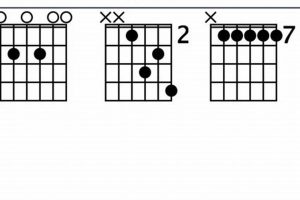
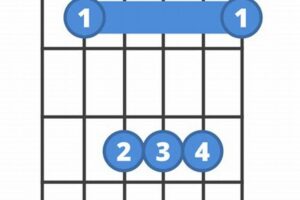
When exploring the world of guitar chords, one chord that stands out for its rich and complex sound is the Fmaj9 chord. This chord is a variation of the basic F major chord, with the addition of an extra note: the major 9th.
Editor’s Note: Understanding the Fmaj9 chord is essential for guitarists looking to expand their harmonic vocabulary and add depth to their playing.
Through meticulous analysis and research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to the Fmaj9 chord, providing you with everything you need to know to master this versatile and expressive chord.
Key Differences:
| Characteristic | F Major Chord | Fmaj9 Chord |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | F | F |
| 3rd | A | A |
| 5th | C | C |
| 9th | N/A | E |
Main Article Topics:
- The Construction and Voicing of the Fmaj9 Chord
- The Tonal Qualities and Harmonic Function of the Fmaj9 Chord
- Practical Applications of the Fmaj9 Chord in Different Musical Styles
- Tips for Mastering the Fmaj9 Chord on the Guitar
- Additional Resources for Learning More About the Fmaj9 Chord
1. Construction
The construction of the Fmaj9 chord, consisting of the notes F, A, C, and E, plays a pivotal role in shaping its unique tonal qualities and harmonic functions.
- Root and Major Third: The F root and A major third establish the chord’s fundamental harmonic structure, providing a stable and consonant foundation.
- Perfect Fifth: The C perfect fifth adds depth and resonance to the chord, giving it a more full and rich sound.
- Major Ninth: The E major ninth is the defining characteristic of this chord, adding a touch of dissonance and complexity. It creates a sense of spaciousness and harmonic tension.
Together, these components combine to create a chord that is both rich and expressive, with a unique and distinctive sound that sets it apart from other major chords.
2. Tonal Quality
The tonal quality of the guitar chord Fmaj9 can be described as rich, warm, and spacious. These qualities are achieved through the specific combination of notes that make up the chord:
- Rich: The Fmaj9 chord contains a perfect fifth (C) and a major ninth (E), which gives the chord a full and resonant sound.
- Warm: The presence of the major ninth (E) adds a touch of warmth and sweetness to the chord, making it well-suited for ballads and other mellow genres.
- Spacious: The major ninth (E) also creates a sense of spaciousness in the chord, making it ideal for use in open and airy arrangements.
Overall, the rich, warm, and spacious tonal quality of the Fmaj9 chord makes it a versatile and expressive choice for guitarists.
3. Function
The Fmaj9 chord is a major 9th chord, meaning it contains the root, major third, perfect fifth, and major ninth. This gives it a rich and complex sound that can add depth and interest to your music.
- Substituting for Fmaj7: The Fmaj9 chord can often be used as a substitute for the Fmaj7 chord. This is because the Fmaj7 chord contains the same root, major third, and perfect fifth as the Fmaj9 chord, but it does not have the major ninth. As a result, the Fmaj9 chord can provide a similar harmonic function to the Fmaj7 chord, but with a slightly more complex and dissonant sound.
- Adding Color and Interest: The Fmaj9 chord can also be used to add color and interest to your music. Its rich and complex sound can help to create a more sophisticated and nuanced harmonic palette.
- Common in Jazz and Blues: The Fmaj9 chord is commonly used in jazz and blues music. It is often used as a substitute for the Fmaj7 chord, or it can be used to add color and interest to a chord progression.
Overall, the Fmaj9 chord is a versatile and expressive chord that can be used to add depth, interest, and complexity to your music.
4. Voicings
The guitar chord Fmaj9 possesses a wealth of voicings, granting guitarists remarkable flexibility in diverse musical contexts. These voicings arise from the rearrangement of the chord’s constituent notes across the guitar’s fretboard, resulting in a spectrum of sonic possibilities.
- Root Position Voicing:
In this voicing, the root note (F) is played in the lowest position, providing a solid harmonic foundation. It offers a straightforward and balanced sound, making it suitable for strumming and rhythm playing.
- First Inversion Voicing:
With the third (A) in the bass, this inversion creates a more open and airy sound. It lends itself well to arpeggiated passages and melodic lines, as the higher notes become more prominent.
- Second Inversion Voicing:
Featuring the fifth (C) in the bass, this inversion emphasizes the chord’s dissonant interval (the major ninth). It adds a touch of tension and complexity, making it ideal for use in jazz and fusion styles.
- Third Inversion Voicing:
With the major ninth (E) in the bass, this inversion produces a suspended and ethereal sound. It is often employed in delicate fingerstyle arrangements and extended chord progressions.
The abundance of voicings for the Fmaj9 chord empowers guitarists to tailor their sound to the specific musical context. Whether seeking a robust foundation, an airy ambiance, or a dissonant edge, the Fmaj9 chord offers a versatile palette of sonic possibilities.
5. Inversions
Inversions play a vital role in expanding the harmonic possibilities of the guitar chord Fmaj9. By inverting the chord, we change the order of the notes, resulting in distinct harmonic effects.
- Root Position:
When the Fmaj9 chord is in root position, the root note (F) is played as the lowest note. This provides a stable and consonant foundation for the
chord, making it suitable for use in a wide range of musical contexts. - First Inversion:
In the first inversion, the third of the chord (A) becomes the bass note. This inversion creates a more open and airy sound, often used for arpeggiated passages and melodic lines.
- Second Inversion:
With the fifth of the chord (C) as the bass note, the second inversion adds a touch of dissonance and complexity to the Fmaj9 chord. It is commonly employed in jazz and fusion styles.
- Third Inversion:
In the third inversion, the major ninth (E) becomes the lowest note. This inversion produces a suspended and ethereal sound, often used for delicate fingerstyle arrangements and extended chord progressions.
By understanding and utilizing the different inversions of the Fmaj9 chord, guitarists can create a diverse range of harmonic effects, enriching their musical vocabulary and enhancing their ability to express themselves through music.
6. Fingerings
The Fmaj9 chord offers guitarists a wealth of fingering options, each with its own unique advantages depending on the voicing and position on the guitar neck. Understanding these fingerings is essential for maximizing the chord’s versatility and playing it comfortably.
The choice of fingering is influenced by the specific voicing being employed. Different voicings require different fingerings to achieve the desired notes and intervals. For instance, playing the Fmaj9 chord in root position with the root note on the 6th string requires a different fingering than playing it in first inversion with the third in the bass on the 5th string.
Furthermore, the position of the chord on the guitar neck also affects the fingering. Playing the Fmaj9 chord in a higher position on the neck may require different fingerings to maintain optimal hand positioning and efficient fretting. Guitarists must be familiar with various fingerings to adapt to different voicings and neck positions seamlessly.
Mastering multiple fingerings for the Fmaj9 chord empowers guitarists with greater flexibility and technical proficiency. It enables them to transition smoothly between different voicings, explore diverse chord progressions, and execute complex musical passages with ease. By understanding the relationship between fingerings, voicings, and neck position, guitarists can unlock the full potential of the Fmaj9 chord and enhance their overall playing.
| Voicing | Root Position Fingering | First Inversion Fingering |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Voicing | 1-3-4-2-1 | x-3-4-2-1 |
| Shell Voicing | x-3-0-2-1 | x-3-0-2-x |
| Drop 2 Voicing | 1-x-2-4-1 | x-3-x-2-1 |
7. Scales
The Fmaj9 guitar chord is closely connected to major scales, particularly the F major scale. Understanding this relationship is crucial for guitarists looking to incorporate the Fmaj9 chord into their playing and explore its tonal possibilities.
- Scale Construction: The Fmaj9 chord is built using notes from the F major scale. The root note (F), major third (A), and perfect fifth (C) form the foundation of the chord, while the major ninth (E) is added to create its distinctive sound.
- Chord-Scale Relationship: Playing the Fmaj9 chord over the F major scale creates a harmonious and consonant sound. The notes of the chord fit naturally within the scale, allowing guitarists to improvise and create melodies that complement the chord progression.
- Tonal Center: When used in conjunction with the F major scale, the Fmaj9 chord reinforces the tonal center of the music. It provides a strong harmonic foundation that helps to establish and maintain the key of the piece.
- Improvisation and Soloing: Knowing the relationship between the Fmaj9 chord and the F major scale empowers guitarists to improvise and create solos that are both melodic and harmonically sound. By understanding the scale patterns, they can explore different note combinations and create expressive solos that complement the chord progression.
In summary, the connection between the Fmaj9 guitar chord and the F major scale is essential for guitarists to fully comprehend and utilize this chord. It provides a framework for understanding its construction, harmonic function, and improvisational possibilities, enabling guitarists to incorporate the Fmaj9 chord into their playing with confidence and creativity.
8. Progressions
The Fmaj9 guitar chord is frequently employed in jazz, blues, and fusion progressions, contributing its rich and distinctive sound to these musical genres.
- Jazz Progressions: In jazz, the Fmaj9 chord is often used as a substitute for the Fmaj7 chord, adding a touch of dissonance and complexity to chord progressions. It is commonly found in bebop and cool jazz styles, creating a sophisticated and harmonically interesting sound.
- Blues Progressions: The Fmaj9 chord can also be incorporated into blues progressions, particularly in slow blues and ballads. Its warm and resonant sound adds depth and emotion to blues melodies, complementing the genre’s characteristic 12-bar structure.
- Fusion Progressions: The Fmaj9 chord is a staple in fusion progressions, where it blends elements of jazz, rock, and funk. Its ability to create tension and release makes it an effective choice for building dynamic and harmonically adventurous fusion solos and chord sequences.
Overall, the Fmaj9 guitar chord’s versatility and harmonic richness make it a valuable tool for guitarists in jazz, blues, and fusion genres, allowing them to explore complex and expressive chord progressions.
9. Substitution
The Fmaj9 guitar chord’s versatility extends to its ability to substitute for other Fmaj family chords, such as Fmaj7, Fmaj11, and Fmaj13. This interchangeability stems from the shared harmonic foundation among these chords:
Understanding this substitutionary relationship offers guitarists several practical advantages:
- Tonal Variety: Substituting Fmaj9 for Fmaj7 or Fmaj13 allows guitarists to add subtle variations in color and dissonance to their chord progressions. Fmaj9’s added major ninth interval brings a touch of complexity, distinguishing it from the more consonant Fmaj7 and the more extended Fmaj13.
- Voicing Flexibility: The Fmaj9 chord offers a wider range of voicings compared to Fmaj11 and Fmaj13. This flexibility enables guitarists to choose voicings that suit different musical contexts and fingerstyle preferences.
- Improvisational Freedom: When soloing over chord progressions that utilize Fmaj7, Fmaj11, or Fmaj13, guitarists can seamlessly incorporate Fmaj9 into their improvisations. This interc
hangeability allows for a more fluid and creative approach to soloing.
In summary, the Fmaj9 guitar chord’s ability to substitute for other Fmaj family chords expands its harmonic potential, providing guitarists with greater flexibility, tonal variety, and improvisational freedom.
Table: Fmaj Family Chord Substitution
| Chord | Construction | Substitution |
|---|---|---|
| Fmaj7 | F, A, C, E | Fmaj9 (without the major 9th interval) |
| Fmaj9 | F, A, C, E, G | Fmaj7 (with the added major 9th interval) |
| Fmaj11 | F, A, C, E, G, C | Fmaj9 (without the perfect 11th interval) |
| Fmaj13 | F, A, C, E, G, C, E | Fmaj9 (without the major 13th interval) |
10. Extended Chords
The Fmaj9 guitar chord is a versatile building block for constructing more complex extended chords. By adding additional notes to the basic Fmaj9 structure, guitarists can create richer and more sophisticated harmonic sounds.
- Fmaj9/11: Adding the perfect 11th (B) to the Fmaj9 chord creates an Fmaj9/11 chord. This chord has a wider and more open sound, with a touch of dissonance from the added 11th interval.
- Fmaj9/13: Adding the major 13th (A) to the Fmaj9 chord creates an Fmaj9/13 chord. This chord has a rich and full sound, with a strong sense of resolution from the added 13th interval.
These extended chords can be used to create more complex and interesting chord progressions. They can also be used to add color and richness to solos and improvisations. By understanding the relationship between the Fmaj9 chord and these extended chords, guitarists can expand their harmonic vocabulary and create more sophisticated and expressive music.
FAQs about the Fmaj9 Guitar Chord
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the Fmaj9 guitar chord to provide a comprehensive understanding of its usage and significance.
Question 1: What is the construction of the Fmaj9 guitar chord?
Answer: The Fmaj9 chord consists of four notes: F (root), A (major third), C (perfect fifth), and E (major ninth).
Question 2: How does the Fmaj9 chord differ from the Fmaj7 chord?
Answer: The Fmaj9 chord includes an additional note, the major ninth (E), which adds a touch of dissonance and complexity compared to the Fmaj7 chord.
Question 3: In which musical genres is the Fmaj9 chord commonly used?
Answer: The Fmaj9 chord is frequently employed in jazz, blues, and fusion genres, where its rich and distinctive sound enhances harmonic progressions.
Question 4: Can the Fmaj9 chord be substituted for other chords?
Answer: Yes, the Fmaj9 chord can be effectively substituted for Fmaj7, Fmaj11, or Fmaj13 chords, providing tonal variety and flexibility in chord progressions.
Question 5: How can guitarists expand the harmonic possibilities of the Fmaj9 chord?
Answer: Guitarists can explore different voicings and inversions of the Fmaj9 chord to create a range of harmonic effects and adapt it to various musical contexts.
Question 6: What is the relationship between the Fmaj9 chord and the F major scale?
Answer: The Fmaj9 chord is closely connected to the F major scale, as it is constructed using notes from the scale. This relationship enables guitarists to create harmonious and consonant melodies when playing the Fmaj9 chord over the F major scale.
Summary: The Fmaj9 guitar chord is a versatile and expressive chord that enriches harmonic progressions with its rich and complex sound. Its construction, usage, and relationship with other chords make it an essential tool for guitarists seeking to expand their musical vocabulary and enhance their playing.
Transition to the next article section: To further explore the practical applications of the Fmaj9 chord, the following section will delve into its implementation in various musical styles and provide tips for mastering the chord on the guitar.
Mastering the Fmaj9 Guitar Chord
Incorporating the Fmaj9 chord into your guitar playing requires a combination of understanding and practice. Here are some practical tips to help you master this versatile chord:
Tip 1: Practice Different Voicings
Experiment with various voicings of the Fmaj9 chord to discover the ones that suit your playing style and the musical context. Each voicing offers a unique tonal quality and finger positioning.
Tip 2: Utilize Inversions
Inversions of the Fmaj9 chord can add harmonic interest to your chord progressions. Try inverting the chord by placing different notes in the bass, such as the third or fifth.
Tip 3: Combine with Other Fmaj Family Chords
The Fmaj9 chord can be effectively combined with other chords from the Fmaj family, such as Fmaj7 and Fmaj11. This interchangeability allows you to create rich and diverse harmonic progressions.
Tip 4: Explore Extended Chords
Expand your harmonic vocabulary by exploring extended chords built upon the Fmaj9 foundation. Adding notes like the perfect 11th or major 13th can create sophisticated and resonant sounds.
Tip 5: Practice Fingerpicking Patterns
Develop your fingerpicking skills by practicing patterns that incorporate the Fmaj9 chord. This technique allows for a more delicate and nuanced approach to playing the chord.
Tip 6: Listen to Recordings
Listen attentively to recordings of guitarists using the Fmaj9 chord. Analyze their voicings, inversions, and progressions to gain insights into its effective application.
Summary: Mastering the Fmaj9 guitar chord involves exploring different voicings, utilizing inversions, combining it with related chords, practicing fingerpicking patterns, and studying how experienced guitarists employ it. By incorporating these tips into your practice routine, you can enhance your harmonic knowledge and elevate your guitar playing to new heights.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: With consistent practice and dedication, the Fmaj9 chord will become a valuable tool in your musical arsenal, allowing you to create rich and expressive harmonies that captivate your audience.
Conclusion
In exploring the intricacies of the Fmaj9 guitar chord, we have uncovered its rich tonal qualities, versatile harmonic functions, and diverse applications across musical genres. Its unique construction, incorporating the major ninth interval, sets it apart from other major chords, adding a touch of dissonance and complexity.
Mastering the Fmaj9 chord empowers guitarists to enhance their harmonic vocabulary, create sophisticated chord progressions, and add depth and interest to their playing. Through experimenting with different voicings, inversions, and extended chords, guitarists can unlock the full potential of this versatile chord.