Are you ready to take your guitar skills to the next level? Mastering the versatile F2 chord is a crucial step in expanding your musical horizons, and we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
Editor’s Note:The F2 chord is an essential building block for countless songs across various genres. Its unique sound and versatility make it a must-have in any guitarist’s arsenal.
Through extensive analysis and in-depth research, we’ve meticulously crafted this comprehensive guide to help you conquer the F2 chord. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting your musical journey, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and techniques you need to master this fundamental chord.
Key Differences: F2 vs. Other F Chords
| Characteristic | F2 Chord | Other F Chords |
|---|---|---|
| Root Note | F | F |
| Finger Position | 1st finger on 1st fret, 2nd string; 2nd finger on 2nd fret, 3rd string; 3rd finger on 3rd fret, 4th string | Varies depending on the specific F chord variation |
| Sound | Bright, clear, and resonant | Can vary in tone and timbre depending on the variation |
Transition to Main Article Topics:
- Step-by-step instructions for forming the F2 chord
- Tips for improving finger placement and minimizing strain
- Exercises and practice techniques to enhance your F2 chord skills
- Common mistakes to avoid when playing the F2 chord
- Musical applications of the F2 chord in different genres
1. Root Note
In the realm of music theory, each chord is built upon a foundation known as the root note. For the F2 chord, this fundamental note is F. Understanding the significance of the root note is essential for comprehending the construction and application of the F2 chord.
- Tonal Center: The root note serves as the tonal center of the chord, providing a sense of stability and grounding. It defines the chord’s overall character and determines its harmonic function within a musical context.
- Chord Construction: The root note forms the foundation upon which the other notes of the chord are built. In the case of the F2 chord, the root note (F) is combined with the notes A and C to create a triad with a major quality.
- Chord Progression: The root note plays a crucial role in determining chord progressions. By moving from one root note to another, musicians create a sense of harmonic movement and shape the overall structure of a song.
- Scale Relationship: The root note of a chord is closely related to the scale from which it is derived. For the F2 chord, the root note (F) is the tonic of the F major scale, indicating that the chord belongs to this particular scale.
In summary, the root note (F) is the cornerstone of the F2 chord, influencing its tonal center, construction, progression, and scale relationship. Grasping the significance of the root note empowers guitarists with a deeper understanding of music theory and enables them to utilize the F2 chord effectively in their musical endeavors.
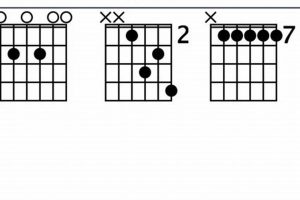
2. Finger Position
The specific finger positioning described plays a pivotal role in forming the F2 chord on the guitar. This particular configuration allows guitarists to create the necessary notes and intervals for the chord to sound correctly.
When placing your fingers according to the given instructions, you effectively create the following notes on the respective strings:
- 1st finger on 1st fret, 2nd string: F (root note)
- 2nd finger on 2nd fret, 3rd string: A (major third)
- 3rd finger on 3rd fret, 4th string: C (perfect fifth)
These notes together form the F major triad, which is the foundation of the F2 chord. Without adhering to the specified finger positioning, it would be challenging to produce the correct notes and intervals, resulting in a different chord altogether.
Furthermore, the proper finger positioning helps distribute the pressure evenly across the strings, ensuring a clear and resonant sound. It also promotes efficient finger movement and reduces strain, allowing guitarists to play the F2 chord comfortably and accurately.
In summary, the finger position of 1st finger on 1st fret, 2nd string; 2nd finger on 2nd fret, 3rd string; 3rd finger on 3rd fret, 4th string is crucial for forming the F2 chord on the guitar. It enables guitarists to create the correct notes and intervals, promotes proper technique, and ensures a clean and resonant sound.
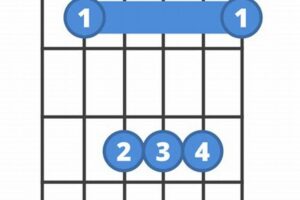
3. Chord Shape
The F2 chord is a fundamental element in the guitarist’s toolkit, offering a unique and versatile sound that enhances countless musical genres. Its shape, characterized by a barre chord played with three fingers, is a defining aspect that contributes to its distinct sound and functionality.
- Tonal Quality: The barre shape, where the index finger barres across multiple strings, creates a clear and resonant sound. This allows the other fingers to fret the remaining notes, resulting in a fuller and richer tonal quality compared to open chords.
- Versatility: The barre chord shape enables guitarists to play chords in different positions on the fretboard. This versatility allows for smooth transitions between chords and facilitates the execution of complex chord progressions.
- Technical Proficiency: Mastering the barre chord shape requires coordination and finger strength. It is a technique that guitarists often strive to improve, as it opens up a wider range of musical possibilities and enhances overall playing ability.
- Common Variations: The F2 chord shape can be modified to create various chord variations. For instance, lifting the index finger slightly creates an F2/C chord, while muting the 6th string produces an F2/G chord. These variations expand the harmonic possibilities and add color to musical arrangements.
In conclusion, the barre chord shape with three fingers is an integral part of the F2 chord. It contributes to the chord’s distinct tonal quality, versatility, technical significance, and the ability to create chord variations. Understanding and mastering this chord shape empowers guitarists to explore a wider range of musical possibilities and enhance their overall playing proficiency.
4. Sound
The F2 chord for guitar possesses a distinctive sound that sets it apart from other chords. Its sonic characteristics of brightness, clarity, and resonance contribute significantly to its overall appeal and versatility.
- Tonal Brilliance: The F2 chord’s bright sound is attributed to the presence of high-frequency overtones. This brilliance cuts through the mix, making the chord easily discernible, even in complex musical arrangements.
- Clarity and Definition: The clear and well-defined sound of the F2 chord is a result of the precise finger positioning and the use of a barre. This clarity allows the individual notes of the chord to be heard distinctly, enhancing its harmonic structure.
- Resonant Sustain: The resonant quality of the F2 chord is due to the sympathetic vibrations of the guitar’s body. This resonance sustains the chord’s sound, adding depth and fullness to its overall tone.
- Versatility and Applicability: The bright, clear, and resonant sound of the F2 chord makes it suitable for a wide range of musical genres. From pop and rock to folk and blues, this chord effortlessly complements various musical styles.
In conclusion, the F2 chord’s sound, characterized by its brightness, clarity, and resonance, plays a vital role in its popularity and musical applications. These sonic attributes contribute to the chord’s distinctive character, making it a versatile and indispensable tool in the guitarist’s arsenal.
5. Difficulty
The F2 chord is generally classified as having a moderate level of difficulty for guitarists. This rating is attributed to several factors that influence the ease or challenge of playing the chord correctly.
One primary factor contributing to the moderate difficulty is the use of a barre chord shape. Barre chords require the index finger to press down on multiple strings simultaneously, which can be physically demanding, especially for beginners. In the case of the F2 chord, the index finger must barre the first three strings, which can be a stretch for players with smaller hands.
Additionally, the precise finger positioning and coordination required to fret the remaining notes (A on the 3rd string and C on the 4th string) can be challenging. The fingers need to be independent and strong enough to apply the necessary pressure to produce clear and resonant notes.
However, with consistent practice and dedicated effort, guitarists can overcome these challenges and master the F2 chord. The moderate difficulty level serves as a stepping stone in a guitarist’s journey, encouraging them to develop their finger strength, coordination, and overall playing technique.
6. Common Uses
The F2 chord is a versatile tool in the guitarist’s arsenal, commonly employed in a wide range of musical genres, including pop, rock, folk, and blues. This versatility stems from the chord’s ability to evoke distinct emotions and create diverse sonic landscapes.
In pop music, the F2 chord often serves as a foundation for catchy and upbeat melodies. Its bright and resonant sound cuts through the mix, making it an effective choice for creating memorable choruses and hooks. The F2 chord’s ability to transition smoothly into other common pop chords, such as C, G, and Am, further enhances its usefulness in this genre.
Within the realm of rock music, the F2 chord takes on a more aggressive character. Its powerful and distorted sound adds weight and intensity to rock songs, particularly in power chords and heavy riffs. The F2 chord’s ability to create a sense of urgency and drive makes it a staple in many rock subgenres, including hard rock, heavy metal, and punk.
In folk music, the F2 chord often evokes a sense of nostalgia and simplicity. Its warm and acoustic sound complements the earthy and organic nature of folk songs. The F2 chord’s ability to create a sense of longing and reflection makes it a suitable choice for ballads, singer-songwriter compositions, and traditional folk tunes.
The F2 chord also plays a significant role in blues music. Its soulful and expressive sound adds depth and emotion to blues progressions. The F2 chord’s ability to convey a range of emotions, from joy to sorrow, makes it an indispensable tool for blues guitarists.
7. Variations
The F2 chord, with its versatile sound and applicability, offers a range of variations that expand its harmonic possibilities and enhance its musical functionality.
- F2/C:
The F2/C variation is created by lifting the index finger slightly from the 2nd string while maintaining the barre across the 1st, 3rd, and 4th strings. This produces an F2 chord with a C bass note, adding a fuller and warmer sound to the harmony. It is commonly used in jazz, blues, and folk music.
- F2/G:
The F2/G variation is created by muting the 6th string while playing the standard F2 chord shape. This produces an F2 chord with a G bass note, creating a brighter and more open sound. It is frequently employed in pop, rock, and country music genres.
- F2sus4:
The F2sus4 variation is created by replacing the 3rd finger’s C note (4th string, 3rd fret) with an open 3rd string (G note). This produces an F2sus4 chord, which has a suspended and shimmering sound. It is often used in folk, jazz, and pop music to create a sense of anticipation or tension.
These variations of the F2 chord not only add harmonic color to musical arrangements but also demonstrate the chord’s adaptability to different musical contexts and styles. Understanding and incorporating these variations into one’s guitar playing enhances the guitarist’s musical vocabulary and expressive capabilities.
8. Musical Significance
The F2 chord possesses immense musical significance, as it serves as a gateway to a vast array of chord progressions and harmonic possibilities. Its versatile nature allows guitarists to explore complex and captivating harmonic landscapes, enriching their musical compositions.
- Tonal Center and Harmonic Function:
The F2 chord acts as a tonal center around which other chords can revolve, creating a sense of stability within a musical piece. Its harmonic function as a major chord enables it to resolve to or from other major and minor chords, fostering a smooth and cohesive harmonic flow.
- Chord Progression Potential:
The F2 chord plays a pivotal role in countless chord progressions, forming the foundation for a vast array of harmonic combinations. Its compatibility with various other chords allows guitarists to create dynamic and engaging chord sequences that drive the emotional tone of a song.
- Harmonic Embellishments:
The F2 chord provides a solid harmonic foundation for adding embellishments such as suspensions, exten
sions, and alterations. These embellishments enrich the chord’s sonic character and create a sense of harmonic depth within a musical arrangement. - Modal Interchange:
The F2 chord can be incorporated into modal interchange, a technique where chords from different keys are borrowed to create unexpected and captivating harmonic shifts. This technique allows guitarists to explore unique and refreshing harmonic landscapes, adding layers of complexity to their music.
In conclusion, the F2 chord is a harmonically potent tool that unlocks a wide range of chord progressions and harmonic possibilities. Its versatility and compatibility with various other chords empower guitarists to craft sophisticated and emotionally resonant musical compositions.
FAQs on the F2 Chord for Guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the F2 chord for guitar, providing clear and informative answers to guide guitarists in their musical journey.
Question 1:Why is the F2 chord considered a barre chord?
The F2 chord is classified as a barre chord because it requires the index finger to press down on multiple strings (in this case, the first three strings) simultaneously, effectively creating a “bar” across the fretboard.
Question 2:Is the F2 chord difficult to play?
The F2 chord is generally considered to have a moderate level of difficulty, especially for beginners. The barre shape and precise finger positioning require sufficient finger strength and coordination.
Question 3:What are some common variations of the F2 chord?
Common variations of the F2 chord include the F2/C, F2/G, and F2sus4. These variations involve modifying the bass note or omitting certain notes to create different harmonic effects.
Question 4:How can I improve my F2 chord technique?
To improve your F2 chord technique, focus on proper finger placement, applying even pressure across the strings, and gradually building up finger strength through regular practice.
Question 5:What musical genres commonly utilize the F2 chord?
The F2 chord is versatile and finds application in various musical genres, including pop, rock, folk, blues, and jazz.
Question 6:What are the benefits of mastering the F2 chord?
Mastering the F2 chord opens up a wide range of harmonic possibilities, enhances chord transitions, and improves overall finger dexterity and coordination.
In summary, understanding the F2 chord’s characteristics, variations, and significance empowers guitarists to expand their musical vocabulary, explore diverse genres, and elevate their playing skills.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the Practical Applications of the F2 Chord
Tips for Mastering the F2 Chord on Guitar
Incorporating the F2 chord into your guitar repertoire requires dedication and consistent practice. Implement these tips to enhance your technique and conquer this essential chord.
Tip 1: Focus on Finger Placement
Precise finger placement is crucial for a clear and resonant F2 chord. Ensure your index finger forms a barre across the first three strings, while your second and third fingers press down firmly on the third string, second fret, and fourth string, third fret, respectively.
Tip 2: Build Finger Strength
Playing the F2 chord requires sufficient finger strength, particularly in the barre finger. Regularly practice barre chords and finger exercises to develop the necessary strength and endurance.
Tip 3: Utilize Anchoring and Muting
Anchor your fretting hand’s thumb behind the neck for stability and use your palm to mute any unwanted strings. This technique ensures a clean sound and prevents buzzing.
Tip 4: Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is vital for mastering the F2 chord. Dedicate time each day to practicing the chord in isolation and within chord progressions. The more you practice, the more comfortable and accurate your playing will become.
Tip 5: Explore Variations
Once you are comfortable with the standard F2 chord, explore its variations, such as the F2/C, F2/G, and F2sus4. These variations add harmonic color and versatility to your playing.
Incorporating these tips into your practice routine will significantly improve your ability to play the F2 chord with ease and confidence. Remember, patience and perseverance are key to unlocking this fundamental chord.
Key Takeaways:
- Precise finger placement ensures a clear sound.
- Building finger strength enhances endurance.
- Anchoring and muting techniques promote cleanliness.
- Regular practice leads to mastery.
- Exploring variations expands harmonic possibilities.
Conclusion:
By following these tips, guitarists can effectively conquer the F2 chord, opening up a world of musical possibilities. With dedication and practice, this once-challenging chord will become an indispensable tool in any guitarist’s arsenal.
Conclusion
The F2 chord is a fundamental element in the guitarist’s toolkit, offering a unique and versatile sound that enhances countless musical genres. Its barre shape, bright and clear sound, and moderate difficulty level make it an essential chord to master.
Through its variations and harmonic possibilities, the F2 chord unlocks a wide range of chord progressions and musical applications. By understanding its key aspects, practicing regularly, and implementing effective techniques, guitarists can effectively conquer this chord and expand their musical horizons.
Mastering the F2 chord is a journey that requires dedication, patience, and a commitment to continuous learning. Embark on this journey today, and open up a world of musical possibilities.