Acoustic guitars are a popular choice for beginners and experienced musicians alike. They produce a warm, mellow sound that is perfect for a variety of genres, from folk and blues to rock and pop.
Editor’s Note:Understanding the different parts of an acoustic guitar is essential for anyone who wants to play or maintain one. In this guide, we’ll take a close look at the anatomy of an acoustic guitar and explain the function of each part.
We’ve done the research and dug into the details, so you can make informed decisions about your next acoustic guitar purchase. Let’s get started!
1. Body
The body of an acoustic guitar is one of the most important parts of the instrument. It is responsible for producing the sound of the guitar, and the type of wood used will affect the tone and volume of the sound. The most common type of wood used for acoustic guitar bodies is spruce, which produces a bright, clear sound. Other popular woods include mahogany, which produces a warm, mellow sound, and rosewood, which produces a rich, deep sound.
- Facet 1: Shape of the Body
The shape of the body of an acoustic guitar will affect the sound of the guitar. A larger body will produce a louder sound, while a smaller body will produce a quieter sound. The shape of the body will also affect the tone of the guitar. A body with a wider waist will produce a brighter sound, while a body with a narrower waist will produce a darker sound.
- Facet 2: Type of Wood
The type of wood used for the body of an acoustic guitar will also affect the sound of the guitar. Different types of wood have different tonal qualities. For example, spruce is a bright, clear wood that produces a bright, clear sound. Mahogany is a warm, mellow wood that produces a warm, mellow sound. Rosewood is a rich, deep wood that produces a rich, deep sound.
- Facet 3: Construction of the Body
The construction of the body of an acoustic guitar will also affect the sound of the guitar. The body of an acoustic guitar can be constructed in a variety of ways, each of which will produce a different sound. For example, a body that is constructed with a solid top will produce a louder sound than a body that is constructed with a laminated top.
The body of an acoustic guitar is a complex and important part of the instrument. By understanding the different factors that affect the sound of the body, you can choose the right guitar for your needs.
2. Neck
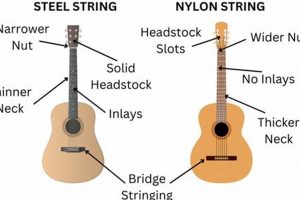
The neck of an acoustic guitar is a crucial component that plays a significant role in the overall playability and sound of the instrument. Its connection to the body and headstock forms the foundation of the guitar’s structure, allowing for the transfer of vibrations and the production of sound.
The choice of wood for the neck is essential as it directly affects the feel and response of the guitar. Different types of wood offer unique characteristics that cater to specific playing styles and preferences. For instance, mahogany is known for its warm, resonant tone and comfortable feel, while maple provides a brighter, more articulate sound with a faster response.
The shape and dimensions of the neck also contribute to the playing experience. The width of the neck, known as the nut width, determines the spacing between the strings, affecting the ease of fretting and chording. The thickness of the neck, or the neck profile, influences the overall feel and comfort while playing.
Understanding the connection between the neck and other acoustic guitar parts is vital for selecting the right instrument that suits your playing style and preferences. By considering factors such as wood type, shape, and dimensions, you can choose a guitar that provides an optimal playing experience and complements your musical aspirations.
| Wood Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Mahogany | Warm, resonant tone, comfortable feel |
| Maple | Bright, articulate sound, faster response |
| Rosewood | Rich, mellow tone, smooth feel |
3. Fretboard
The fretboard is a crucial component of acoustic guitar parts, serving as the platform where the strings are pressed to produce different musical notes. Its construction and materials play a significant role in the overall playability, tone, and feel of the guitar.
The choice of wood for the fretboard directly influences the sound and feel of the guitar. Different types of wood offer unique tonal qualities and tactile sensations. For instance, rosewood is known for its warm, rich sound and smooth feel, while ebony provides a brighter, more articulate tone with a faster response. The hardness and density of the wood also affect the durability and stability of the fretboard.
The fretboard’s shape and dimensions also contribute to the playing experience. The radius of the fretboard, which refers to the curvature from side to side, affects the ease of fretting and chording. A flatter radius allows for easier bending and vibrato, while a more curved radius provides better intonation and stability.
The fretboard is intricately connected to other acoustic guitar parts, forming a cohesive system that produces sound. The frets, which are metal strips embedded into the fretboard, divide the strings into specific intervals, allowing for accurate note production. The nut, located at the end of the fretboard closest to the headstock, ensures proper string spacing and intonation.
Understanding the connection between the fretboard and other acoustic guitar parts is essential for selecting and playing the guitar effectively. By considering factors such as wood type, shape, and dimensions, guitarists can choose an instrument that complements their playing style and musical aspirations.
| Wood Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Rosewood | Warm, rich sound, smooth feel |
| Ebony | Bright, articulate sound, faster response |
| Maple | Clear, bright sound, hard and durable |
4. Headstock
The headstock is an essential component of acoustic guitar parts, serving several crucial functions. It provides the anchor point for the strings, ensuring proper tension and intonation. The shape and design of the headstock also contribute to the overall balance and aestheti
cs of the guitar.
The choice of wood for the headstock is important as it affects the structural integrity and tonal characteristics of the guitar. Heavier woods, such as mahogany or rosewood, provide greater stability and resonance, while lighter woods, such as maple or basswood, offer a brighter and more articulate sound. The shape of the headstock can also influence the guitar’s sound and playability. A larger headstock provides more mass, which can enhance sustain and low-end response, while a smaller headstock reduces weight and improves balance, making it easier to play for extended periods.
Understanding the connection between the headstock and other acoustic guitar parts is essential for selecting and maintaining the instrument. The headstock’s compatibility with the neck and tuners ensures proper string alignment and tuning stability. Additionally, the headstock’s aesthetic design complements the overall appearance of the guitar, making it a visually appealing and functional component.
| Wood Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Mahogany | Heavy, resonant, provides stability and warmth |
| Rosewood | Dense, durable, enhances sustain and low-end response |
| Maple | Lightweight, bright, offers clarity and articulation |
| Basswood | Lightweight, neutral, allows for customization and modification |
5. Tuners
Tuners are an integral part of acoustic guitar parts, playing a crucial role in maintaining the instrument’s intonation and playability. Their primary function is to adjust the tension of the strings, allowing guitarists to fine-tune the pitch of each string to achieve the desired sound. The type of metal used in the construction of tuners impacts their durability and performance.
The connection between tuners and acoustic guitar parts lies in their interdependence. Tuners are designed to fit securely on the headstock of the guitar, interacting with the strings at the nut and bridge. This connection enables precise adjustments to the string tension, ensuring that the guitar remains in tune and produces accurate intonation throughout the entire fretboard.
The durability of tuners is a significant factor in maintaining a guitar’s playability over time. Well-crafted tuners made from sturdy metals, such as steel or brass, can withstand the rigors of regular use and tuning adjustments. Durable tuners minimize the risk of slippage or breakage, ensuring that the guitar stays in tune during performances or practice sessions.
Understanding the connection between tuners and acoustic guitar parts is essential for guitarists of all levels. Regular maintenance and proper use of tuners contribute to the overall longevity and performance of the instrument. By ensuring that the tuners are functioning correctly and the strings are properly tensioned, guitarists can maintain optimal intonation and enjoy a more fulfilling playing experience.
| Tuner Material | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Steel | Durable, strong, provides precise tuning |
| Brass | Corrosion-resistant, offers a smooth and responsive feel |
| Nickel | Lightweight, resistant to wear and tear |
| Zinc | Affordable, suitable for beginner guitars |
6. Bridge
The bridge is a crucial component of acoustic guitar parts, serving as the anchor point for the strings and playing a significant role in transmitting vibrations to the guitar’s body. The type of wood used in the bridge directly affects the sound and tone of the guitar.
The connection between the bridge and acoustic guitar parts lies in its integral role within the instrument’s structure and function. The bridge is designed to transfer the vibrations of the strings to the guitar’s body, which then resonates and amplifies the sound. Different types of wood have unique tonal qualities, density, and stiffness, which influence the overall sound characteristics of the guitar.
For instance, a rosewood bridge contributes to a warm, rich sound with enhanced sustain, while a maple bridge provides a brighter, more articulate tone. The bridge’s design, including its shape, size, and mass, also influences the guitar’s sound and playability. A larger bridge with a higher mass can enhance sustain and low-end response, while a smaller bridge with a lower mass promotes clarity and articulation.
Understanding the connection between the bridge and acoustic guitar parts is essential for selecting and maintaining the instrument. By considering factors such as wood type, design, and construction, guitarists can choose a bridge that complements their playing style and desired sound. Proper care and maintenance of the bridge, including regular cleaning and adjustments, contribute to the overall longevity and performance of the guitar.
In summary, the bridge is a fundamental component of acoustic guitar parts, affecting the instrument’s sound, tone, and playability. Its connection to other guitar parts forms a cohesive system that produces the desired musical output. Understanding this connection empowers guitarists to make informed decisions about their instrument and enhance their musical journey.
| Wood Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Rosewood | Warm, rich sound, enhanced sustain |
| Maple | Bright, articulate tone, improved clarity |
| Mahogany | Balanced tone, good sustain and projection |
7. Soundhole
The soundhole is a crucial component of acoustic guitar parts, serving as the primary outlet for the sound produced by the vibrating strings. Its design and placement significantly impact the guitar’s overall tone and projection.
The connection between the soundhole and acoustic guitar parts lies in its integral role within the instrument’s. The soundhole allows the sound waves generated by the vibrating strings to escape from the guitar’s body, creating the characteristic acoustic sound. The size, shape, and location of the soundhole influence the guitar’s tonal qualities and volume.
A larger soundhole generally produces a louder and more resonant sound, while a smaller soundhole results in a more focused and controlled tone. The shape of the soundhole also affects the sound, with round soundholes providing a more balanced and traditional tone, and non-traditional shapes offering unique tonal characteristics.
The placement of the soundhole is also important, as it affects the guitar’s projection and feedback resistance. A soundhole positioned closer to the center of the body provides a more balanced sound, while a soundhole located near the neck or bridge can enhance certain frequency ranges.
Understanding the connection between the soundhole and acoustic guitar parts is essential for selecting and maintaining the instrument. By considering factors such as size, shape, and placement, guitarists can choose a soundhole that complements their playing style and desired sound. Additionally, proper care and maintenance of the so
undhole, including regular cleaning and inspection, contribute to the overall longevity and performance of the guitar.
In summary, the soundhole is an integral part of acoustic guitar parts, playing a vital role in shaping the instrument’s sound and projection. Its connection to other guitar parts forms a cohesive system that produces the desired musical output. Understanding this connection empowers guitarists to make informed decisions about their instrument and enhance their musical journey.
| Soundhole Size | Tonal Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Larger | Louder, more resonant sound |
| Smaller | More focused and controlled tone |
| Soundhole Shape | Tonal Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Round | Balanced, traditional tone |
| Non-traditional | Unique tonal characteristics |
| Soundhole Placement | Tonal Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Center of the body | More balanced sound |
| Near the neck or bridge | Enhanced certain frequency ranges |
8. Pickguard
The pickguard is an essential component of acoustic guitars, serving a crucial protective function while also contributing to the instrument’s overall aesthetic appeal.
- Protection from Scratches and Wear
The primary purpose of the pickguard is to safeguard the guitar’s body from scratches and wear caused by strumming and picking. It acts as a barrier between the guitar’s surface and the pick, preventing damage to the finish and preserving the instrument’s pristine appearance.
- Customization and Style
Beyond its protective function, the pickguard also serves as a customizable design element. Available in a variety of colors and materials, pickguards allow guitarists to personalize their instruments and express their individual style. From classic black or tortoiseshell to intricate designs and patterns, the pickguard can complement the guitar’s overall aesthetic.
- Tonal Impact
While not as significant as other components, the pickguard can have a subtle influence on the guitar’s tone. Different materials, such as plastic or metal, impart unique tonal characteristics. For example, a metal pickguard may provide a brighter, more articulate sound, while a plastic pickguard may offer a warmer, mellower tone.
- Historical Significance
The pickguard has a long and rich history in guitar making. Early guitars often featured simple pickguards made of tortoise shell or wood to protect the body from wear. Over time, pickguards evolved into more decorative and elaborate elements, becoming an integral part of the guitar’s design.
In conclusion, the pickguard is an important component of acoustic guitars that serves multiple purposes. It protects the body from damage, allows for customization and self-expression, subtly influences the guitar’s tone, and holds historical significance. Understanding the connection between the pickguard and acoustic guitar parts provides a deeper appreciation for the instrument’s construction and its role in shaping its sound and appearance.
Frequently Asked Questions about Acoustic Guitar Parts
This section addresses common queries and misconceptions about the components of an acoustic guitar, providing informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the purpose of the soundhole?
The soundhole is a crucial outlet for the sound produced by the vibrating strings. It allows the sound waves to escape from the guitar’s body, resulting in the characteristic acoustic sound. The size, shape, and placement of the soundhole impact the guitar’s tone and projection.
Question 2: What is the difference between a dreadnought and a jumbo body shape?
Dreadnought and jumbo body shapes represent two common acoustic guitar designs. Dreadnought guitars feature a larger body with a wider waist, producing a louder and more resonant sound. Jumbo guitars have an even larger body with a more pronounced waist, resulting in a richer and bassier tone.
Question 3: What type of wood is best for the guitar’s neck?
The choice of wood for the guitar’s neck depends on the desired tonal qualities and feel. Mahogany is a popular choice for its warm, resonant sound and comfortable feel. Maple provides a brighter, more articulate tone and a faster response. Rosewood offers a rich, mellow tone and a smooth feel.
Question 4: What is the function of the tuners?
Tuners are essential for adjusting the tension of the strings, ensuring the guitar remains in tune. They are usually made of metal, and the type of metal used affects their durability and performance. Steel tuners are durable and provide precise tuning, while brass tuners are corrosion-resistant and offer a smooth feel.
Question 5: What is the difference between a solid top and a laminated top?
A solid top is made from a single piece of wood, providing superior resonance and a richer, more complex sound. A laminated top, on the other hand, is constructed from several layers of wood, making it more affordable and less susceptible to warping.
Question 6: How often should I change my guitar strings?
The frequency of string changes depends on playing habits and the environment. As a general rule, strings should be changed every 3 to 6 months for optimal tone and performance. Regular string changes prevent breakage, maintain intonation, and reduce the risk of damage to the guitar’s neck and bridge.
Understanding these aspects of acoustic guitar parts empowers guitarists to make informed decisions about their instrument’s maintenance and upgrades, ultimately enhancing their playing experience and musical expression.
Transition: Explore the diverse range of acoustic guitars available, considering factors such as body shape, wood selection, and electronic options, to find the perfect instrument that suits your musical style and aspirations.
Tips for Acoustic Guitar Parts
Maintaining and understanding the different parts of an acoustic guitar is crucial for guitarists of all levels. Here are a few tips to help you care for and enhance your instrument:
Tip 1: Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regularly cleaning your guitar removes dirt, sweat, and oils that can accumulate over time. Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe down the body, neck, and strings. For deeper cleaning, use a guitar cleaner specifically designed for acoustic guitars.
Tip 2: Proper String Care
Strings are essential for producing sound, so it’s important to take care of them. Change your strings regularly (every 3-6 months) to maintain optimal tone and intonation. Avoid over-tightening the strings, as this can damage the guitar’s neck.
Tip 3: Humidification
Acoustic guitars are susceptible to changes in humidity, which can affect their sound and playability. Use a humidifier in dry climates to maintain the proper humidity level for your guitar. This will prevent the wood from drying out and cracking.
Tip 4: Truss Rod Adjustment
The truss rod is a metal rod inside the neck that helps to adjust the curvature of the neck. If the neck is too bowed or back-bowed, you may nee
d to adjust the truss rod. It’s important to have this done by a qualified guitar technician to avoid damaging the guitar.
Tip 5: Professional Setup
A professional guitar setup involves adjusting the guitar’s action, intonation, and truss rod to optimize its playability and sound. Having your guitar set up regularly by a qualified technician will ensure that it’s always in top condition.
Summary: By following these tips, you can maintain your acoustic guitar’s appearance, playability, and sound quality. Regular care and maintenance will extend the life of your instrument and enhance your playing experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the different parts of an acoustic guitar is essential for guitarists of all levels. By learning about the functions and interconnections of these components, you can make informed decisions about your instrument and enhance your playing experience.
The acoustic guitar is a versatile and expressive instrument that can produce a wide range of sounds. By understanding the different parts of the guitar and how they work together, you can unlock the full potential of this instrument and create beautiful music.
Youtube Video: