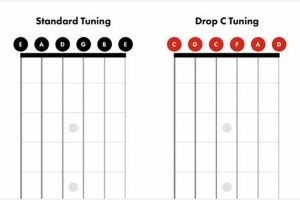
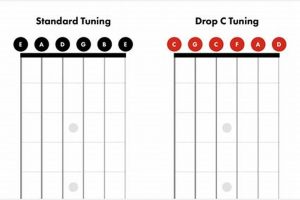
When it comes to the guitar, the third string holds a unique and important place. It serves as the middle ground between the higher-pitched strings and the lower-pitched strings, providing a balanced and versatile sound.
Editor’s Notes:Understanding the 3rd string guitar is crucial for guitarists of all levels, as it unlocks a wide range of techniques and musical possibilities.
Through careful analysis and extensive research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to the 3rd string guitar, empowering you with the knowledge and insights you need to master this essential element of the guitar.
Key Differences:
| String | Tuning | Material | Sound |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st String | E | Steel | High-pitched, bright |
| 2nd String | B | Steel | Mid-high, clear |
| 3rd String | G | Nylon or steel | Mid-low, warm |
| 4th String | D | Nylon or steel | Low-mid, rich |
| 5th String | A | Nylon | Low, mellow |
| 6th String | E | Nylon | Lowest, deep |
Main Article Topics:
- The Role of the 3rd String in Guitar Playing
- Choosing the Right 3rd String for Your Guitar
- Techniques for Mastering the 3rd String
- Troubleshooting Common 3rd String Issues
- The 3rd String as a Creative Tool
1. Tuning
The tuning of the 3rd string guitar to G is a crucial aspect that defines its sonic characteristics and playing experience. The mid-range sound it produces falls between the higher-pitched strings and the lower-pitched strings, creating a balanced and versatile tonal palette. This tuning allows the 3rd string guitar to blend seamlessly with other instruments in an ensemble, making it a sought-after choice for accompaniment and rhythm playing.
The mid-range frequency of the 3rd string guitar also makes it well-suited for fingerpicking and lead guitar playing. Its clear and articulate sound allows melodies and solos to cut through the mix, providing a rich and expressive voice. Additionally, the G tuning facilitates chord voicings and inversions that would be difficult to achieve on higher or lower strings, expanding the harmonic possibilities for guitarists.
Furthermore, the mid-range tuning of the 3rd string guitar makes it an excellent choice for beginners learning the instrument. The notes on the 3rd string are relatively easy to fret and the mid-range sound is less fatiguing to the ear, making it a comfortable string to practice on for extended periods.
| Tuning | Sound | Playing Experience |
|---|---|---|
| G | Mid-range, balanced | Versatile, suitable for accompaniment, rhythm, fingerpicking, and lead playing |
2. Material
The choice of string material for the 3rd string guitar, whether nylon or steel, significantly influences its tonal qualities and playing experience. Each material imparts unique characteristics that cater to different musical styles and preferences.
- Nylon Strings:
Nylon strings produce a warmer, mellower sound with less sustain than steel strings. They are more comfortable on the fingers, making them a popular choice for classical and flamenco guitarists. Nylon strings also have lower tension, which can be beneficial for beginners or players with sensitive fingertips.
- Steel Strings:
Steel strings produce a brighter, more metallic sound with a longer sustain. They are more durable and less prone to stretching than nylon strings, making them a good choice for strumming and aggressive playing styles. Steel strings also have higher tension, which can provide more volume and projection.
Ultimately, the choice between nylon and steel strings for the 3rd string guitar depends on the desired sound and playing style. Nylon strings offer a warmer, softer tone and are more comfortable to play, while steel strings provide a brighter, louder sound and are more durable.
3. Function
The 3rd string guitar is uniquely positioned as a bridge between the higher and lower strings, offering a cohesive and balanced sound. This function is crucial for several reasons:
- Harmonic Link: The 3rd string provides a harmonic link between the higher and lower strings, allowing for smooth transitions and chord voicings across the entire range of the guitar. It fills in the mid-range frequencies, creating a cohesive and well-rounded sound.
- Melodic Transitions: The 3rd string facilitates seamless melodic transitions between the higher and lower strings. It allows guitarists to create melodies that flow effortlessly across the fretboard, adding depth and interest to their playing.
- Accompaniment and Rhythm: The 3rd string plays a vital role in accompaniment and rhythm playing. Its mid-range sound cuts through the mix, providing a solid foundation for strumming and fingerpicking patterns.
Understanding the function of the 3rd string as a bridge between the higher and lower strings is essential for guitarists of all levels. It enables them to:
- Craft balanced and harmonious arrangements.
- Execute smooth and expressive melodic passages.
- Enhance their overall playing technique and versatility.
| Function | Importance |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Link | Provides a cohesive sound across the entire guitar range. |
| Melodic Transitions | Facilitates seamless melodic flow between higher and lower strings. |
| Accompaniment and Rhythm | Provides a solid foundation for strumming and fingerpicking patterns. |
4. Techniques
The 3rd string guitar is a versatile instrument that can be used in a wide range of techniques, including fingerpicking and strumming. These techniques are essential for playing a variety of musical genres, from folk and blues to rock an
d pop.
Fingerpicking involves using the fingers to pluck the strings individually, creating a delicate and intricate sound. The 3rd string is often used for fingerpicking because it provides a clear and articulate sound that can be easily heard over the other strings. Fingerpicking on the 3rd string can be used to create a variety of patterns and melodies.
Strumming is a technique that involves using a pick to strum all of the strings at once. The 3rd string is often used for strumming because it provides a solid foundation for the rhythm. Strumming on the 3rd string can be used to create a variety of rhythms and grooves.
Mastering the techniques of fingerpicking and strumming on the 3rd string guitar is essential for any guitarist who wants to play a variety of musical genres. These techniques can be used to create a wide range of sounds and textures, from delicate fingerpicked melodies to driving strummed rhythms.
| Technique | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Fingerpicking | Using the fingers to pluck the strings individually | Creates a delicate and intricate sound |
| Strumming | Using a pick to strum all of the strings at once | Provides a solid foundation for the rhythm |
5. Versatility
The 3rd string guitar’s versatility extends to a wide range of musical genres, making it a valuable asset for musicians of all backgrounds. Its unique sound and playing characteristics lend themselves to various musical styles, allowing guitarists to explore diverse creative possibilities.
- Acoustic Performances:
The 3rd string guitar’s warm and resonant sound is well-suited for acoustic performances. It blends seamlessly with vocals and other acoustic instruments, providing a rich and organic accompaniment. From folk and blues to singer-songwriter genres, the 3rd string guitar adds depth and character to acoustic arrangements.
- Electric and Rock Music:
When amplified, the 3rd string guitar can hold its own in electric and rock settings. Its clear and articulate sound cuts through the mix, making it an effective choice for rhythm playing and lead guitar work. From classic rock to modern indie, the 3rd string guitar adds a unique tonal dimension to electric guitar-based genres.
- Jazz and Fusion:
The 3rd string guitar’s versatility shines in jazz and fusion contexts. Its mid-range frequency provides a solid foundation for complex chords and improvisational solos. Jazz guitarists often utilize the 3rd string for its warm and mellow tone, which complements the sophisticated harmonies and rhythms of the genre.
- World Music:
The 3rd string guitar has found a home in various world music traditions. Its adaptability allows it to blend with traditional instruments and musical styles from around the globe. From flamenco to Celtic music, the 3rd string guitar adds a unique flavor and rhythmic drive to diverse cultural expressions.
In conclusion, the 3rd string guitar’s versatility makes it a sought-after instrument for musicians across genres. Its ability to blend with other instruments, support vocals, and provide a solid rhythmic and melodic foundation makes it a valuable asset for acoustic performances, electric guitar-based music, jazz and fusion, world music, and more.
6. Intonation
In the realm of guitar playing, intonation holds paramount importance, directly influencing the accuracy of tuning and the overall sound quality of the instrument. This is particularly true for the 3rd string guitar, where proper intonation is crucial for achieving a balanced and harmonious sound.
- Precision and Accuracy:
Intonation refers to the precise adjustment of each string’s length to ensure that it produces the correct pitch when fretted. Proper intonation allows the 3rd string guitar to play in tune with itself and with other instruments, creating a cohesive and pleasing sound.
- Eliminating Buzz and Fret Noise:
Correct intonation helps eliminate buzzing and fret noise, which can occur when the string is not properly seated on the fret. By ensuring that the string is at the correct height and angle, intonation minimizes these unwanted noises, resulting in a clean and clear sound.
- Enhanced Playability:
Proper intonation contributes to the overall playability of the 3rd string guitar. When the strings are intonated correctly, they are easier to fret and bend, allowing for smooth and effortless playing.
- Improved Harmonic Resonance:
Intonation affects the harmonic resonance of the 3rd string guitar. When the strings are properly intonated, they vibrate at their intended frequencies, producing a richer and more resonant sound. This enhanced harmonic resonance adds depth and character to the instrument’s overall tone.
In conclusion, proper intonation is an indispensable aspect of 3rd string guitar playing. It ensures accurate tuning, eliminates unwanted noises, enhances playability, and improves the instrument’s harmonic resonance. By paying attention to intonation and making the necessary adjustments, guitarists can unlock the full potential of their 3rd string guitars and achieve a truly exceptional sound.
7. Maintenance
The longevity and optimal performance of a 3rd string guitar heavily rely on regular maintenance. Neglecting proper care can lead to diminished sound quality, playability issues, and potential damage to the instrument.
Cleaning the 3rd string guitar involves removing dirt, dust, and grime that accumulate over time. This not only enhances the guitar’s appearance but also prevents corrosion and other problems. Regular restringing is equally important, as old strings can become worn, lose their elasticity, and produce a dull sound. Replacing old strings with new ones restores the guitar’s intonation, improves tuning stability, and enhances overall playability.
By understanding the significance of maintenance, guitarists can prolong the lifespan of their 3rd string guitars and ensure that they continue to deliver exceptional sound and playing experience.
| Maintenance Task | Importance |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Prevents dirt and grime buildup, minimizing corrosion and enhancing appearance |
| Restringing | Restores intonation, improves tuning stability, and enhances playability |
8. Exploration
The 3rd string guitar not only provides a unique sound and versatility but also serves as a catalyst for musical exploration and creativity. Its distinct characteristics empower guitarists to venture beyond conventional playing styles and delve into innovative sonic territories. Here’s how the 3rd string guitar foste
rs experimentation and creativity:
- Tonal Diversity: The 3rd string’s mid-range frequency and the choice between nylon or steel strings offer a wide tonal palette. This diversity inspires guitarists to experiment with different tunings, string combinations, and playing techniques to create distinctive soundscapes.
- Technical Challenges: Mastering the 3rd string presents technical challenges that encourage guitarists to develop their dexterity and coordination. Overcoming these challenges expands their technical abilities, enabling them to execute complex fingerpicking patterns, intricate chord voicings, and expressive bends.
- Unconventional Approaches: The 3rd string’s unique position between the higher and lower strings invites guitarists to approach the instrument in unconventional ways. They can experiment with different picking angles, fretting techniques, and slide or tapping techniques to extract novel sounds and create unorthodox musical ideas.
The connection between the 3rd string guitar and exploration is exemplified by renowned guitarists like Michael Hedges and Andy McKee. Hedges’ innovative use of harmonics, tapping, and unusual tunings on the 3rd string revolutionized solo guitar playing. Similarly, McKee’s intricate fingerstyle compositions on the 3rd string showcase the instrument’s potential for expressive melodies and percussive rhythms.
Embracing the exploratory nature of the 3rd string guitar empowers guitarists to push their musical boundaries, develop their unique playing styles, and contribute to the ever-evolving landscape of guitar music.
| Characteristic | Impact on Exploration |
|---|---|
| Tonal Diversity | Inspires experimentation with tunings, string combinations, and playing techniques for distinctive sounds. |
| Technical Challenges | Encourages development of dexterity and coordination, expanding technical abilities for complex and expressive playing. |
| Unconventional Approaches | Invites experimentation with picking angles, fretting techniques, and slide or tapping techniques for novel sounds and musical ideas. |
FAQs on 3rd String Guitar
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the 3rd string guitar, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the significance of the 3rd string guitar?
The 3rd string guitar plays a vital role in providing a balanced and versatile sound, serving as a bridge between the higher and lower strings. Its unique tuning and material options allow for a wide range of playing techniques and musical styles.
Question 2: How does the 3rd string guitar differ from other strings?
The 3rd string is typically tuned to G, offering a mid-range sound. It can be made of nylon or steel, each material imparting distinct tonal qualities. Nylon strings produce a warmer, mellower sound, while steel strings provide a brighter, louder sound.
Question 3: What are the key techniques used on the 3rd string guitar?
Essential techniques include fingerpicking and strumming. Fingerpicking involves using the fingers to pluck the strings individually, creating intricate melodies. Strumming involves using a pick to strum all the strings at once, providing a solid rhythmic foundation.
Question 4: How can I maintain my 3rd string guitar for optimal performance?
Regular maintenance is crucial, including cleaning to remove dirt and grime, and restringing to ensure proper intonation and playability. Additionally, proper storage in a controlled environment is recommended to protect the guitar from extreme temperatures and humidity.
Question 5: What are some tips for playing the 3rd string guitar effectively?
Practice regularly to develop finger dexterity and coordination. Experiment with different tunings and string combinations to expand your sonic palette. Focus on developing a clean and accurate picking or strumming technique.
Question 6: What musical genres are best suited for the 3rd string guitar?
The 3rd string guitar’s versatility makes it suitable for various genres, including folk, blues, rock, pop, jazz, and fusion. Its warm and resonant sound blends well with vocals and other instruments, providing a solid foundation for accompaniment and lead playing.
Summary: Understanding the nuances of the 3rd string guitar unlocks its potential for creating diverse and expressive music. Proper care and maintenance are essential for preserving its sound and playability. Embrace the instrument’s versatility and experiment with different techniques to enhance your musical journey.
Transition to the next article section:
Tips for Mastering the 3rd String Guitar
Unleashing the full potential of the 3rd string guitar requires dedication, practice, and a focused approach. Here are several valuable tips to enhance your playing skills and musical expression:
Tip 1: Practice Regularly and Consistently
Regular practice is paramount to developing muscle memory, improving coordination, and refining technique. Dedicate time each day to practicing scales, exercises, and songs that challenge your abilities on the 3rd string.
Tip 2: Focus on Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy in fretting and picking is crucial for producing clear and resonant notes. Strive for precision in your finger placement and picking technique to minimize buzzing and unwanted noises.
Tip 3: Experiment with Different Tunings and String Combinations
The 3rd string guitar offers a wide range of sonic possibilities through alternative tunings and string combinations. Experiment with different tunings, such as open tunings or drop tunings, to explore unique soundscapes and expand your musical vocabulary.
Tip 4: Develop Fingerpicking and Strumming Techniques
Mastering fingerpicking and strumming techniques unlocks the expressive capabilities of the 3rd string guitar. Practice fingerpicking patterns to create intricate melodies and arpeggios. Develop strumming techniques to provide a solid rhythmic foundation for accompaniment and solo playing.
Tip 5: Pay Attention to Intonation and Maintenance
Proper intonation ensures that the 3rd string guitar plays in tune with itself and other instruments. Regularly check the intonation and make necessary adjustments to maintain accurate pitch. Additionally, proper maintenance, including cleaning and restringing, is essential for preserving the instrument’s sound and playability.
Tip 6: Explore Different Musical Styles and Techniques
The 3rd string guitar’s versatility allows for exploration across various musical styles. Immerse yourself in different genres, such as folk, blues, rock, jazz, and classical, to broaden your musical horizons and incorporate diverse techniques into your playing.
Summary: Embracing these tips and incorporating them into your practice routine will significantly enhance your 3rd string guitar playing abilities. Remember to approach your musical journey with patience, dedication, and a willingness to experiment. The rewards of mastering this instrument lie in the expressive and fulfilling musical experiences it offers.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Conclusion
The 3rd string guitar, with its unique tonal qualities, technical challenges, and expressive potential, stands as a versatile and rewarding instrument for guitarists of all
levels. Its distinctive sound, coupled with the choice between nylon or steel strings, offers a wide range of sonic possibilities.
Embracing the 3rd string guitar’s versatility requires dedication, practice, and a willingness to experiment. By incorporating regular practice, focusing on accuracy, and exploring different tunings and techniques, guitarists can unlock the instrument’s full potential. Furthermore, proper maintenance ensures the 3rd string guitar’s longevity and optimal performance.
As you embark on your musical journey with the 3rd string guitar, remember to approach it with patience and perseverance. The rewards of mastering this instrument lie in the expressive and fulfilling musical experiences it offers. Embrace the challenge, explore its possibilities, and let the 3rd string guitar ignite your creativity and passion for music.