Allows guitarists to explore a broader range of harmonic possibilities. |
| Emotional expressiveness | Enables guitarists to convey a wide range of emotions through their solos. |
FAQs on the “e dim 7 Guitar Chord”
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” providing concise and informative answers to enhance understanding and practical application on the guitar.
Question 1: What is the significance of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” in music theory and practical playing?
Answer: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” holds a prominent place in music theory and practice due to its unique dissonant sound and versatile functionality. Its dissonant intervals create tension and intrigue, while its ability to resolve to both major and minor chords provides harmonic depth and movement. This makes it a valuable tool for guitarists seeking to add sophistication and expressiveness to their playing.
Question 2: How can I incorporate the “e dim 7 guitar chord” into my guitar playing?
Answer: To incorporate the “e dim 7 guitar chord” into your playing, start by familiarizing yourself with its various voicings and inversions. Practice transitioning smoothly between the chord and other commonly used chords, such as major and minor chords. Experiment with using the chord in different musical contexts, such as chord progressions, solos, and improvisational passages.
Question 3: What are some practical tips for mastering the “e dim 7 guitar chord”?
Answer: To master the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” focus on developing finger dexterity and accuracy when playing its various voicings. Practice resolving the chord to both major and minor chords to enhance your harmonic understanding. Additionally, listen to recordings of guitarists who effectively utilize the chord to gain insights into its musical applications.
Question 4: How does the “e dim 7 guitar chord” contribute to the overall sound and mood of a musical piece?
Answer: The “e dim 7 guitar chord” can significantly impact the sound and mood of a musical piece. Its dissonant nature adds tension and a sense of anticipation, while its resolution provides a release and emotional catharsis. Composers and musicians often use the chord to create a sense of drama, intrigue, or melancholy.
Question 5: Are there any limitations or considerations when using the “e dim 7 guitar chord”?
Answer: While the “e dim 7 guitar chord” is a versatile tool, it is essential to use it judiciously to avoid overwhelming or confusing the listener. Pay attention to the overall harmonic context and ensure that the chord serves a specific musical purpose. Additionally, consider the skill level of the audience when incorporating the chord into your playing.
Question 6: How can I further explore the “e dim 7 guitar chord” and its applications?
Answer: To further explore the “e dim 7 guitar chord” and its applications, refer to reputable guitar instruction books, online resources, and video tutorials. Attend workshops or masterclasses led by experienced guitarists who can provide personalized guidance. Additionally, actively listen to music that features the chord and analyze how guitarists incorporate it into their playing.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” empowering guitarists to effectively utilize this chord in their musical endeavors.
Transition to the next article section: With a solid foundation in the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” guitarists can now explore advanced concepts and techniques to enhance their playing and musical expression.
Tips for Mastering the “e dim 7 Guitar Chord”
Incorporating the “e dim 7 guitar chord” into your playing can elevate your guitar skills and enhance your musical expression. Here are five essential tips to help you master this versatile chord:
Tip 1: Practice Various Voicings
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” has multiple voicings, each offering a unique sound and application. Familiarize yourself with these voicings and practice transitioning between them smoothly. This versatility will expand your harmonic possibilities and enable you to adapt to different musical contexts.
Tip 2: Understand the Harmonic Function
Comprehend the harmonic function of the “e dim 7 guitar chord” in various progressions. Study its role as a substitute for the iim7 chord in minor key progressions and its ability to create tension and resolution. This knowledge will empower you to use the chord effectively and add depth to your compositions.
Tip 3: Develop Finger Dexterity
Mastering the “e dim 7 guitar chord” requires finger dexterity and accuracy. Practice playing the chord in different positions and inversions to enhance your finger coordination. Finger exercises and scales can also improve your overall dexterity and facilitate effortless chord transitions.
Tip 4: Explore Inversions and Substitutions
Experiment with inversions and substitutions based on the “e dim 7 guitar chord” to expand your harmonic vocabulary. Inversions provide alternative fingerings and voicings, while substitutions can add harmonic interest and variety to your playing. Explore these techniques to enhance your creativity and musical expression.
Tip 5: Listen and Analyze
Listen attentively to recordings of guitarists who effectively utilize the “e dim 7 guitar chord.” Analyze their techniques, voicings, and harmonic progressions to gain insights into its practical applications. This active listening will improve your understanding and inspire your own musical ideas.
Summary and Conclusion
By following these tips, you can master the “e dim 7 guitar chord” and unlock its full potential in your guitar playing. Its dissonant and resolving qualities, combined with its harmonic versatility, make this chord an essential tool for creating depth, tension, and emotional expression in music.
Conclusion
The “e dim 7 guitar chord” stands as a dissonant yet versatile tool in the guitarist’s arsenal. Its unique harmonic qualities and ability to resolve to both major and minor chords make it an essential element in jazz, blues, and various musical styles.
Mastering this chord requires an understanding of its construction, voicings, and harmonic function. By incorporating it into your playing, you can add depth, intrigue, and emotional resonance to your music. Practice, e
xperimentation, and careful listening will unlock the full potential of the “e dim 7 guitar chord,” inspiring creativity and enhancing your musical expression.