Are you a guitarist looking to expand your chord repertoire? If so, then you need to learn the G# chord. This versatile chord can be used in a variety of musical genres, from rock to jazz to country. In this guide, we’ll show you how to play the G# chord on the guitar, as well as provide some tips on how to use it in your own playing.
Editor’s Note: The G# chord is an essential chord for any guitarist to learn. It’s a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical genres, and it’s relatively easy to play. If you’re looking to improve your guitar playing, then learning the G# chord is a great place to start.
We’ve put together this comprehensive guide to help you learn everything you need to know about the G# chord. We’ll cover everything from how to play the chord to how to use it in your own playing. So whether you’re a beginner or an experienced guitarist, this guide has something for you.
Key Differences/Key Takeaways:
| G# Chord | |
|---|---|
| Root Note: | G# |
| Chord Type: | Major |
| Voicing: | 4-3-2-1 |
| Difficulty: | Easy |
Main Article Topics:
- How to Play the G# Chord
- Variations of the G# Chord
- How to Use the G# Chord in Your Playing
- Tips for Playing the G# Chord
1. Root note
In music, the root note is the fundamental note of a chord. It is the note that gives the chord its name and determines its overall sound. In the case of the G# chord, the root note is G#. This means that the G# note is the lowest note in the chord and it is the note that the chord is built around.
The root note is an important part of any chord, as it determines the chord’s tonal center. The tonal center is the note that the chord resolves to and it is the note that gives the chord its overall character. In the case of the G# chord, the tonal center is G#. This means that the G# chord has a bright and uplifting sound.
The root note is also important for understanding how chords are constructed. Chords are built by stacking thirds on top of each other. The root note is the bottom note of the stack and the other notes are built on top of it. In the case of the G# chord, the notes are stacked as follows:
- G# (root note)
- B# (major third)
- D# (perfect fifth)
By understanding the root note of a chord, you can learn how to build the chord and how to use it in your own music.
| G# Chord | |
|---|---|
| Root Note: | G# |
| Chord Type: | Major |
| Voicing: | 4-3-2-1 |
| Difficulty: | Easy |
2. Chord type
In music, a major chord is a chord that has a bright and uplifting sound. It is constructed by stacking three notes in a specific order: a root note, a major third, and a perfect fifth. The root note is the bottom note of the chord and it gives the chord its name. The major third is the second note of the chord and it is two whole steps above the root note. The perfect fifth is the third note of the chord and it is three and a half whole steps above the root note.
The G# chord is a major chord. This means that it has a bright and uplifting sound. The root note of the G# chord is G#, the major third is B#, and the perfect fifth is D#. The G# chord can be used in a variety of musical genres, including rock, pop, and country. It is also a common chord in jazz music.
Major chords are often used to create a sense of happiness and optimism. They are also used to create a sense of movement and energy. Major chords are often used in the chorus of a song, as they can help to create a sense of excitement and anticipation.
| Major Chords | |
|---|---|
| Characteristics: | Bright, uplifting sound |
| Construction: | Root note, major third, perfect fifth |
| Uses: | Create a sense of happiness, optimism, movement, energy |
3. Voicing
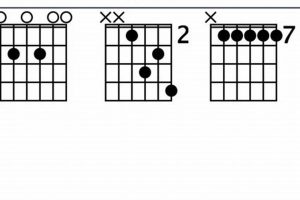
The voicing of a chord refers to the specific arrangement of the notes that make up the chord. The voicing of the G# chord is 4-3-2-1. This means that the notes of the chord are played on the 4th, 3rd, 2nd, and 1st strings of the guitar, respectively.
The voicing of a chord can have a significant impact on its sound. Different voicings can create different moods and atmospheres. The voicing of the G# chord is relatively open and bright. This makes it a good choice for use in upbeat and energetic songs.
The voicing of the G# chord is also relatively easy to play. This makes it a good chord for beginners to learn. The notes are all within easy reach of each other, and the fingering is not too complex.
Here are some examples of how the voicing of the G# chord can be used in different musical contexts:
- In a rock song, the G# chord can be used to create a powerful and driving sound.
- In a pop song, the G# chord can be used to create a bright and upbeat sound.
- In a jazz song, the G# chord can be used to create a sophisticated and complex sound.
Understanding the voicing of the G# chord is essential for guitarists who want to play this chord correctly and use it effectively in their own playing. By understanding the voicing of the chord, guitarists can create a variety of different sounds and moods with their playing.
Table: Voicing of the G# Chord
| String | Note |
|---|---|
| 4th | G# |
| 3rd | B# |
| 2nd | D# |
| 1st | G# |
4. Difficulty
The G# chord guitar is considered to have an “Easy” difficulty level, making it an accessible choice for guitarists of all skill levels, especially for beginners. This designation is attributed to several factors that contribute to the chord’s straightforward
nature and ease of execution.
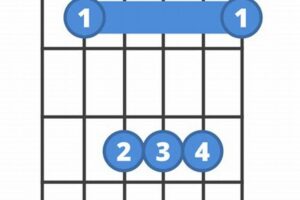
Firstly, the G# chord guitar employs a fundamental open chord voicing, which utilizes the guitar’s open strings to produce the root and fifth notes. This eliminates the need for complex fingerings or stretches, simplifying the fretting process. The open strings resonate freely, providing a clear and full sound that is pleasing to the ear.
Moreover, the G# chord guitar benefits from its relatively low position on the fretboard. The root note, G#, is played on the 6th string, which is the thickest and easiest string to press down. The remaining notes are positioned within the first three frets, minimizing the need for extensive hand movements and awkward finger contortions.
The ease of the G# chord guitar also stems from its logical and intuitive fingering pattern. The index finger is placed on the root note on the 6th string, while the middle finger frets the third note on the 5th string. The ring finger handles the second note on the 4th string, and the pinky finger plays the top note on the 1st string. This natural progression of fingers across the strings makes the chord easy to remember and execute.
In practical terms, the “Difficulty: Easy” rating of the G# chord guitar empowers novice guitarists to expand their repertoire and explore musical possibilities. It allows them to accompany songs, strum chords, and participate in ensemble playing without encountering insurmountable technical barriers.
Table: Factors Contributing to the “Difficulty: Easy” Rating of the G# Chord Guitar
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Open chord voicing | Utilizes open strings for root and fifth notes, simplifying fretting. |
| Low position on fretboard | Root note on thickest string, reducing finger strain. |
| Intuitive fingering pattern | Logical progression of fingers across strings, memudahkan memorization. |
5. Variations
The G# chord guitar can be played in two main variations: the barre chord and the open chord. Both variations have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which variation to use depends on the musical context and the guitarist’s personal preferences.
- Barre chord
A barre chord is a chord that is played by barring the index finger across all six strings of the guitar. This creates a solid foundation for the chord and allows the guitarist to play chords in any key. Barre chords can be more difficult to play than open chords, but they offer a greater degree of flexibility and control.
- Open chord
An open chord is a chord that is played without barring any of the strings. This makes open chords easier to play than barre chords, but they are limited to certain keys and voicings. Open chords are often used in folk and country music, as well as in beginner guitar lessons.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between barre chords and open chords:
| Characteristic | Barre chord | Open chord |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty | More difficult | Easier |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Less flexible |
| Common uses | Jazz, rock, blues | Folk, country, beginner guitar lessons |
Ultimately, the best way to learn how to play the G# chord guitar is to practice both variations. This will give you the flexibility to play any song in any key, and it will also help you to develop your overall guitar playing skills.
6. Uses
The G# chord guitar is a versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical genres, including major key songs and jazz chords. In major key songs, the G# chord can be used to create a bright and uplifting sound. It is often used in the chorus or bridge of a song to create a sense of excitement or anticipation. In jazz chords, the G# chord can be used to add a sophisticated and complex sound. It is often used in conjunction with other chords, such as the C#m7 chord or the F#7 chord, to create a rich and harmonic sound.
Understanding the connection between the G# chord guitar and its uses in major key songs and jazz chords is important for guitarists who want to expand their musical knowledge and skills. By understanding how the G# chord can be used in different musical contexts, guitarists can create more interesting and sophisticated music.
Here are some examples of how the G# chord guitar can be used in major key songs and jazz chords:
- In the Beatles song “Hey Jude,” the G# chord is used in the chorus to create a bright and uplifting sound.
- In the jazz standard “Autumn Leaves,” the G# chord is used in the bridge to create a sophisticated and complex sound.
By understanding how the G# chord can be used in different musical contexts, guitarists can create more interesting and sophisticated music.
| Characteristic | G# chord guitar |
|---|---|
| Uses | Major key songs, jazz chords |
| Effect | Bright and uplifting sound in major key songs; sophisticated and complex sound in jazz chords |
| Importance | Versatile chord that can be used in a variety of musical genres |
| Examples | The Beatles song “Hey Jude,” the jazz standard “Autumn Leaves” |
7. Inversions
In music, an inversion is a chord that has been rearranged so that a different note is in the bass. The root note of a chord is the lowest note in the chord, and the bass note is the lowest note that is played. In a root position chord, the root note is in the bass. In an inverted chord, the root note is not in the bass.
There are two types of inversions: first inversion and second inversion. In a first inversion chord, the third of the chord is in the bass. In a second inversion chord, the fifth of the chord is in the bass.
The G# chord guitar can be inverted to create first inversion and second inversion chords. The first inversion of the G# chord is the G#/B chord. The second inversion of the G# chord is the G#/D# chord.
Inversions are important because they can be used to create different sounds and voicings. First inversion chords often have a more mellow sound than root position chords. Second inversion chords often have a more dissonant sound than root position chords.
Inversions can also be used to create voice leading. Voice leading is the smooth movement of voices from one chord to another. By using inversions, you can create voice leading that is more melodic and interesting.
Here are some examples of how inversions can be used in practice:
- A first inversion G# chord can be used to create a more mellow sound in a ballad.
- A second inversion G# chord can be used to create a more dissonant sound in a jazz solo.
- Inversions can be used to create voice leading that is more melodic and interesting.
U
nderstanding inversions is an important part of learning how to play the guitar. Inversions can be used to create a variety of different sounds and voicings. By understanding how to use inversions, you can expand your guitar playing skills and create more interesting and sophisticated music.
Table: Inversions of the G# Chord Guitar
| Inversion | Bass Note | Chord Voicing |
|---|---|---|
| Root position | G# | G# – B# – D# – G# |
| First inversion | B# | B# – D# – G# – G# |
| Second inversion | D# | D# – G# – G# – B# |
8. Embellishments
Embellishments are techniques that can be used to add interest and variety to your guitar playing. Three common embellishments are hammer-ons, pull-offs, and slides. These techniques can be used with the G# chord guitar to create a variety of different sounds.
- Hammer-ons
A hammer-on is a technique where you fret a note with your picking hand. This creates a percussive sound that can be used to add emphasis to a note. To perform a hammer-on, simply pick the note that you want to hammer on and then tap the fret with your picking hand.
- Pull-offs
A pull-off is the opposite of a hammer-on. To perform a pull-off, simply fret a note with your picking hand and then pull off the string with your picking hand. This creates a smooth, legato sound that can be used to create melodic lines.
- Slides
A slide is a technique where you slide your finger from one fret to another on the same string. This creates a smooth, glissando sound that can be used to add interest to a chord or melody.
These are just a few of the many embellishments that can be used with the G# chord guitar. By experimenting with different embellishments, you can create your own unique sound and style.
9. Theory
Understanding the theoretical underpinnings of the G# chord guitar is essential for guitarists who want to expand their musical knowledge and skills. The G# chord guitar is based on the G# major scale and the G# major triad.
- G# major scale
The G# major scale is a seven-note scale that consists of the following notes: G#, A#, B#, C#, D#, E#, and F. The G# major scale is used to create chords and melodies in the key of G# major.
- G# major triad
The G# major triad is a three-note chord that consists of the root note (G#), the major third (B#), and the perfect fifth (D#). The G# major triad is the foundation of the G# chord guitar.
By understanding the connection between the G# major scale and the G# major triad, guitarists can learn how to construct the G# chord guitar and how to use it in different musical contexts.
10. Practice
Regular practice is essential for mastering the G# chord guitar and improving your overall guitar playing skills. There are two main types of practice that are particularly beneficial for learning the G# chord guitar: finger exercises and chord progressions.
Finger exercises are a great way to improve your finger dexterity and strength. They can also help you to develop muscle memory, which will make it easier to play the G# chord guitar and other chords quickly and accurately. There are many different finger exercises that you can do, but some of the most effective exercises include:
- Playing scales
- Playing arpeggios
- Doing finger rolls
- Practicing chord transitions
Chord progressions are a great way to practice playing the G# chord guitar in a musical context. They can also help you to develop your sense of rhythm and timing. There are many different chord progressions that you can practice, but some of the most common progressions include:
- I – IV – V
- I – V – vi – IV
- I – vi – IV – V
Practicing finger exercises and chord progressions is essential for developing the skills you need to play the G# chord guitar and other chords with confidence and accuracy. By practicing regularly, you can improve your finger dexterity, strength, and muscle memory, and you can also develop your sense of rhythm and timing.
Here is a table summarizing the key insights about the connection between “Practice: Finger exercises, chord progressions” and “g# chord guitar”:
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Regular practice is essential for mastering the G# chord guitar. | Playing the G# chord guitar requires finger dexterity, strength, and muscle memory. Regular practice can help you to develop these skills. |
| Finger exercises can help you to improve your finger dexterity and strength. | Finger exercises are a great way to warm up your fingers before playing the G# chord guitar. They can also help you to develop the strength and dexterity you need to play the chord accurately and quickly. |
| Chord progressions can help you to practice playing the G# chord guitar in a musical context. | Chord progressions are a great way to practice playing the G# chord guitar with other chords. This can help you to develop your sense of rhythm and timing, and it can also help you to learn how to use the G# chord guitar in different songs. |
Understanding the connection between “Practice: Finger exercises, chord progressions” and “g# chord guitar” is essential for guitarists who want to develop the skills they need to play the G# chord guitar and other chords with confidence and accuracy.
11. Tips
Developing proficiency with the G# chord guitar requires dedication and consistent practice. Two valuable tips that can enhance your learning journey are utilizing a metronome and establishing a regular practice routine.
A metronome is a device that emits a steady pulse, assisting musicians in maintaining an accurate tempo. Incorporating a metronome into your practice sessions provides several benefits. Firstly, it helps you develop a strong sense of rhythm, ensuring that your chord changes and strumming patterns are precise and consistent. Secondly, practicing with a metronome trains your timing and allows you to gradually increase your speed and accuracy. This is particularly important for mastering the G# chord guitar, as it involves coordinating multiple fingers and transitioning smoothly between different chord shapes.
Regular practice is equally crucial for mastering the G# chord guitar. Consistent practice allows your fingers to develop muscle memory, making it easier to fret the chords correctly and effortlessly. Aim to set aside dedicated practice time each day, even if it’s just for 15-20 minutes. Regular practice helps solidify the techniques and muscle movements required for playing
the G# chord guitar, leading to improved dexterity and proficiency.
The following table provides a summary of the key insights regarding the connection between “Tips: Use a metronome, practice regularly” and “g# chord guitar”:
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Using a metronome improves rhythm and timing. | Practicing with a metronome helps develop a steady beat, which translates into precise chord changes and strumming patterns. |
| Regular practice builds muscle memory. | Consistent practice allows your fingers to remember the correct fretting positions, leading to improved dexterity and accuracy. |
Understanding the importance of “Tips: Use a metronome, practice regularly” is essential for guitarists seeking to master the G# chord guitar. By incorporating these tips into your practice routine, you can develop a strong foundation and enhance your overall guitar playing skills.
FAQs on the G# Chord Guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the G# chord guitar, providing clear and informative answers to enhance your understanding and playing skills.
Question 1: Is the G# chord guitar difficult to learn?
The G# chord guitar is generally considered to have an “Easy” difficulty level, making it accessible to guitarists of all skill levels, especially beginners. Its open chord voicing and relatively low position on the fretboard contribute to its ease of playability.
Question 2: What are the variations of the G# chord guitar?
The G# chord guitar has two main variations: the barre chord and the open chord. Barre chords involve barring the index finger across all six strings, providing greater flexibility and control, while open chords utilize open strings for a simpler fingering pattern.
Question 3: How is the G# chord guitar used in music?
The G# chord guitar finds applications in various musical genres, including major key songs and jazz chords. In major key songs, it contributes a bright and uplifting sound, often used in choruses or bridges to create a sense of excitement or anticipation. In jazz chords, the G# chord guitar adds a sophisticated and complex dimension when combined with other chords.
Question 4: What is the significance of inversions in the G# chord guitar?
Inversions involve rearranging the notes of the G# chord, resulting in different voicings and sounds. First inversions place the third of the chord in the bass, while second inversions feature the fifth in the bass. Inversions provide harmonic variety and enable smoother voice leading between chords.
Question 5: How can I practice effectively to master the G# chord guitar?
Regular practice is crucial for developing proficiency with the G# chord guitar. Incorporating a metronome into your practice routine helps improve your rhythm and timing, while consistent practice builds muscle memory and enhances finger dexterity. Aim to set aside dedicated practice time each day, even for short durations.
Question 6: What are some tips for playing the G# chord guitar well?
To play the G# chord guitar effectively, ensure that your fingers are properly positioned and fretting the correct notes. Practice transitioning smoothly between the G# chord and other chords in different progressions. Additionally, utilizing embellishments such as hammer-ons and pull-offs can add interest and variety to your playing.
By gaining a deeper understanding of these aspects, guitarists can enhance their playing skills and incorporate the G# chord guitar into their musical repertoire with confidence.
Transition to the next article section: Dive deeper into the world of guitar chords by exploring the construction, variations, and applications of the C major chord in our next section.
Tips for Playing the G# Chord Guitar
Mastering the G# chord guitar requires dedication and consistent practice. Here are several valuable tips to enhance your playing skills:
Tip 1: Finger Positioning
Ensure that your fingers are correctly positioned and fretting the notes accurately. Place your index finger on the root note, middle finger on the third note, ring finger on the second note, and pinky finger on the top note.
Tip 2: Smooth Transitions
Practice transitioning smoothly between the G# chord and other chords in different progressions. This will improve your overall chord playing fluidity and enable you to create seamless chord changes during performances.
Tip 3: Embellishments
Incorporate embellishments such as hammer-ons and pull-offs to add interest and variety to your playing. These techniques can enhance the dynamics of your chord progressions and create a more expressive sound.
Tip 4: Use a Metronome
Utilize a metronome during practice to improve your rhythm and timing. Playing along with a steady beat will help you develop a consistent tempo and ensure that your chord changes are precise and synchronized.
Tip 5: Regular Practice
Regular practice is essential for developing muscle memory and enhancing finger dexterity. Aim to practice the G# chord guitar for at least 15-20 minutes each day. Consistent practice will significantly improve your proficiency and allow you to play the chord effortlessly.
Summary of Key Takeaways:
- Proper finger positioning ensures accurate fretting.
- Smooth chord transitions enhance playing fluidity.
- Embellishments add interest and expression to your playing.
- Using a metronome improves rhythm and timing.
- Regular practice is crucial for developing proficiency.
By following these tips and dedicating yourself to consistent practice, you can master the G# chord guitar and expand your musical abilities.
Transition to the Article’s Conclusion:
Incorporating these tips into your practice routine will empower you to play the G# chord guitar with confidence and precision. As you continue to practice and explore different techniques, you will unlock new possibilities and elevate your guitar playing skills to new heights.
Conclusion
The G# chord guitar, with its versatile nature and rich sound, is an essential addition to any guitarist’s repertoire. Through our exploration of its construction, variations, applications, practice techniques, and tips, we have gained a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental chord.
Mastering the G# chord guitar not only enhances your technical skills but also opens up a world of musical possibilities. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, incorporating this chord into your playing will expand your harmonic horizons and deepen your appreciation for the guitar.
As you continue your musical journey, remember that consistent practice and dedication are the keys to unlocking the full potential of the G# chord guitar. Embrace the learning process, experiment with different techniques, and let the music flow through your fingers. With each strum and chord change, you’ll grow as a guitarist and discover new ways to express yourself through this timeless instrument.