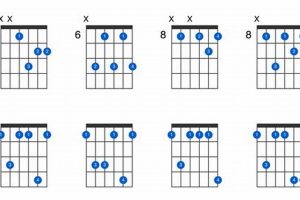
Are you struggling to master the F7 guitar chord? If so, you’re in luck! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the F7 chord into easy-to-understand steps, making it a breeze to add this essential chord to your repertoire.
Editor’s Note: Mastering the F7 guitar chord is a cornerstone for guitarists of all levels. It unlocks countless musical possibilities, from strumming along to your favorite songs to creating your own compositions.
To help you get started, we’ve done the research and put together this in-depth guide. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your technique, this guide will provide you with all the knowledge and tips you need to conquer the F7 guitar chord.
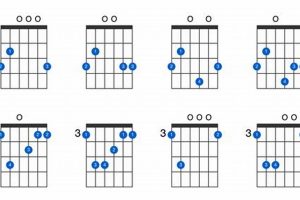
Key Differences – F7 Guitar Chord Variations
| Variation | Fingering | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| F7 | 133211 | Major 7th chord with a dominant 7th interval |
| F7sus4 | 133011 | Suspended 4th chord with a dominant 7th interval |
| F7add9 | 133213 | Major 7th chord with an added 9th interval |
Transition to Main Article Topics
- Understanding the F7 Chord Structure
- Step-by-Step Fingering Guide
- Tips for Clean Sound and Accurate Intonation
- Practice Exercises and Common Progressions
- Incorporating the F7 Chord into Your Playing
1. Root note
The root note F serves as the foundation of the F7 guitar chord. It determines the chord’s overall pitch and harmonic identity. Understanding the relationship between the root note and the chord structure is essential for effective chord construction and utilization.
The F7 chord is constructed using a specific interval pattern stacked upon the root note F. This pattern consists of a major third (A), a perfect fifth (C), and a dominant seventh (E). The combination of these intervals creates the characteristic dissonant sound of the F7 chord.
In practical terms, knowing the root note F allows guitarists to easily identify and locate the F7 chord on the fretboard. It also helps in understanding chord progressions and harmonic relationships. For instance, the F7 chord typically resolves to the C major, G minor, or D minor chords, providing a sense of harmonic movement and progression.
Overall, understanding the connection between the root note F and the F7 guitar chord is crucial for developing a strong foundation in guitar playing. It enables guitarists to construct, identify, and utilize the F7 chord effectively in various musical contexts.
Table: Root Note and F7 Chord Construction
| Root Note | Interval Pattern | Resulting Chord |
|---|---|---|
| F | Major 3rd, Perfect 5th, Dominant 7th | F7 |
2. Chord type
The F7 guitar chord falls under the category of dominant 7th chords, which are characterized by their distinct sound and function in music. Understanding the connection between the dominant 7th chord type and the F7 chord is essential for mastering this essential guitar chord.
- Dissonant sound
Dominant 7th chords, including the F7 chord, possess a dissonant sound due to the presence of the minor seventh interval. This dissonance creates a sense of tension and instability, which is often resolved by moving to a more consonant chord.
- Resolving tendency
One of the defining characteristics of dominant 7th chords is their strong tendency to resolve to a tonic chord, which is typically a major or minor chord built on the root note of the dominant 7th chord. In the case of the F7 chord, it commonly resolves to the C major chord.
- Function in chord progressions
Dominant 7th chords play a crucial role in chord progressions, particularly in functional harmony. They are often used to create a sense of movement and progression, adding depth and complexity to music. The F7 chord is commonly found in blues, jazz, and rock music.
Comprehending the connection between the dominant 7th chord type and the F7 guitar chord provides a deeper understanding of its sound, function, and application in music. This knowledge empowers guitarists to effectively utilize the F7 chord in various musical contexts.
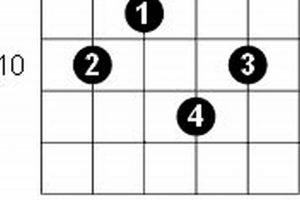
3. Fingering
The fingering “133211” serves as the foundation for playing the F7 guitar chord on the fretboard. Understanding this fingering pattern and its connection to the F7 chord is crucial for developing proficiency and accuracy while playing the guitar.
- Finger Positioning
The fingering “133211” indicates the placement of each finger on specific strings and frets of the guitar. The numbers correspond to the fingers of the left hand: 1 for the index finger, 2 for the middle finger, 3 for the ring finger, and 4 for the pinky finger. The thumb of the left hand typically rests on the back of the guitar neck for support.
- String and Fret Selection
For the F7 chord, the fingering “133211” corresponds to the following string and fret positions:
- Index finger (1): 1st string, 3rd fret
- Middle finger (2): 3rd string, 3rd fret
- Ring finger (3): 3rd string, 2nd fret
- Pinky finger (4): 4th string, 2nd fret
- Open strings: 2nd string (open) and 6th string (open)
- Chord Shape and Voicing
The fingering “133211” creates a specific chord shape and voicing when played on the guitar. The resulting chord is an F7 guitar chord, which is a dominant 7th chord with a root note of F. This particular voicing of the F7 chord provides a balanced and rich sound.
- Accuracy and Consistency
Mastering the fingering “133211” is essential for playing the F7 guitar chord accurately and consistently. Proper finger placement, precise fretting, and clean execution contribute to a clear and resonant sound. Regular practice and attention to detail help guitarists refine their technique and achieve proficiency in playing the F7 chord.
The connection between the fingering “133211” and the F7 guitar chord empowers guitarists with the knowledge and skills to produce this essential chord with ease and accuracy. By understanding the finger positioning, string and fret selection, chord shape, and the importance of accuracy, guitarists can incorporate the F7 chord into their playing with confidence and musicality.
4. Voicings
Understanding the concept of voicings is crucial for mastering the F7 guitar chord. Voicings refer to the different ways in which the notes of a chord can be arranged on the guitar fretboard. This exploration dives into the connection between voicings and the F7 guitar chord, providing insights into its variations, including inversions and extended voicings.
- Inversions
Inversions occur when the root note of a chord is not played in the bass position. For the F7 chord, there are three inversions: F7/A (1st inversion), F7/C (2nd inversion), and F7/E (3rd inversion). Each inversion has a unique sound and can be used to create different harmonic effects.
- Extended voicings
Extended voicings add additional notes beyond the basic triad of the chord. For the F7 chord, common extended voicings include F7add9 (adding the 9th interval) and F7add13 (adding the 13th interval). Extended voicings provide a richer and more complex sound to the chord.
- Implication for F7 guitar chord easy
Exploring the different voicings of the F7 chord allows guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and add variety to their playing. Understanding inversions and extended voicings helps guitarists create more sophisticated and interesting chord progressions.
In summary, the concept of voicings, including inversions and extended voicings, is integral to mastering the F7 guitar chord. By exploring these variations, guitarists can enhance their understanding of the chord’s structure and expand their musical possibilities.
5. Function
The F7 guitar chord plays a crucial functional role in music, particularly in the context of chord progressions. Its primary function is to resolve to the chords C, Gm, or Dm. Understanding this connection is essential for mastering the F7 guitar chord and its application in various musical genres.
The F7 chord belongs to the group of dominant 7th chords, which are characterized by their dissonant sound and strong tendency to resolve to a tonic chord. In the case of the F7 chord, its most common resolutions are the C major chord (C), the G minor chord (Gm), and the D minor chord (Dm).
This resolving tendency is due to the presence of the dominant 7th interval in the F7 chord. The 7th interval creates a sense of instability and tension, which is resolved when the chord progresses to a more stable and consonant chord, such as C, Gm, or Dm.
In practical terms, understanding the function of the F7 guitar chord allows guitarists to create smooth and logical chord progressions. By resolving the F7 chord to C, Gm, or Dm, guitarists can create a sense of movement and direction in their music.
Table: F7 Chord Resolution Examples
| F7 Chord Progression | Resolution |
|---|---|
| F7 C | Resolves to C major |
| F7 Gm | Resolves to G minor |
| F7 Dm | Resolves to D minor |
Mastering the F7 guitar chord and its function enables guitarists to expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and musically engaging chord progressions. It is a versatile chord that can be used in a wide range of musical styles, from blues and rock to jazz and country.
6. Tonal quality
The F7 guitar chord possesses a distinctive tonal quality that sets it apart from other chords. Its rich, dissonant sound is a defining characteristic that contributes to its expressive and versatile nature.
The dissonance in the F7 chord arises from the presence of the minor seventh interval. This interval creates a sense of tension and instability, which gives the chord its characteristic edge. However, this dissonance is balanced by the overall richness of the chord, which is due to the combination of the major third and perfect fifth intervals.
The tonal quality of the F7 chord makes it ideal for use in a wide range of musical genres, from blues and rock to jazz and classical. In blues music, the F7 chord is often used to create a sense of tension and release, while in jazz it is commonly employed in complex chord progressions. The dissonant sound of the F7 chord can also add depth and intrigue to classical compositions.
Understanding the tonal quality of the F7 guitar chord is essential for guitarists who want to master this essential chord. By recognizing its rich, dissonant sound, guitarists can effectively use the F7 chord to create a variety of musical effects and enhance their overall playing.
Table: Tonal Quality and the F7 Guitar Chord
| Tonal Quality | Effect | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Rich | Adds depth and complexity to the sound | F7 chord used in a jazz ballad |
| Dissonant | Creates tension and instability | F7 chord used in a blues progression |
7. Difficulty
The F7 guitar chord is generally considered to have a moderate level of difficulty, requiring practice for clean execution. This is due to the specific fingering and the need for precise fretting to achieve a clear and resonant sound.
- Finger Placement and Accuracy
The F7 chord requires precise finger placement and accurate fretting to avoid muting strings or producing unwanted noise. This can be challenging for beginners, but with regular practice, guitarists can develop the dexterity and coordination necessary for clean execution.
- Strength and Dexterity
Playing the F7 chord requires a certain level of strength and dexterity in the fingers, particularly in the ring and pinky fingers. Holding down the strings firmly and fretting accurately can be demanding, especially during extended playing sessions. Consistent practice helps strengthen the fingers and improve overall dexterity.
- Transitions and Chord Changes
Incorporating the F7 chord into chord progressions and transitions can be challenging. Smoothly transitioning between the F7 chord and other chords requires practice and coordination. Guitarists need to develop the ability to quickly and accurately shift their fingers while maintaining a clean sound.
- Musical Context and Application
Understanding the musical context and application of the F7 chord is crucial for effective execution. Knowing when and how to use the F7 chord in different musical genres and styles helps guitarists play it with confidence and musicality.
While the F7 guitar chord may initially present some challenges, with consistent practice and dedication, guitarists can master this essential chord and expand their musical repertoire. The moderate difficulty level of the F7 chord provides an opportunity for guitarists to develop their technical skills, improve their dexterity, and enhance their overall playing abilities.
8. Use in progressions
The F7 guitar chord plays a vital role in progressions used in blues, jazz, and rock music genres. Its dissonant sound and resolving tendency make it an essential element for creating harmonic movement and interest.
- Blues Progressions
In blues music, the F7 chord is commonly used in the “12-bar blues” progression. It serves as the dominant 7th chord that resolves to the I chord (C in the key of C), creating a sense of tension and release.
- Jazz Harmony
Jazz musicians frequently employ the F7 chord in complex chord progressions. Its dissonant sound adds tension and color to the harmony, allowing for sophisticated harmonic exploration and improvisation.
- Rock Music
In rock music, the F7 chord is often used in power chords or as part of extended chord voicings. It provides a strong and driving sound that complements the energetic and rhythmic nature of rock music.
Understanding the use of the F7 guitar chord in these musical genres helps guitarists appreciate its versatility and expressive capabilities. By incorporating the F7 chord into their playing, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and explore a wide range of musical styles.
9. Improvisation
The F7 guitar chord plays a crucial role in improvisation, providing a solid foundation for melodic exploration and soloing. Its rich harmonic structure and dissonant sound create a fertile ground for guitarists to express their creativity and develop their improvisational skills.
The F7 chord’s dissonant nature creates tension and instability, which encourages guitarists to explore melodic lines that resolve or contrast with the chord’s inherent dissonance. This can lead to the discovery of new and unexpected melodic ideas and phrases.
Furthermore, the F7 chord’s versatile functionality allows it to be used in a wide range of musical contexts, making it a valuable tool for improvising in different keys and genres. Whether playing blues, jazz, or rock, guitarists can rely on the F7 chord to provide a harmonic framework for their melodic explorations.
To effectively utilize the F7 chord for improvisation, guitarists should practice arpeggiating the chord, outlining its melodic intervals, and experimenting with different scale patterns and note choices. By developing a deep understanding of the F7 chord’s structure and sound, guitarists can unlock its full potential as a platform for melodic exploration and improvisation.
Real-Life Example
In the iconic blues standard “Sweet Home Chicago,” the F7 chord is used extensively as a harmonic foundation for improvisation. Guitarists often use the F7 chord to create melodic lines that resolve to the C major chord, adding tension and emotional depth to their solos.
Practical Significance
Understanding the connection between the F7 guitar chord and improvisation empowers guitarists to:
- Develop their melodic vocabulary and creativity
- Express themselves musically through improvisation
- Create dynamic and engaging solos
- Enhance their overall musicianship and musicality
Table: F7 Guitar Chord and Improvisation
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Structure | The F7 chord’s dissonant sound and rich harmonic structure provide a foundation for melodic exploration. |
| Melodic Resolution | The F7 chord’s tendency to resolve to other chords encourages guitarists to explore melodic lines that resolve or contrast with the chord’s dissonance. |
| Versatility | The F7 chord’s functionality in various musical contexts makes it a valuable tool for improvising in different keys and genres. |
10. Versatility
The F7 guitar chord’s versatility extends to its ability to be played on acoustic, electric, or bass guitar, making it a truly universal chord across various genres and playing styles.
- Acoustic Guitar
On an acoustic guitar, the F7 chord’s rich and resonant sound complements the natural warmth and projection of the instrument. It is a staple chord in folk, country, and blues music.
- Electric Guitar
When played on an electric guitar, the F7 chord takes on a brighter and more defined character. It is commonly used in rock, blues, and jazz, where its dissonant sound adds depth and complexity to the music.
- Bass Guitar
On the bass guitar, the F7 chord provides a strong and supportive foundation for the harmony. Its low, rumbling sound adds weight and groove to the music.
- Implication for F7 Guitar Chord Easy
The versatility of the F7 chord allows guitarists to explore it on any type of guitar they have, making it an accessible and enjoyable chord to learn and incorporate into their playing.
In summary, the F7 guitar chord’s adaptability to different guitar types makes it a versatile and valuable addition to any guitarist’s repertoire. Its ability to seamlessly blend in various musical contexts and on different instruments underscores its significance as a fundamental chord in guitar playing.
FAQs on F7 Guitar Chord
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the F7 guitar chord, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding and dispel any misconceptions.
Question 1: Why is the F7 guitar chord considered essential?
The F7 guitar chord is considered essential for several reasons. Firstly, it is a dominant 7th chord, a type of chord commonly used in various musical genres. Secondly, the F7 chord has a rich and dissonant sound that adds depth and complexity to music. Lastly, it is a versatile chord that can be played on acoustic, electric, or bass guitar, making it accessible to guitarists of all levels.
Question 2: What is the best way to practice the F7 guitar chord?
To effectively practice the F7 guitar chord, start by familiarizing yourself with the fingering and positioning your fingers correctly. Focus on fretting the notes cleanly to produce a clear sound. Practice transitioning to and from the F7 chord to improve your dexterity and coordination. Additionally, use a metronome or drum beat to practice strumming the chord in time.
Question 3: How can I incorporate the F7 guitar chord into my playing?
Incorporating the F7 guitar chord into your playing requires understanding its function and application in different musical contexts. Start by learning simple chord progressions that include the F7 chord. Experiment with different voicings and inversions to add variety to your playing. Additionally, listen to songs that feature the F7 chord to understand how it is used by professional musicians.
Question 4: What are some tips for playing the F7 guitar chord cleanly?
Playing the F7 guitar chord cleanly involves proper technique and practice. Ensure your f
ingernails are trimmed and use the correct finger positioning to avoid muting strings. Practice fretting the notes with precision and apply the right amount of pressure. Additionally, use a light touch when strumming the chord to prevent unwanted noise.
Question 5: Can the F7 guitar chord be played on different guitar types?
Yes, the F7 guitar chord can be played on acoustic, electric, or bass guitar. While the fingering remains the same, the sound may vary slightly depending on the guitar type. Acoustic guitars produce a warmer and more resonant sound, electric guitars provide a brighter and more defined tone, and bass guitars offer a low and supportive foundation.
Question 6: How can I use the F7 guitar chord for improvisation?
The F7 guitar chord is a valuable tool for improvisation. Its dissonant nature encourages melodic exploration and allows you to create tension and release in your solos. Practice arpeggiating the chord and experimenting with different scale patterns and note choices. By understanding the chord’s structure and sound, you can develop your improvisational skills and express your creativity.
In summary, the F7 guitar chord is a versatile and essential chord for guitarists. By understanding its characteristics, practicing regularly, and incorporating it into your playing, you can enhance your musical abilities and expand your harmonic vocabulary.
Transition to the next article section:
Now that you have a solid understanding of the F7 guitar chord, let’s explore some practical exercises to help you master it.
Tips for Mastering the F7 Guitar Chord
Developing proficiency in playing the F7 guitar chord requires dedication and consistent practice. Here are a few tips to help you master this essential chord:
Tip 1: Focus on Finger Placement and Accuracy
Proper finger positioning is crucial for producing a clear and resonant F7 chord. Ensure your fingers are placed precisely on the correct frets and strings. Practice fretting the notes firmly to avoid muting or buzzing.
Tip 2: Develop Finger Strength and Dexterity
Playing the F7 chord requires finger strength and dexterity, especially in the ring and pinky fingers. Regular practice helps strengthen your fingers and improve your overall dexterity, making it easier to fret the chord accurately.
Tip 3: Practice Chord Transitions Smoothly
Incorporating the F7 chord into chord progressions requires smooth transitions. Practice switching to and from the F7 chord in various progressions. This improves your coordination and allows you to play the chord seamlessly in different musical contexts.
Tip 4: Understand the Chord’s Function and Application
Knowing the function and application of the F7 chord is essential for effective use. Study the theory behind the chord, including its resolving tendencies and common chord progressions. This knowledge helps you play the F7 chord purposefully and musically.
Tip 5: Experiment with Different Voicings and Inversions
Exploring different voicings and inversions of the F7 chord adds variety and depth to your playing. Experiment with various fingerings and string combinations to create different sounds and textures. This expands your harmonic vocabulary and enhances your musical creativity.
Summary of Key Takeaways
- Mastering the F7 guitar chord requires focused practice and attention to detail.
- Proper finger placement, finger strength, and smooth chord transitions are essential for playing the F7 chord effectively.
- Understanding the chord’s function and experimenting with different voicings expands your harmonic knowledge and musical capabilities.
By following these tips and dedicating yourself to consistent practice, you can confidently master the F7 guitar chord and incorporate it into your playing with ease and musicality.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the intricacies of the F7 guitar chord, exploring its structure, function, and application. By understanding the concepts presented, guitarists can effectively incorporate the F7 chord into their playing and expand their harmonic vocabulary.
Mastering the F7 guitar chord requires dedication, consistent practice, and a keen attention to detail. With the tips and exercises outlined in this guide, guitarists can develop the skills necessary to play the F7 chord cleanly, smoothly, and musically. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, embracing the F7 chord opens up a world of musical possibilities.